Overview
Calcium ions are universal and versatile signaling molecules. Their functions include muscle contraction, neuron excitability, and cell growth. Mitochondria regulate and decode calcium inputs that are necessary for many functions. Mitochondrial calcium regulates mitochondrial metabolism and has an impact in apoptosis, which will be talked about in greater depths later. This is important due to the fact an uncontrolled increase of calcium in the cytoplasm or prolonged presence of calcium in the mitochondria leads to apoptosis[1] The history behind the MCU came from the idea that individual mitochondria could take up high levels of calcium using ATP-derived energy founded in the 1960s.At resting conditions, the concentration of calcium in the mitochondria is around the same as in the cytoplasm (100-200 nM), but it can accumulate up to 10-20x that amount when stimulated. Calcium uptake into the mitochondrial matrix is driven by the membrane potential created by the electron transport chain. The calcium can flow through the outer membrane with ease as it is highly permeable, due to the pores formed by voltage-dependent anion-selective channel proteins. Now for the calcium pass through the inner membrane the MCU is needed. There are other pathways for calcium to get through the inner membrane but MCU is by far the most dominant. [2]
Structure
The precise identity of the MCU as the major calcium transporter remained elusive until 2011. Thanks to a series of combined efforts involving NMR spectroscopy, cry-EM, and x-ray crystallography they were able to see the structure of the membrane-bound transporter and its regulatory machinery. [1] The actual MCU complex is a tetrameric dimer of dimers assembly. As show in the 3D image to the right. What the 3D image does not show is MICU1 and MICU 2, which are tight regulators of the MCU-mediated calcium uptake that actual bring in the calcium and move it towards the selectivity filter in the main MCU complex. There are three other proteins in the complete complex. EMRE, MCUb, and MCUR1. The EMRE is what associates MICU1 and MICU2 with main MCU protein. The MCUR1 has never been truly determined as to what it does for the structure but scientists are saying it helps with building of the overall structure and is non functional once the MCU becomes functional. [2]
Selectivity Filter
The pore-forming subunit of the MCU contains 351 amino acid residues with both the N- and C-terminal domains located in the matrix of the mitochondria. The two transmembrane domains, TM1 and TM2, are connected by a solvent- exposed loop with a highly conserved DXXE motif, which is essential for the calcium transport, located in the upper helix of TM2. The first pore-lining residues are Asp 333 and Glu336, that are both part of the highly conserved DXXE motif connecting TM1 and TM2. Each monomer has a Glu336 whose carboxylate group points toward the pore center. The diameter of the ring is 5Å meaning that the calcium is dehydrated. Trp332 stabilizes the carboxyl groups of two neighboring Glu336 residues through hydrogen bonding. The additional interaction of Trp332 with Pro337 serves to orient Glu336 for calcium coordination. Therefore, Glu336, Trp332, and Pro337 make up the highly conserved selectivity filter. [3]
Common Mutations
Medical Relevance
A number of medical conditions all over the body are caused by disruption of the homeostasis of mitochondrial calcium. Diabetes, heart failure, and cancer are just a few members of this broad group of conditions.
Diabetes
In healthy individuals, the 𝛽-cells in the pancreas are responsible for sensing the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream and releasing the appropriate amount of insulin in response. While the mechanism of this activation isn't entirely understood, we can explain a large portion of it in the context of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis. Increased concentration of glucose causes glycolysis in the cell, which increases the amount of ATP. This increase of ATP closes potassium channels in the membrane of the 𝛽-cell which causes depolarization of the membrane. When a certain threshold potential is reached, calcium channels open and create microdomains of calcium below the plasma membrane which allows insulin release by activating PKC 𝛽-type II. Furthermore, there is a pool of mitochondria in 𝛽-cells near the calcium channels which take in the calcium through the MCU. The mitochondria then create more ATP which sustains and amplifies insulin secretion [2].
Any defect in the MCU affects the homeostasis of calcium in the mitochondria. In this case, it can cause insulin secretion to be diminished which can be a causal factor for diabetes I and II.
Heart Failure
Calcium impacts cardiac function in many ways. It is a key modulator of the cardiac functional cycle made up of excitation, contraction (diastole), and relaxation (systole). It also has an impact in cardiac cell death. Mitochondrial calcium contributes to control of oxidative metabolism in excitation-metabolism (EM) coupling which generates the ATP needed for cardiac excitation and contraction in each heartbeat. In sinoatrial nodal cells, an action potential is created by opening of sodium channels to increase the positive charge of the membrane potential. This opens calcium channels (TTCCs and LTCCs) to increase cytosolic calcium levels which activates mitochondrial function and ATP production. This also causes calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) in which the presence of calcium causes the release of more calcium. This initiates muscle contraction by binding troponin C on microfilaments and promotes calcium uptake into the mitochondria. In summary, mitochondrial calcium uptake provides the link between ATP supply and demand during cardiomyocyte contraction. The MCU favors rapid calcium intake which increases heartbeat frequency.[2]
Ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) is caused by the rapid restoration of oxygen to ischemic (oxygen-deficient) tissues. In ischemic conditions, cells undergo anaerobic glycolysis. Because of the cessation of oxidative phosphorylation, the mitochondrial membrane potential is diminished. Additionally, the cytosolic pH is decreased. This drop in pH causes an increase in calcium concentration in the cytoplasm. When oxygen returns, there's a rapid restoration of membrane potential as oxidative phosphorylation resumes. This provides a strong driving force for the entry of calcium into the mitochondria which triggers mitochondrial calcium overload and cell death.[1]
Therefore, certain issues with the MCU that cause an imbalance in mitochondrial calcium can lead to heart failure. Additionally, even if there is nothing wrong with the MCU, it can have an impact in conditions like IRI. This makes the MCU an interesting target for therapies for both cardiac conditions and many other ailments.
Cancer
Cancer is another condition that can impacted by the MCU, though not much is known about the exact mechanisms. It has mostly been studied in the context of breast and colorectal cancers. Overexpression or overactivation of the MCU complex was shown to promote cancer proliferation. Additionally, the overexpression of MICU1 and MICU2 was shown to decrease mitochondrial calcium levels and prevent apoptosis in cancer cells.[1] Again, not much is known about the connection between the MCU and cancer cell growth, but the MCU's control over apoptosis and cell growth indicates that mitochondrial calcium regulation is fundamental to cancer cell growth and migration.
Regulation/Inhibition
Uptake of calcium into the mitochondria is pivotal for signalling and bioenergetic processes, but overload of calcium causes release of cytochrome c, overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), swelling of the mitochondria, and opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) which all contribute to cell death. Therefore, the MCU has become a target of interest for therapies for certain conditions (like the ones above).[1] Part of this process is research that looks into inhibitors for the MCU.
Finding an good inhibitor of MCU is no small task. First of all, in the inhibitors that have already been discovered, there is no apparent structure-activity relationship that could predict their inhibitory activity. Additionally, many inhibitors of the MCU are not selective enough for the MCU or have other off-target effects that negatively affect the cell. Among the discovered inhibitors of the MCU are Mitoxantrone and DS16570511 with DS16570511 being the most potent. Furthermore, NecroX-5, KB-R7943, minocycline, and doxycycline have been shown to have inhibitory activity. However, all of these inhibitors are subject to the issues listed before.[1]
Inorganic salts and coordination complexes have also been shown to inhibit calcium uptake. Specifically, the trivalent lanthanide ions can competitively inhibit the uniporter because of their similar ionic radii and coordination preferences to calcium. In addition, several transition metal coordination complexes (most notably Co, Cr, and Rh) with amine ligands have been shown to inhibit calcium uptake. Again, there is no apparent structure-activity relationship that predicts this behavior.[1]
CALCIUM, CO, CR, RH
The most well-known and commonly used inhibitor of calcium uptake into the mitochondria is ruthenium red (
RuRed).
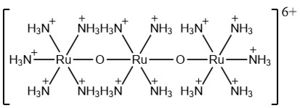
Structure of Ruthenium Red
RuRed effectively inhibits calcium uptake without affecting mitochondrial respiration or calcium efflux. Additionally, it has been shown to mitigate tissue damage due to IRI and slow cancer cell migration. The issue with RuRed is that its purification has always been a challenging matter.
[1] Interestingly enough, this led to even more developments in the search for an inhibitor. Many scientists had observed that impure RuRed actually had greater inhibition than pure RuRed. One of the common minor impurities of RuRed,
Ru360, was found to be the active component of the RuRed mixtures, meaning it responsible for calcium inhibition. Ru360 is now commercially available and has been widely used for the study of calcium-dependent cellular processes and as a therapeutic agent. Very little is known about its mechanism of inhibtion, but studies show that it interacts with the DXXE motif of the loop connecting the TM1 and TM2 helices.
[1]
MCU STRUCTURE DXXE MOTIF
Ru360 was a very successful inhibitor, but it showed low cell permeability. So, a new inhibitor called Ru265 was developed which could be easily synthesized and didn't need chromatographic purification. Ru265 had all of the benefits of Ru360, with with twice the cell permeability. Additionally, the same mutations didn't seem to affect it. Mutations of D261 and S259 in human MCU reduced inhibitory effect of Ru360, but not Ru265. Additionally, there were other mutations that affected Ru265, but not Ru360.[1] This shows how much more research is needed before a mechanism is understood for any inhibitor of the MCU.
D261 AND S259

