We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1095
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(References) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
=== Interaction with drugs === | === Interaction with drugs === | ||
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan Olmesartan] anchored to ATR1 by the residues <scene name='82/829348/Tyr35/6'>Tyr 35</scene>, <scene name='82/829348/Trp84/4'>Trp84</scene> and <scene name='82/829348/Arg167/ | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan Olmesartan] anchored to ATR1 by the residues <scene name='82/829348/Tyr35/6'>Tyr 35</scene>, <scene name='82/829348/Trp84/4'>Trp84</scene> and <scene name='82/829348/Arg167/3'>Arg167</scene>. |
| - | Those three amino acids seem to play an important role in the binding of the drug to AT1R, thanks to the formation of extensive networks of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges with the ligand <ref> [http://www.jbc.org/content/290/49/29127 Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor, Haitao Zhang et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015] </ref>. | + | Those three amino acids seem to play an important role in the binding of the drug to AT1R, thanks to the formation of extensive networks of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges with the ligand <ref name="Zhang2015"> [http://www.jbc.org/content/290/49/29127 Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor, Haitao Zhang et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015] </ref>. |
Many drugs used to cure diseases linked with the angiotensin receptor contain a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrazole tetrazole] group. Studies showed that tetrazole plays an important role in the binding with AT1R. | Many drugs used to cure diseases linked with the angiotensin receptor contain a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrazole tetrazole] group. Studies showed that tetrazole plays an important role in the binding with AT1R. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
=== Interaction with other GPCRs === | === Interaction with other GPCRs === | ||
| - | It has been discovered that AT1Rs were also able to bind with other GPCRs to form homo- or heterodimers. Those interactions can modify the sensitivity of the receptor, which leads to different physiological and pathological conditions than the GPCR monomer <ref | + | It has been discovered that AT1Rs were also able to bind with other GPCRs to form homo- or heterodimers. Those interactions can modify the sensitivity of the receptor, which leads to different physiological and pathological conditions than the GPCR monomer <ref name="Zhang2015" /><ref name="Takanobu2017"> https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.013 </ref>. The most known heterodimers including AT1 receptor are with ß2-adrenergic receptor, the apelin receptor, and AT2 receptor. Those interactions could be facilitated by several transmembrane domains. |
| - | The oligomeric complexes' formation | + | The oligomeric complexes' formation complicate the understanding of AT1R pharmacology. |
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
Since angiotensin receptor is involved in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renin%E2%80%93angiotensin_system renin-angiotenisin system], it represents a target of choice to cure some diseases like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertension hypertension] or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_failure heart failure]. | Since angiotensin receptor is involved in the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renin%E2%80%93angiotensin_system renin-angiotenisin system], it represents a target of choice to cure some diseases like [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertension hypertension] or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart_failure heart failure]. | ||
| - | An over-stimulation of this receptor seems to be involved in hypertension, coronary artery disease, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, arrhythmia, stroke, diabetic nephropathy and ischemic heart and renal diseases <ref | + | An over-stimulation of this receptor seems to be involved in hypertension, coronary artery disease, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, arrhythmia, stroke, diabetic nephropathy and ischemic heart and renal diseases <ref name="Takanobu2017"/>. |
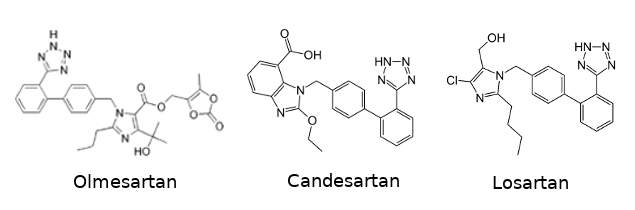
| - | Several anti-hypertensive drugs are targeting the angiotensin receptor in order to block it. This | + | Several anti-hypertensive drugs are targeting the angiotensin receptor in order to block it. This kind of drugs are called [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensin_II_receptor_blocker angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)]. This category include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan olmesartan], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candesartan candesartan], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Losartan losartan]. One of the common characteristic they share is their biphenyl-tetrazole scaffold. |
[[Image:Sartan_drugs.png]] | [[Image:Sartan_drugs.png]] | ||
Revision as of 13:48, 15 January 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 25/11/2019, through 30/9/2020 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1091 through Sandbox Reserved 1115. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human Angiotensin Receptor
Angiotensin receptors belong to the G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. This is the hormone receptor of the angiotensin II type 1. This is a trans-membrane protein located mainly in heart, brain, liver and kidneys.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Angiotensin receptors: History and mysteries, T.L. Goodfriend. American Journal of Hypertension, Volume 13, Issue 4, April 2000, Pages 442–449, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(99)00212-5
- ↑ "Nomenclature for angiotensin receptors. A report of the Nomenclature Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research." Hypertension, 17(5), pp. 720–721.
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4705918/
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3605637/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6457125/#!po=8.33333
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor, Haitao Zhang et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.013