Sandbox Reserved 1606
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| - | Dysfunctions in ABCG2 is linked to hyperuricemia which can lead to gout, kidney disease, and hypertension, all of which are thought to be the result of impaired transport of uric acid. | + | Dysfunctions in ABCG2 is linked to hyperuricemia which can lead to gout, kidney disease, and hypertension, all of which are thought to be the result of impaired transport of uric acid.<ref name="Jackson"/> |
| - | === | + | |
| + | ===ABCG2 as a Target for Inhibition=== | ||
ABCG2 contributes to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_drug_resistance multidrug resistance] in cancer cells by exporting anti-tumor drugs out of cells which introduces an obstacle in cancer treatment.<ref name="Taylor"/> | ABCG2 contributes to [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_drug_resistance multidrug resistance] in cancer cells by exporting anti-tumor drugs out of cells which introduces an obstacle in cancer treatment.<ref name="Taylor"/> | ||
brief description of the cancer genes listed in the papers (papers talk about how some cancers had more expression of abcg2 genes) | brief description of the cancer genes listed in the papers (papers talk about how some cancers had more expression of abcg2 genes) | ||
| - | ===ABCG2 as a Target for Inhibition=== | ||
| - | Talk about how and why it would be a good target for the treatment of cancer and include paper talking about inhibition of it | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 6 April 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 13 through September 1, 2020 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1598 through Sandbox Reserved 1627. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
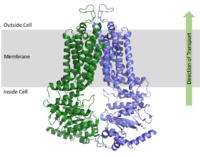
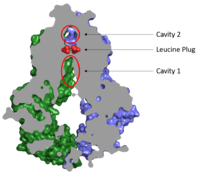
ABCG2 Multidrug Transporter
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Taylor NMI, Manolaridis I, Jackson SM, Kowal J, Stahlberg H, Locher KP. Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nature. 2017 Jun 22;546(7659):504-509. doi: 10.1038/nature22345. Epub 2017 May, 29. PMID:28554189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature22345
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Manolaridis I, Jackson SM, Taylor NMI, Kowal J, Stahlberg H, Locher KP. Cryo-EM structures of a human ABCG2 mutant trapped in ATP-bound and substrate-bound states. Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7731):426-430. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0680-3. Epub 2018 Nov, 7. PMID:30405239 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0680-3
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Robey RW, Pluchino KM, Hall MD, Fojo AT, Bates SE, Gottesman MM. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Jul;18(7):452-464. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0005-8. PMID:29643473 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0005-8
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Jackson SM, Manolaridis I, Kowal J, Zechner M, Taylor NMI, Bause M, Bauer S, Bartholomaeus R, Bernhardt G, Koenig B, Buschauer A, Stahlberg H, Altmann KH, Locher KP. Structural basis of small-molecule inhibition of human multidrug transporter ABCG2. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;25(4):333-340. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0049-1. Epub, 2018 Apr 2. PMID:29610494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41594-018-0049-1
Student Contributors
Julia Pomeroy