We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Cell division protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='2vam' size='340' side='right' caption='FtsZ of Bacillus subtilis' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2vam' size='340' side='right' caption='FtsZ of Bacillus subtilis complex with sulfate (PDB code [[2vam]])' scene=''> |
== Bacillus subtilis division protein == | == Bacillus subtilis division protein == | ||
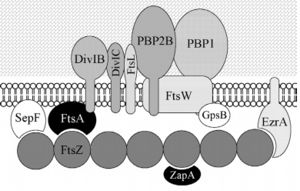
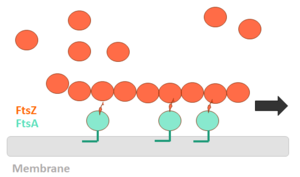
Bacillus subtilis is a prokaryotic organism, a Gram-positive bacterium, and thus has a cytoplasmic membrane plus a thick cell wall made of peptidoglycan and associated anionic polymers, such as teicoic acid. Bacteria are recognized for the reproductive success and conquest of various environments on Earth, with the presence of a complex and sophisticated machinery of cell division and formation of identical daughter cells a potent factor in this success. There are currently 24 proteins known to be associated with division in B. subtilis: ClpX, DivIB,DivIC, DivIVA, EzrA, FtsA, FtsL, FtsW, FtsZ,GpsB, MciZ, MinC, MinD, MinJ, Noc, PBP1,PBP2B, SepF, SftA, SpoIIE, SpoIIIE, UgtP, YneA and ZapA. These proteins can be divided in two main groups: proteins that make up the divisome - macromolecular complex composed of about 20 proteins, which promotes the construction of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane, forming the division septum (DivIB, DivIC, EzrA, FtsA, FtsL, FtsW,FtsZ, GpsB, PBP1, PBP2B, SepF and ZapA) and proteins that regulate the assembly of the divisome (ClpX, DivIVA, MciZ, MinC, MinD, MinJ,Noc, UgtP and YneA). | Bacillus subtilis is a prokaryotic organism, a Gram-positive bacterium, and thus has a cytoplasmic membrane plus a thick cell wall made of peptidoglycan and associated anionic polymers, such as teicoic acid. Bacteria are recognized for the reproductive success and conquest of various environments on Earth, with the presence of a complex and sophisticated machinery of cell division and formation of identical daughter cells a potent factor in this success. There are currently 24 proteins known to be associated with division in B. subtilis: ClpX, DivIB,DivIC, DivIVA, EzrA, FtsA, FtsL, FtsW, FtsZ,GpsB, MciZ, MinC, MinD, MinJ, Noc, PBP1,PBP2B, SepF, SftA, SpoIIE, SpoIIIE, UgtP, YneA and ZapA. These proteins can be divided in two main groups: proteins that make up the divisome - macromolecular complex composed of about 20 proteins, which promotes the construction of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane, forming the division septum (DivIB, DivIC, EzrA, FtsA, FtsL, FtsW,FtsZ, GpsB, PBP1, PBP2B, SepF and ZapA) and proteins that regulate the assembly of the divisome (ClpX, DivIVA, MciZ, MinC, MinD, MinJ,Noc, UgtP and YneA). | ||
Revision as of 08:16, 3 June 2021
| |||||||||||
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8]
- ↑ Bisson-Filho AW, Discola KF, Castellen P, Blasios V, Martins A, Sforca ML, Garcia W, Zeri AC, Erickson HP, Dessen A, Gueiros-Filho FJ. FtsZ filament capping by MciZ, a developmental regulator of bacterial division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 6. pii: 201414242. PMID:25848052 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1414242112
- ↑ Wang, X. & Lutkenhaus, J. FtsZ ring: the eubacterial division apparatus conserved in archaebacteria.Mol. Microbiol. 21, 313–319 (1996). Gueiros-Filho, F. J. & Losick, R. A widely conserved bacterial cell division protein that promotes assembly of the tubulin-like protein FtsZ. Genes Dev. 16, 2544–2556 (2002).
- ↑ Wang, X., Huang, J., Mukherjee, A., Cao, C., and Lutkenhaus, J. (1997). Analysis of the interaction of FtsZ with itself, GTP, and FtsA. J. Bacteriol. 179, 5551–5559.
- ↑ Vaughan S, Wickstead B, Gull K, Addinall SG. Molecular evolution of FtsZ protein sequences encoded within the genomes of archaea, bacteria, and eukaryota. J Mol Evol. 2004 Jan;58(1):19-29. doi: 10.1007/s00239-003-2523-5. PMID:14743312 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-2523-5
- ↑ Szwedziak P, Wang Q, Bharat TA, Tsim M, Lowe J. Architecture of the ring formed by the tubulin homologue FtsZ in bacterial cell division. Elife. 2014 Dec 9;3:e04601. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04601. PMID:25490152 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.04601
- ↑ Huecas, S. et al. Energetics and geometry of FtsZ polymers: nucleated self-assembly of single protofilaments. Biophys. J. 94, 1796–1806 (2008).
- ↑ Lan, G. et al. (2009) Condensation of FtsZ filaments can drive bacterial cell division. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 121–126
- ↑ FILHO, Frederico Gueiros. Cell Division. In: GRAUMANN, Peter L. et al. Bacillus: Cellular and Molecular Biology. Germany: Caister Academic Press, 2017.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Jonathan Cardoso C. Vieira, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky