Davis L. Martinec/Sandbox 4eqv
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=== Catalytic β-propeller Domain === | === Catalytic β-propeller Domain === | ||
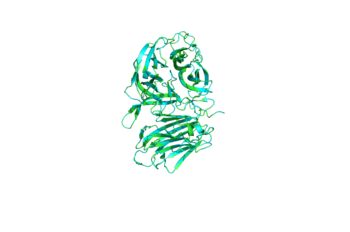
| - | The <scene name='84/842891/Beta-propeller_domain/4'>β-propeller Domain</scene> of 4EQV, shown in crimson, is the catalytic domain of the monomer. The domain is composed mostly of antiparallel β-strands which form five blades, each containing four antiparallel β-strands. The <scene name='84/842891/Closed_active_site/2'>active site</scene> of the β-propeller domain is formed at the axis of the five blades. This catalytic pocket is contains nucleophilic residue Asp22 at its base and is lined with multiple hydrophobic residues, namely Trp48, Phe82, Trp291, Phe296, and Phe388. The <scene name='84/842891/Closed_pocket_with_nucleophile/2'>catalytic pockets</scene> of the A/B and C/D chains are rather specific for sucrose. This specificity is due to Gln201, which binds to sucrose and Asp228 conveys an affinity for glucose moiety<ref>DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11</ref>. | + | The <scene name='84/842891/Beta-propeller_domain/4'>β-propeller Domain</scene> of 4EQV, shown in crimson, is the catalytic domain of the monomer. The domain is composed mostly of antiparallel β-strands which form five blades, each containing four antiparallel β-strands. The <scene name='84/842891/Closed_active_site/2'>active site</scene> of the β-propeller domain is formed at the axis of the five blades. This catalytic pocket is contains nucleophilic residue Asp22 at its base and is lined with multiple hydrophobic residues, namely Trp48, Phe82, Trp291, Phe296, and Phe388. The <scene name='84/842891/Closed_pocket_with_nucleophile/2'>catalytic pockets</scene> of the A/B and C/D chains are rather specific for sucrose. This specificity is due to Gln201, which binds to sucrose and Asp228 conveys an affinity for glucose moiety<ref name="fructo">DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05032-11</ref>. |
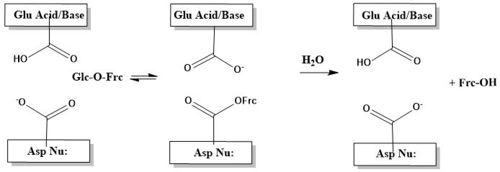
| - | The catalytic process, is two-step. First, there is the nucleophilic attack of the anomeric carbon of the fructose moiety by Asp22, to form a covalent enzyme-substrate complex<ref | + | The catalytic process, is two-step. First, there is the nucleophilic attack of the anomeric carbon of the fructose moiety by Asp22, to form a covalent enzyme-substrate complex<ref name="fructo" />. Glucose the leaving group, is simulaneously protonated by Glu203, which then deprontonates the "acceptor" molecule to activate it as a nucleophile, which then releases fructose<ref name="fructo" />. The figure below illustrates this process using a cartoon. |
[[Image:Catalysis_4eqv_mech.JPG| 500 px]] | [[Image:Catalysis_4eqv_mech.JPG| 500 px]] | ||
Revision as of 01:42, 27 April 2020
4EQV - Saccharomyces Invertase
| |||||||||||