This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1627
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | The insulin receptor's function in regards to glucose homeostasis is to begin the signaling pathway that will eventually move glucose transporters to the cell surface which will allow glucose to passively defuse into the cell. The glucose receptor is inactive in the absence of insulin. When insulin does bind to the receptor, it undergoes a conformation change, activating it. Once activated, the intracellular Beta subunits autophosphorylate, and downstream signaling begins by the phosphorylation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS). | ||
| - | |||
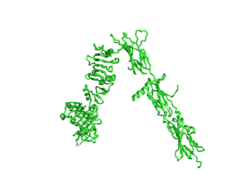
[[Image:Insulin inverted v.png|250px|right|thumb|Figure 1. An image of the Insulin Receptor Alpha subunit in V conformation.]] | [[Image:Insulin inverted v.png|250px|right|thumb|Figure 1. An image of the Insulin Receptor Alpha subunit in V conformation.]] | ||
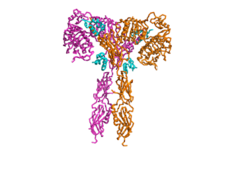
[[Image:T shape.png|250px|right|thumb|Figure 2. An image of the Insulin Receptor in T conformation (showing both Alpha and Beta subunits).]] | [[Image:T shape.png|250px|right|thumb|Figure 2. An image of the Insulin Receptor in T conformation (showing both Alpha and Beta subunits).]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The insulin receptor's function in regards to glucose homeostasis is to begin the signaling pathway that will eventually move glucose transporters to the cell surface which will allow glucose to passively defuse into the cell. The glucose receptor is inactive in the absence of insulin. When insulin does bind to the receptor, it undergoes a conformation change, activating it. Once activated, the intracellular Beta subunits autophosphorylate, and downstream signaling begins by the phosphorylation of the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS). | ||
| + | |||
===Conformation Change=== | ===Conformation Change=== | ||
Revision as of 22:26, 23 March 2020
Homo sapiens Insulin Receptor Ectodomain
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Weis F, Menting JG, Margetts MB, Chan SJ, Xu Y, Tennagels N, Wohlfart P, Langer T, Muller CW, Dreyer MK, Lawrence MC. The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 24;9(1):4420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6. PMID:30356040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6
- ↑ Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005 May;26(2):19-39. PMID:16278749
- ↑ Riddle MC. Treatment of diabetes with insulin. From art to science. West J Med. 1983 Jun;138(6):838-46. PMID:6351440
Student Contributors
- Harrison Smith
- Alyssa Ritter