We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1095
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan Olmesartan] anchored to ATR1 by the residues <scene name='82/829348/Tyr35/6'>Tyr 35</scene>, <scene name='82/829348/Trp84/4'>Trp84</scene> and <scene name='82/829348/Arg167/3'>Arg167</scene>. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan Olmesartan] anchored to ATR1 by the residues <scene name='82/829348/Tyr35/6'>Tyr 35</scene>, <scene name='82/829348/Trp84/4'>Trp84</scene> and <scene name='82/829348/Arg167/3'>Arg167</scene>. | ||
Those three amino acids seem to play an important role in the binding of the drug to AT1R, thanks to the formation of extensive networks of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges with the ligand <ref name="Zhang2015"/>. | Those three amino acids seem to play an important role in the binding of the drug to AT1R, thanks to the formation of extensive networks of hydrogen bonds and salt bridges with the ligand <ref name="Zhang2015"/>. | ||
| + | An other amino acid, the <scene name='82/829348/Lys199/1'>Lys 199</scene>, seems to be involved in the binding of the angiotensin II | ||
Many drugs used to cure diseases linked with the angiotensin receptor contain a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrazole tetrazole] group. Studies showed that tetrazole plays an important role in the binding with AT1R. | Many drugs used to cure diseases linked with the angiotensin receptor contain a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrazole tetrazole] group. Studies showed that tetrazole plays an important role in the binding with AT1R. | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='82/829348/Lys199/1'>Lys 199</scene> : an important role for AngII binding | ||
=== Interaction with other GPCRs === | === Interaction with other GPCRs === | ||
| Line 55: | Line 54: | ||
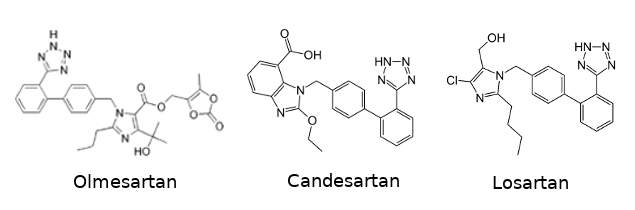
Several anti-hypertensive drugs are targeting the angiotensin receptor in order to block it. This kind of drugs are called [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensin_II_receptor_blocker angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)]. This category include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan olmesartan], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candesartan candesartan], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Losartan losartan]. One of the common characteristic they share is their biphenyl-tetrazole scaffold. | Several anti-hypertensive drugs are targeting the angiotensin receptor in order to block it. This kind of drugs are called [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensin_II_receptor_blocker angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)]. This category include [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olmesartan olmesartan], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candesartan candesartan], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Losartan losartan]. One of the common characteristic they share is their biphenyl-tetrazole scaffold. | ||
[[Image:Sartan_drugs.png]] | [[Image:Sartan_drugs.png]] | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 14:55, 15 January 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 25/11/2019, through 30/9/2020 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1091 through Sandbox Reserved 1115. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human Angiotensin Receptor
Angiotensin receptors belong to the G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. This is the hormone receptor of the angiotensin II type 1. This is a trans-membrane protein located mainly in heart, brain, liver and kidneys.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Angiotensin receptors: History and mysteries, T.L. Goodfriend. American Journal of Hypertension, Volume 13, Issue 4, April 2000, Pages 442–449, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(99)00212-5
- ↑ "Nomenclature for angiotensin receptors. A report of the Nomenclature Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research." Hypertension, 17(5), pp. 720–721.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Zhang H, Unal H, Desnoyer R, et al. Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Functional Selectivity at Angiotensin Receptor. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(49):29127–29139. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.689000
- ↑ Zhang H, Unal H, Gati C, et al. Structure of the Angiotensin receptor revealed by serial femtosecond crystallography. Cell. 2015;161(4):833–844. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.011
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl
- ↑ Fillion D, Cabana J, Guillemette G, Leduc R, Lavigne P, Escher E. Structure of the human angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor bound to angiotensin II from multiple chemoselective photoprobe contacts reveals a unique peptide binding mode. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(12):8187–8197. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.442053
- ↑ Singh KD, Unal H, Desnoyer R, Karnik SS. Mechanism of Hormone Peptide Activation of a GPCR: Angiotensin II Activated State of AT1R Initiated by van der Waals Attraction. J Chem Inf Model. 2019;59(1):373–385. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00583
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Takezako T, Unal H, Karnik SS, Node K. Current topics in angiotensin II type 1 receptor research: Focus on inverse agonism, receptor dimerization and biased agonism. Pharmacol Res. 2017;123:40–50. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.013