We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Aminopeptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== S. griseus aminopeptidase == | == S. griseus aminopeptidase == | ||
| - | <applet load='1xjo' size='500' color='white' frame='true' align='right /> | + | <applet load='1xjo' size='500' color='white' frame='true' align='right' /> |
| - | + | ||
''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline. | ''S. griseus'' aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline. | ||
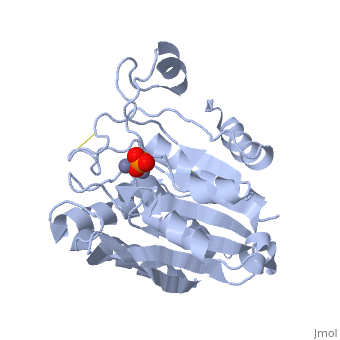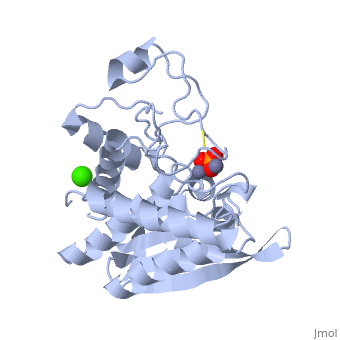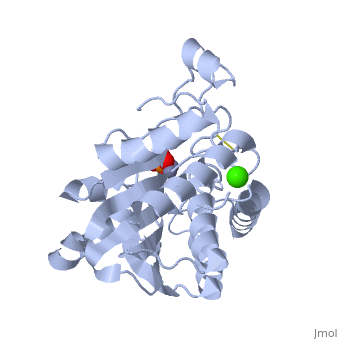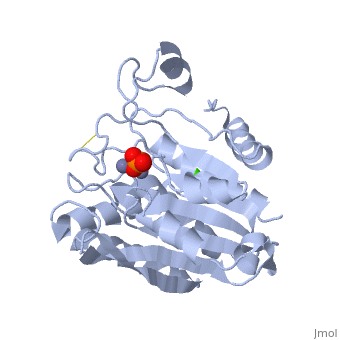
| - | The active site of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. | + | The <scene name='Aminopeptidase/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme. |
Revision as of 14:15, 7 November 2007
Aminopeptidases catalyze a release of an N-terminal amino acid from a peptide, amide, or arylamide.
S. griseus aminopeptidase
|
S. griseus aminopeptidase (SGAP) cleaves the N-terminal amino acid from a peptide or protein, and is specific for larger hydrophobic acids, especially leucine. No cleavage occurs if the next residue is proline.
The of the enzyme contains two Zn2+ ions with His85 and Asp160 as ligands for one ion, and Glu132 and His247 as ligands for the second ion. Asp97 is a common ligand to both ions. What appears to be a phosphate anion is bound to both zinc atoms, replacing the water molecule/hydroxide ion normally found in this class of enzyme.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Eran Hodis