We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Samuel Boyson/Sandbox 900
From Proteopedia
< User:Samuel Boyson(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
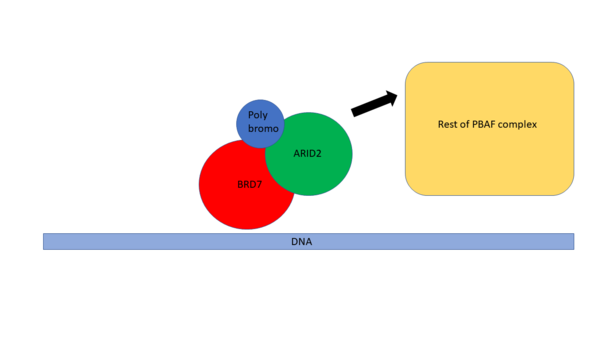
BRD7 along with many other Bromodomains has been widely implicated in a variety of diseases like Cancer(12-14). There is increasing evidence that BRD7 is highly downregulated in a variety of human cancers and BRD7 is known to act as a crucial component of both the p53 and BRCA1 oncogenic pathways(3). BRD7 is most notably associated with NPC. In NPC cells, it is frequently found that BRD7 is under expressed, which may play a large role in NPC development and progression(15). When BRD7 is overexpressed, it slows the growth of NPC cells through transcriptional regulation and inhibits the G1 to S phase cell cycle transition (1). | BRD7 along with many other Bromodomains has been widely implicated in a variety of diseases like Cancer(12-14). There is increasing evidence that BRD7 is highly downregulated in a variety of human cancers and BRD7 is known to act as a crucial component of both the p53 and BRCA1 oncogenic pathways(3). BRD7 is most notably associated with NPC. In NPC cells, it is frequently found that BRD7 is under expressed, which may play a large role in NPC development and progression(15). When BRD7 is overexpressed, it slows the growth of NPC cells through transcriptional regulation and inhibits the G1 to S phase cell cycle transition (1). | ||
BRD7 has also been widely studied in breast cancer (13). It is a known binding partner of BRCA1 and has been found to be essential to expression of the Estrogen receptor on breast cancer cells. Inhibition of BRD7 in these cells has been shown to prevent Estrogen receptor expression causing the cancer cells to become more resistant to treatment(13). BRD7 was also found to be frequently deleted or downregulated in breast cancer cells suggesting its importance in the formation or sustainability of these cell lines (12). | BRD7 has also been widely studied in breast cancer (13). It is a known binding partner of BRCA1 and has been found to be essential to expression of the Estrogen receptor on breast cancer cells. Inhibition of BRD7 in these cells has been shown to prevent Estrogen receptor expression causing the cancer cells to become more resistant to treatment(13). BRD7 was also found to be frequently deleted or downregulated in breast cancer cells suggesting its importance in the formation or sustainability of these cell lines (12). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Peng, C., Zhou, J., Liu, H. Y., Zhou, M., Wang, L. L., Zhang, Q. H., Yang, Y. X., Xiong, W., Shen, S. R., Li, X. L., and Li, G. Y. (2006) The transcriptional regulation role of BRD7 by binding to acetylated histone through bromodomain. J Cell Biochem 97, 882-892 | ||
| + | 2. Staal, A., Enserink, J. M., Stein, J. L., Stein, G. S., and van Wijnen, A. J. (2000) Molecular characterization of celtix-1, a bromodomain protein interacting with the transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 2. J Cell Physiol 185, 269-279 | ||
| + | 3. Yu, X., Li, Z., and Shen, J. (2016) BRD7: a novel tumor suppressor gene in different cancers. Am J Transl Res 8, 742-748 | ||
| + | 4. Mashtalir, N., D'Avino, A. R., Michel, B. C., Luo, J., Pan, J., Otto, J. E., Zullow, H. J., McKenzie, Z. M., Kubiak, R. L., St Pierre, R., Valencia, A. M., Poynter, S. J., Cassel, S. H., Ranish, J. A., and Kadoch, C. (2018) Modular Organization and Assembly of SWI/SNF Family Chromatin Remodeling Complexes. Cell 175, 1272-1288 e1220 | ||
| + | 5. Yan, Z., Cui, K., Murray, D. M., Ling, C., Xue, Y., Gerstein, A., Parsons, R., Zhao, K., and Wang, W. (2005) PBAF chromatin-remodeling complex requires a novel specificity subunit, BAF200, to regulate expression of selective interferon-responsive genes. Genes Dev 19, 1662-1667 | ||
| + | 6. Kaeser, M. D., Aslanian, A., Dong, M. Q., Yates, J. R., 3rd, and Emerson, B. M. (2008) BRD7, a novel PBAF-specific SWI/SNF subunit, is required for target gene activation and repression in embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 283, 32254-32263 | ||
| + | 7. Drost, J., Mantovani, F., Tocco, F., Elkon, R., Comel, A., Holstege, H., Kerkhoven, R., Jonkers, J., Voorhoeve, P. M., Agami, R., and Del Sal, G. (2010) BRD7 is a candidate tumour suppressor gene required for p53 function. Nat Cell Biol 12, 380-389 | ||
| + | 8. Wang, H., Zhao, R., Guo, C., Jiang, S., Yang, J., Xu, Y., Liu, Y., Fan, L., Xiong, W., Ma, J., Peng, S., Zeng, Z., Zhou, Y., Li, X., Li, Z., Li, X., Schmitt, D. C., Tan, M., Li, G., and Zhou, M. (2016) Knockout of BRD7 results in impaired spermatogenesis and male infertility. Sci Rep 6, 21776 | ||
| + | 9. Sun, H., Liu, J., Zhang, J., Shen, W., Huang, H., Xu, C., Dai, H., Wu, J., and Shi, Y. (2007) Solution structure of BRD7 bromodomain and its interaction with acetylated peptides from histone H3 and H4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358, 435-441 | ||
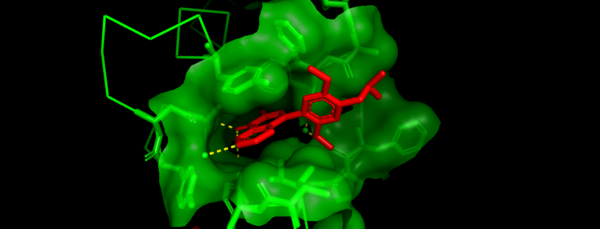
| + | 10. Karim, R. M., Chan, A., Zhu, J. Y., and Schonbrunn, E. (2020) Structural Basis of Inhibitor Selectivity in the BRD7/9 Subfamily of Bromodomains. J Med Chem 63, 3227-3237 | ||
| + | 11. Clark, P. G., Vieira, L. C., Tallant, C., Fedorov, O., Singleton, D. C., Rogers, C. M., Monteiro, O. P., Bennett, J. M., Baronio, R., Muller, S., Daniels, D. L., Mendez, J., Knapp, S., Brennan, P. E., and Dixon, D. J. (2015) LP99: Discovery and Synthesis of the First Selective BRD7/9 Bromodomain Inhibitor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54, 6217-6221 | ||
| + | 12. Beroukhim, R., Mermel, C. H., Porter, D., Wei, G., Raychaudhuri, S., Donovan, J., Barretina, J., Boehm, J. S., Dobson, J., Urashima, M., Mc Henry, K. T., Pinchback, R. M., Ligon, A. H., Cho, Y. J., Haery, L., Greulich, H., Reich, M., Winckler, W., Lawrence, M. S., Weir, B. A., Tanaka, K. E., Chiang, D. Y., Bass, A. J., Loo, A., Hoffman, C., Prensner, J., Liefeld, T., Gao, Q., Yecies, D., Signoretti, S., Maher, E., Kaye, F. J., Sasaki, H., Tepper, J. E., Fletcher, J. A., Tabernero, J., Baselga, J., Tsao, M. S., Demichelis, F., Rubin, M. A., Janne, P. A., Daly, M. J., Nucera, C., Levine, R. L., Ebert, B. L., Gabriel, S., Rustgi, A. K., Antonescu, C. R., Ladanyi, M., Letai, A., Garraway, L. A., Loda, M., Beer, D. G., True, L. D., Okamoto, A., Pomeroy, S. L., Singer, S., Golub, T. R., Lander, E. S., Getz, G., Sellers, W. R., and Meyerson, M. (2010) The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463, 899-905 | ||
| + | 13. Harte, M. T., O'Brien, G. J., Ryan, N. M., Gorski, J. J., Savage, K. I., Crawford, N. T., Mullan, P. B., and Harkin, D. P. (2010) BRD7, a subunit of SWI/SNF complexes, binds directly to BRCA1 and regulates BRCA1-dependent transcription. Cancer Res 70, 2538-2547 | ||
| + | 14. Zhu, B., Tian, J., Zhong, R., Tian, Y., Chen, W., Qian, J., Zou, L., Xiao, M., Shen, N., Yang, H., Lou, J., Qiu, Q., Ke, J., Lu, X., Song, W., Li, H., Liu, L., Wang, L., and Miao, X. (2015) Genetic variants in the SWI/SNF complex and smoking collaborate to modify the risk of pancreatic cancer in a Chinese population. Mol Carcinog 54, 761-768 | ||
| + | 15. Zhou, J., Ma, J., Zhang, B. C., Li, X. L., Shen, S. R., Zhu, S. G., Xiong, W., Liu, H. Y., Huang, H., Zhou, M., and Li, G. Y. (2004) BRD7, a novel bromodomain gene, inhibits G1-S progression by transcriptionally regulating some important molecules involved in ras/MEK/ERK and Rb/E2F pathways. J Cell Physiol 200, 89-98 | ||
Current revision
Bromodomain Containing Protein 7 (BRD7)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644