User:Isabela Fonseca de Oliveira Granha/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Cell Adhesion== | ==Cell Adhesion== | ||
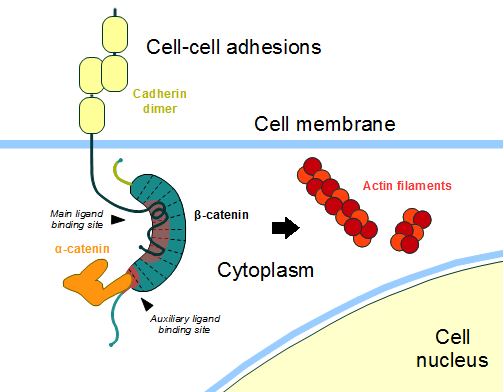
| - | In the absence of Wnt stimulus, the ß-catenin is located at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane as a component of cadherin-based cell-cell connections. [[Cadherin|Cadherins]] are transmembrane glycoproteins calcium-dependent adhesion that can link to ß-catenin through their cytoplasmic tails. The cadherin-catenin complex forms adherens junctions that polarize epithelial tissues and hold the cells together. <ref>Developmental Biology . Eleventh Edition. By Scott F. Gilbert and Michael J. F. Barresi. Sunderland (Massachusetts): Sinauer Associates. ISBN: 978-1-60535-470-5. 2016. </ref> | + | In the absence of Wnt stimulus, the ß-catenin is located at the cytoplasmic side of the membrane as a component of cadherin-based cell-cell connections (Figure 1). [[Cadherin|Cadherins]] are transmembrane glycoproteins calcium-dependent adhesion that can link to ß-catenin through their cytoplasmic tails. The cadherin-catenin complex forms adherens junctions that polarize epithelial tissues and hold the cells together. <ref>Developmental Biology . Eleventh Edition. By Scott F. Gilbert and Michael J. F. Barresi. Sunderland (Massachusetts): Sinauer Associates. ISBN: 978-1-60535-470-5. 2016. </ref> |
The most known interaction occurs between <scene name='84/848919/Correctbeta-catenin_e-cadherin/2'>ß-catenin (green) and E-cadherin (pink)</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1I7X 1I7X]) (epithelial cadherin). They are associated while still in the endoplasmic reticulum and interfering with the binding of these proteins results in proteasomal degradation of the [[cadherin]]. First, alpha-catenin binds to ß-catenin at the first ARM repeat, amino acids <scene name='84/848919/Corretoam118-149/1'>118-149</scene>, resulting in an alpha-catenin/ß-catenin heterodimer. This binding stabilizes ß-catenin in the hinged form, and E-cadherin can connect simultaneously. The <scene name='84/848919/Surfacebeta-catenin_e-cadherin/1'>interaction surface</scene> is extensive, covering the entire length of the ß-catenin ARM repeat domain and involving the C-terminal 100 residues of the cadherin cytoplasmic domain. <ref name="valenta2012">DOI 10.1038/emboj.2012.150</ref> <ref name="huber2001">Huber, A. H., & Weis, W. I. (2001). The structure of the β-catenin/E-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell, 105(3), 391-402.</ref> | The most known interaction occurs between <scene name='84/848919/Correctbeta-catenin_e-cadherin/2'>ß-catenin (green) and E-cadherin (pink)</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1I7X 1I7X]) (epithelial cadherin). They are associated while still in the endoplasmic reticulum and interfering with the binding of these proteins results in proteasomal degradation of the [[cadherin]]. First, alpha-catenin binds to ß-catenin at the first ARM repeat, amino acids <scene name='84/848919/Corretoam118-149/1'>118-149</scene>, resulting in an alpha-catenin/ß-catenin heterodimer. This binding stabilizes ß-catenin in the hinged form, and E-cadherin can connect simultaneously. The <scene name='84/848919/Surfacebeta-catenin_e-cadherin/1'>interaction surface</scene> is extensive, covering the entire length of the ß-catenin ARM repeat domain and involving the C-terminal 100 residues of the cadherin cytoplasmic domain. <ref name="valenta2012">DOI 10.1038/emboj.2012.150</ref> <ref name="huber2001">Huber, A. H., & Weis, W. I. (2001). The structure of the β-catenin/E-cadherin complex and the molecular basis of diverse ligand recognition by β-catenin. Cell, 105(3), 391-402.</ref> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==The ß-catenin destruction complex== | ==The ß-catenin destruction complex== | ||
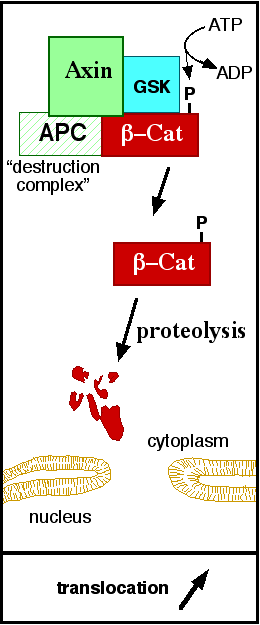
| - | In baseline conditions without Wnt signaling, ß-catenin concentrations are low in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Then, the destruction complex (Figure | + | In baseline conditions without Wnt signaling, ß-catenin concentrations are low in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Then, the destruction complex (Figure 2), formed by APC, [[Axin]], CK1ɑ and [[Glycogen synthase kinase 3|GSK]], is active and causes the degradation of the protein through proteasome. Initially it is recognized by APC and [[Axin]] that promote the phosphorylation of Ser45 by CK1ɑ. This facilitates the phosphorylation by [[Cyclin-dependent kinase|GSK]] in the residues of the amino acids Thr41, Ser37 and Ser33. The last two, when phosphorylated, leads to recognition by ß-TrCP and consequently ubiquitination by an [[Ubiquitin protein ligase|E3 ligase]] and degradation by [[Proteasome|26S proteasome]]. <ref name="valenta2012" /> |
[[Image:Axindestructioncomplex.png]] | [[Image:Axindestructioncomplex.png]] | ||
| - | '''Figure | + | '''Figure 2''': A simplified diagram of the ß-catenin destruction complex. The destruction complex proteins promote the ß-catenin proteolysis in cytoplasm. |
==DNA binding and transcription== | ==DNA binding and transcription== | ||
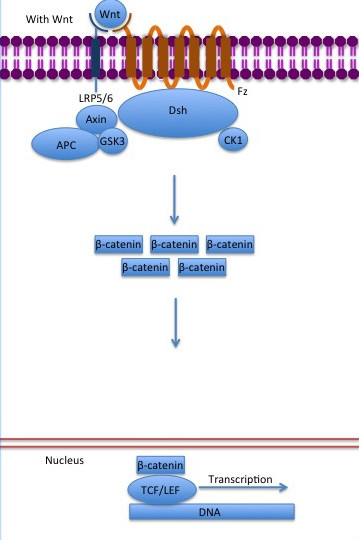
| - | The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure | + | The inhibition of ß-catenin destruction complex through activation of the Wnt pathway (Figure 3) leads to increased levels of the protein in cytoplasm and its translocation into the nucleus. ß-catenin interacts with different nuclear pore complex components and ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R10-12/1'>R10-R12</scene> are critical for its import and export. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] also facilitates its nuclear translocation directly interacting with ARM repeats <scene name='84/848919/R11-12/2'>R11-R12</scene>. [[Forkhead box protein|FoxM1]] forms a complex with ß-catenin/TCF on the promoters of Wnt target genes. Once in the nucleus, ß-catenin and its DNA binding partners can activate transcription of Wnt/ß-catenin target genes. Therefore, ß-catenin can only initiates transcription in a multimeric complex, as its central transcriptional activator. <ref name="valenta2012" /> |
[[Image:Canonical Wnt pathway with Wnt..jpg]] | [[Image:Canonical Wnt pathway with Wnt..jpg]] | ||
| - | '''Figure | + | '''Figure 3''': The canonical Wnt pathway when Wnt is present. The inhibition of the destruction complex allows ß-catenin translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus. |
TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to <scene name='84/848919/R12andhelix-c/1'>the last ARM repeat and interacts with Helix-C</scene> and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as <scene name='84/848919/Icat_bcat/3'>ICAT (orange), which interacts with the central ARM repeat of ß-catenin (green).</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1M1E 1M1E]) <ref name="valenta2012" /> | TCF transcription factors works as the principal nuclear member of ß-catenin multimeric complex. TCFs bind to DNA enhancers and ß-catenin acts as a link in a chain between them and others transcriptional coactivators. This interaction can be modulated to enhance, repress os switch off ß-catenin-mediated transcription. The majority of these transcription coactivators binds to <scene name='84/848919/R12andhelix-c/1'>the last ARM repeat and interacts with Helix-C</scene> and many of them can affect chromatin structure. Indeed, it seems that the C-terminus region of ß-catenin coordinates the recruitment and sequential exchange of these proteins. Binding of ß-catenin to TCF is blocked by some proteins such as <scene name='84/848919/Icat_bcat/3'>ICAT (orange), which interacts with the central ARM repeat of ß-catenin (green).</scene> ([http://www.rcsb.org/structure/1M1E 1M1E]) <ref name="valenta2012" /> | ||
Revision as of 21:41, 20 June 2020
ß-catenin
ß-catenin is an important element in cell adherens junctions connecting cytoplasmic proteins. Besides that, it is an essential regulator of the canonical Wnt pathway ([1]) (related to embryonic development). Disturbance of this activity is associated with cancer and other diseases. Therefore, ß-catenin is an important target for developing medication for many diseases, with considerable interest in its structure. [1]
| |||||||||||