We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1606
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
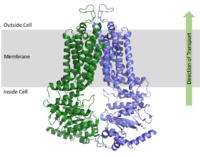
| - | + | ABCG2 is a homodimer with each dimer containing two domains, the nucleotide binding domain (NBD) and the transmembrane domain. The NDB is located inside of the cell while the transmembrane domain is located in the cell membrane. [[Image:membrane domains.png|200 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Domains of ABCG2 Multidrug transporter]] | |
| - | [[Image:membrane domains.png|200 px|right|thumb| | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===ATP Bound and Unbound Conformations=== | ===ATP Bound and Unbound Conformations=== | ||
| + | As an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATP-binding_cassette_transporter ABC Transporter], ABCG2 exhibits ATPase activity in which it binds and hydrolyzes ATP in order to cultivate the energy needed for the transport of molecules across the cell membrane. Two molecules of ATP bind the | ||
<scene name='83/832932/Atp_bound_use/1'>ATP Bound</scene> | <scene name='83/832932/Atp_bound_use/1'>ATP Bound</scene> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 17: | ||
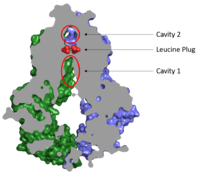
===Cavities and Leucine Plug=== | ===Cavities and Leucine Plug=== | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Map_leucine_plug.png|200 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Locations of Cavities 1 and 2 and the Leucine Plug in ABCG2.]] |
<scene name='83/832932/Lysine_plug_use/1'>Leucine Plug</scene> | <scene name='83/832932/Lysine_plug_use/1'>Leucine Plug</scene> | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 4 April 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 13 through September 1, 2020 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1598 through Sandbox Reserved 1627. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
ABCG2 Multidrug Transporter
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Taylor NMI, Manolaridis I, Jackson SM, Kowal J, Stahlberg H, Locher KP. Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nature. 2017 Jun 22;546(7659):504-509. doi: 10.1038/nature22345. Epub 2017 May, 29. PMID:28554189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature22345
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Manolaridis I, Jackson SM, Taylor NMI, Kowal J, Stahlberg H, Locher KP. Cryo-EM structures of a human ABCG2 mutant trapped in ATP-bound and substrate-bound states. Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7731):426-430. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0680-3. Epub 2018 Nov, 7. PMID:30405239 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0680-3