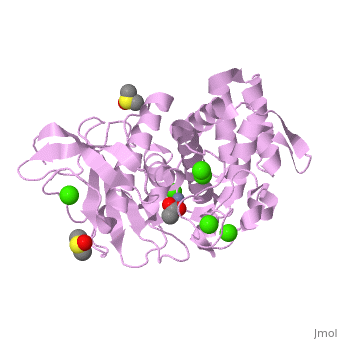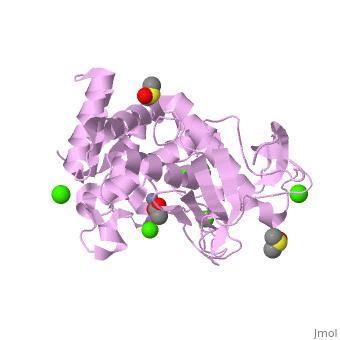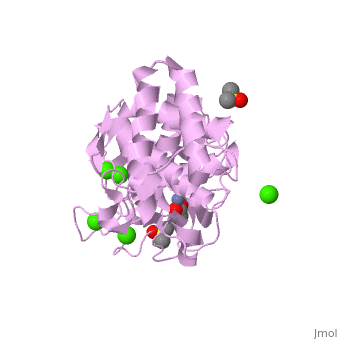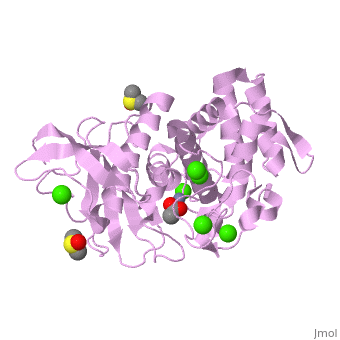We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Thermolysin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='2a7g' size='350' side='right' scene= caption='Thermolysin complex with acetate, DMS, Zn+2 (grey) and Ca+2 (green) ions, [[2a7g]]'> | <StructureSection load='2a7g' size='350' side='right' scene= caption='Thermolysin complex with acetate, DMS, Zn+2 (grey) and Ca+2 (green) ions, [[2a7g]]'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [[Thermolysin]] (TML) is a thermostable metalloproteinase enzyme from ''Bacillus thermoproteolyticus''. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic residues. See [[Metalloproteases]] and [[Matrix metalloproteinase]] for discussion. | + | [[Thermolysin]] or '''thermostable neutral proteinase''' (TML) is a thermostable metalloproteinase enzyme from ''Bacillus thermoproteolyticus''. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic residues. See [[Metalloproteases]] and [[Matrix metalloproteinase]] for discussion. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Matthews, BW. (1988): Structural basis of the action of thermolysin and related zinc peptidases. In: Acc. Chem. Res. 21(9); 333–340; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar00153a003
- ↑ Pelmenschikov V, Blomberg MR, Siegbahn PE. A theoretical study of the mechanism for peptide hydrolysis by thermolysin. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2002 Mar;7(3):284-98. Epub 2001 Sep 27. PMID:11935352 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s007750100295