Overview
Nucleocapsid (NC) has an important role in many steps of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1) life cycle. NC has been shown to initiate dimerization of HIV-1 genomic RNA (gRNA) and formation of the viral particle. NC also plays a vital role in initiating reverse transcription and elongation of cDNA. Many of these functions are the result of the RNA binding properties of NC as well as NC’s ability to destabilize regions of base paring. NC is an important HIV-1 chaperone.
See also Nucleoprotein.
Function
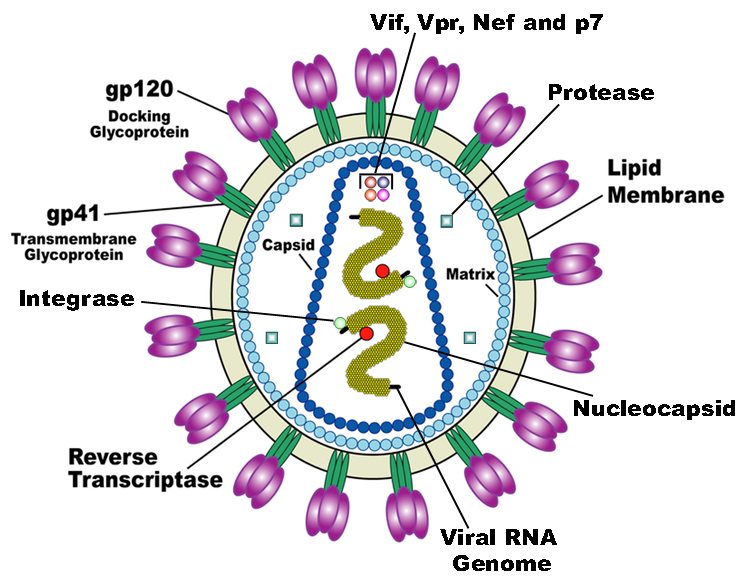
Structure of HIV-1 Virus Particle
[1].
NC facilitates the dimerization of gRNA. HIV-1 genomic information is packaged in the viral particle as a dimer. The palindromic sequence GCGCGC at the dimerization initiation site (DIS) (nt 240-280) initiates complimentary base pairing with another copy of gRNA and forms a kissing loop complex. This kissing loop complex is considered a loose dimer due to its low thermal stability. NC protein facilitates the transition from the low stability kissing loop complex to the stable extended dimer by promoting the refolding of the 5’-end regions via formation of cruciform intermediates (Dubois, Marquet, Paillart, & Bernacchi, 2018). NC makes up the c-terminal end of HIV-1 Gag protein, composed of three domains that is eventually cleaved to form matrix (MA), capsid (CA), and nucleocapsid (NC). Gag is responsible for formation of the final viral particle.
The NC domain of Gag binds to gRNA with high specificity to the . In this way, gRNA serves as a scaffold for the oligomerization of Gag in viral particle formation. NC binding facilitated by the electrostatic interactions between the two zinc fingers and double stranded RNA. NC-gRNA binding is important for gRNA association with and growth of the viral particle as it migrates to the cell plasma membrane (PM). The NC domain initially binds to the gRNA, and then MA domain facilitates Gag migration (along with the bound gRNA) to the cell membrane. This is supported by the fact that NC mutant Gag (Gag with a leucine or isoleucine zipper motif instead of NC, but still able to oligomerize without RNA) localized and oligomerized at the PM but lacked gRNA specificity and would form empty virus like particles (VPLs) (Yang, et al., 2018). Gag proteins lacking the NC domain (∆NC-Gag) has greatly reduced Gag assembly at the PM. It has been shown that Gag binds to gRNA in clusters (dimers and trimers) and then subsequent Gag proteins multimerizes between these Gag clusters (Yang, et al., 2018). NC protein is important for this multimerization as ∆NC-Gag is unable to oligomerize.
NC plays an important gRNA reverse transcription. NC is known to destabilize hairpin and other secondary structures in the 5’ untranslated regions (5’ UTR). This helix unwinding prevents stalling of reverse transcriptase (RT) in vitro. With Selective 2’ Hydroxyl Acylation with Primer Extension (SHAPE), NC was has a high binding affinity for the five g rich ssRNA regions, a splice donor (SD) location and a Psi element site which are both adjacent to helices (Levin , Mithun, Mascarenhas, & Musier-Forsyth, 2010). NC was also shown to destabilize the first 185 nt locations including the primer binding site (PBS). This destabilization is important for the annealing of the tRNA primer. NC is also responsible for the initial association and placement of the primer during annealing, and just as with dimerization, NC catalyzes the nucleation of both the gRNA and the tRNA to facilitate optimal base paring between the two nucleic acid polymers. This was supported by the fact that in the presence of NC at the level of saturation (6 RNA nt:1 NC protein), tRNA/PBS annealing increased by a factor of fifty (Levin , Mithun, Mascarenhas, & Musier-Forsyth, 2010). An interesting note was that NC mutations lacking the zinc fingers were less effective than wt NC, while the same mutated NC exhibited more efficient nucleation.
Another important role NC playes in reverse transcription is complementary DNA elongation. After ssDNA is synthesized, minus-strand transfer is required for extension of the short strand to get the full-length DNA copy of gRNA. This is facilitated by the complementary annealing to the repeat region (R-region). This R region is composed of the transactivation response element (TAR) and poly A. The donar RNA is then degraded and the ssDNA is then translocated to the acceptor RNA. NC role in minus strand transfer is based on its chaperone activity. NC facilitates annealing of the complimentary minus strand ssDNA ( (-) ssDNA ) to the acceptor RNA and increases its rate of binding by ~3000 fold (Levin , Mithun, Mascarenhas, & Musier-Forsyth, 2010). There are two mechanisms for the NC facilitated annealing: kissing loop and zipper. One is the TAR RNA and TAR DNA forming an initial kissing loop in the apical loops. In an experiment where the DNA version of TAR RNA and complementary TAR DNA was complexed with NC, the kissing loop was the slower and minor pathway. Kissing loop was observed in 27-nt mini TAR tRNA and DNA hairpins in the absence of NC. For full length 59-nt TAR tRNA and DNA was used, the addition of NC complete switched the annealing pathway from kissing loop to zipper. Because TAR is a very stable, the is necessary for annealing. With FRET, NC was shown to shift equilibrium from the closed conformation of TAR a predominantly open conformation. NC also protected TAR (-) ssDNA from self-priming via nonspecific folding back on itself due to binding of the zinc fingers. If TAR RNA is also present, NC ensures that the more thermodynamically stable bp of TAR DNA with TAR RNA.
An interesting property necessary for NC chaperone activity is the quick association and dissociation. In order to facilitate nuclear acid stand annealing NC has to have rapid binding/unbinding kinetics which is due in large part to the zinc fingers. This NC rapid dissociation kinetics may also play an important role in regulating the timing of reverse transcription. At low Gag concentration, the dissociation kinetics of Gag matches that of mature NC. However, at higher concentrations (roughly 0.23 μM), the rate of Gag dissociation from ssRNA or ssDNA was greatly reduced relative to mature NC, and at a concentration of 0.46 μM, the (-) DNA transfer system stopped (Levin , Mithun, Mascarenhas, & Musier-Forsyth, 2010). It is believed that the higher Gag concentration facilitates the oligomerization of Gag along the gRNA and blocks the binding of RT, inhibiting reverse transcription. Gag’s reduced dissociation kinetics also prevented the extended binding of tRNA to the PBS site after initial kissing loop formation. Mature NC and unspliced Gag, demonstrates different dissociation kinetics and thereby exhibited different chaperone activities (Levin , Mithun, Mascarenhas, & Musier-Forsyth, 2010) .
Structural highlights
NC is 55 residues long and possess two zinc fingers , . The zinc fingers contain metal binding motifs composed basic cystines and histidine residues. This motif is referred to as a . It is a basic protein that binds tightly to single stranded RNA via its Arg7, Arg32, and Lys 33 residues.
Gag is the 55 kDA multidomain precursor protein that is composed of MA, CA, spacer peptide 1 (sp1), NC, spacer peptide 2 (sp2) and p6. with gaps that allow for formation of the curved viral surface (Mariia Novikova, 2018). Gag oligomerization begins on the gRNA facilitated by binding of the NC domain with gRNA within the cytoplasm. The Gag-gRNA complex is then translocate to the plasma membrane via MA basic residues interactions with the acidic phospholipid head groups, to complete oligomerization to form the immature particle (Lingappa, Reed, Tanaka, Chutiraka, & Robinson, 2014). Once the particle is released, viral protease cleaves Gag into the individual domains to form the mature viral particle. Gag is the only protein necessary for viral particle formation.
References
Dubois, N., Marquet, R., Paillart, J.-C., & Bernacchi, S. (2018). Retroviral RNA Dimerization: Form Structure to Functions. Frontiers in Microbiology.
Levin , J. G., Mithun, M., Mascarenhas, A., & Musier-Forsyth, K. (2010). Role of HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein in HIV-1 reverse transcription. RNA Biology, 754-774.
Lingappa, J. R., Reed, J. C., Tanaka, M., Chutiraka, K., & Robinson, B. A. (2014). How HIV-1 Gag assembles in cells: Putting together pieces of the puzzel. Virus Research, 87-107.
Mariia Novikova, L. J. (2018). Identification of a Structural Element in HIV-1 Gag Required for Virus Particle Assembly and Maturation. American Society for Microbiology.
Yang, Y., Qu, N., Tan, J., Rushdi, M. N., Krueger, C. J., & Chen, A. K. (2018). Roles of Gag-RNA interactions in HIV-1 virus assembly deciphered by singled-molecule localization microscopy. PNAS, 6721-6726.
- ↑ [1] was obtained from Wikipedia.

