We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1627
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Conformation Change=== | ===Conformation Change=== | ||
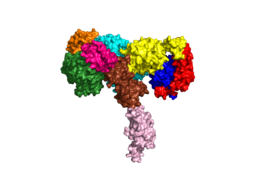
| - | When the receptor is in an <scene name='83/832953/Inactive_insulin_receptor/3'>inverted V</scene> shape, the FnIII-3 domains are separated by about 120Å. This distance prevents the initiation of autophosphorylation and downstream signaling by the tyrosine kinase domains on the intracellular side of the receptor. Upon the binding of insulin to three binding sites, 1, 1', and either 2 or 2', the conformation change will begin and bring the FnIII-3 domains within 40Å of each other to induce the <scene name='83/832953/Ir_dimer_t_state/3'>T shape</scene> conformation. <ref> DOI 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6</ref> <ref name="Uchikawa" /> The T shape conformation is well observed in the alpha subunit. It is horizontally composed of L1, CR (including the α-CT chain), and L2 domains and vertically composed of the FnIII-1, 2, and 3 domains. The insulin receptor's structural [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conformational_change conformation change] is what allows it to go from the inactive state to the active state in order to facilitate the autophosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain. | + | When the receptor is in an <scene name='83/832953/Inactive_insulin_receptor/3'>inverted V</scene> shape, the FnIII-3 domains are separated by about 120Å. This distance prevents the initiation of autophosphorylation and downstream signaling by the tyrosine kinase domains on the intracellular side of the receptor. Upon the binding of insulin to three binding sites, 1, 1', and either 2 or 2', the conformation change will begin and bring the FnIII-3 domains within 40Å of each other to induce the <scene name='83/832953/Ir_dimer_t_state/3'>T shape</scene> conformation. <ref> DOI 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6</ref> <ref name="Uchikawa" /> The T shape conformation is well observed in the alpha subunit. It is horizontally composed of L1, CR (including the α-CT chain), and L2 domains and vertically composed of the FnIII-1, 2, and 3 domains (Figure 1). The insulin receptor's structural [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conformational_change conformation change] is what allows it to go from the inactive state to the active state in order to facilitate the autophosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase domain. |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 19 April 2020
Homo sapiens Insulin Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 De Meyts P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network PMID:27512793
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Tatulian SA. Structural Dynamics of Insulin Receptor and Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry. 2015 Sep 15;54(36):5523-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805. Epub , 2015 Sep 3. PMID:26322622 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00805
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Scapin G, Dandey VP, Zhang Z, Prosise W, Hruza A, Kelly T, Mayhood T, Strickland C, Potter CS, Carragher B. Structure of the Insulin Receptor-Insulin Complex by Single Particle CryoEM analysis. Nature. 2018 Feb 28. pii: nature26153. doi: 10.1038/nature26153. PMID:29512653 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature26153
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ Weis F, Menting JG, Margetts MB, Chan SJ, Xu Y, Tennagels N, Wohlfart P, Langer T, Muller CW, Dreyer MK, Lawrence MC. The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 24;9(1):4420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6. PMID:30356040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06826-6
- ↑ Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jan 1;6(1). pii: 6/1/a009191. doi:, 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191. PMID:24384568 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
- ↑ Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005 May;26(2):19-39. PMID:16278749
- ↑ Riddle MC. Treatment of diabetes with insulin. From art to science. West J Med. 1983 Jun;138(6):838-46. PMID:6351440
Student Contributors
- Harrison Smith
- Alyssa Ritter