User:Jaelyn M. Voyles/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
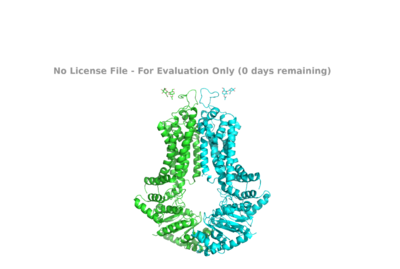
| - | ABCG2 is a transmembrane multidrug transporter which moves molecules across the intra-cellular membrane and out of the cell by utilizing ATP. | + | ABCG2 is a transmembrane multidrug transporter which moves molecules across the intra-cellular membrane and out of the cell by utilizing ATP. Each ABCG2 protein is a homodimer of transmembrane domains and nucleotide binding domains. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | + | ABCG2 transporters are usually seen in apical membranes found in the liver and kidneys in order to move xenobiotics (undesirables) out of the cells. They also excrete the vitamins riboflavin and biotin into breast milk. A xenobiotic will bind to the binding pocket of ABCG2 on the inside of the cell and ATP will move to bind in two places on each dimer. This causes ABCG2 to undergo a conformational change and pushes the xenobiotic through the channel and out of the cell. | |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 24 March 2020
ATP-Binding Cassette Super Family G Member 2, ABCG2
| |||||||||||