We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Prolyl hydroxylase domain
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
See also [[Hydroxylase]] | See also [[Hydroxylase]] | ||
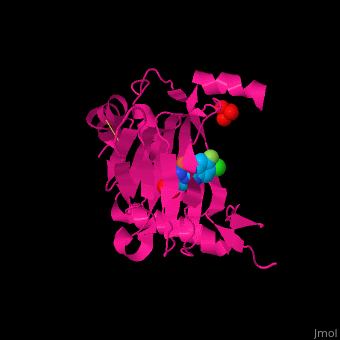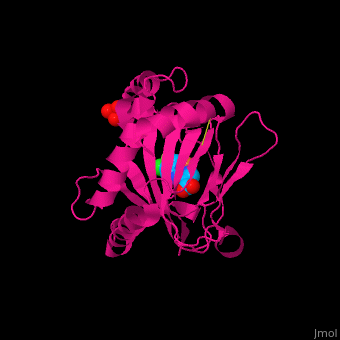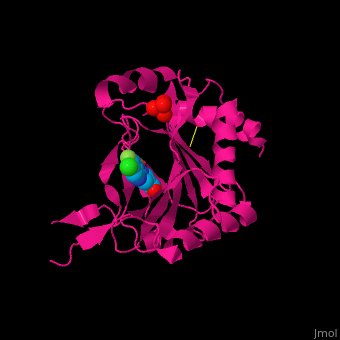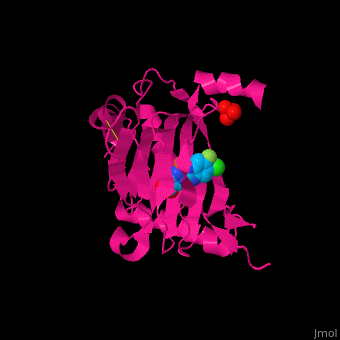
| - | '''Prolyl hydroxylase domain''' (PHD) proteins mediate oxygen-dependent degradation of Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) α subunit. They include PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3. The PHD is a Fe+2/oxogluterate (2OG)-dependent enzyme. [[3ouh]] is the crystallized structure of the enzyme PHD2, an [[oxidoreductase]] that is 237 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 27 kDa. [[3ouh]] is found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and is a homolog of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EGLN1 EGLN1] found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans C. elegans]. | + | '''Prolyl hydroxylase domain''' (PHD) or '''egl nine homolog 1''' (PHD2/EGLN1) proteins mediate oxygen-dependent degradation of Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) α subunit. They include PHD1, PHD2 and PHD3. The PHD is a Fe+2/oxogluterate (2OG)-dependent enzyme. [[3ouh]] is the crystallized structure of the enzyme PHD2, an [[oxidoreductase]] that is 237 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 27 kDa. [[3ouh]] is found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and is a homolog of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EGLN1 EGLN1] found in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caenorhabditis_elegans C. elegans]. |
The protein has three ligands: <scene name='45/459221/Cv/4'>O14</scene> (a 1-(5-chloro-6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid), <scene name='45/459221/Cv/3'>Fe+2 (an iron ion)</scene>, and SO<sub>4</sub> (a sulfate ion). Water molecules are shown as red spheres. It is involved in mediating physiological responses to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypoxia_(medical) hypoxia] by degrading the transcription factor of a hypoxia-inducible factor HIF1-α. In hypoxic conditions, the activity of PHD2 lessens, causing an increase in HIF1-α, resulting in secretion of erythropoietin, anaerobic [[glycolysis]], and angiogenesis<ref>PMID:16686427</ref>. | The protein has three ligands: <scene name='45/459221/Cv/4'>O14</scene> (a 1-(5-chloro-6-fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid), <scene name='45/459221/Cv/3'>Fe+2 (an iron ion)</scene>, and SO<sub>4</sub> (a sulfate ion). Water molecules are shown as red spheres. It is involved in mediating physiological responses to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypoxia_(medical) hypoxia] by degrading the transcription factor of a hypoxia-inducible factor HIF1-α. In hypoxic conditions, the activity of PHD2 lessens, causing an increase in HIF1-α, resulting in secretion of erythropoietin, anaerobic [[glycolysis]], and angiogenesis<ref>PMID:16686427</ref>. | ||
<ref>Rosen M D, Venkatesan H, Peltier H M, Bembenek S D, Kanelakis K C, Zhao L X, Leonard B E, Hocutt F M, Wu X, Palomino H L, Brondtetter T I, Haugh P V, Cagnon L, Yan W, Liotta L A, Young A, Mirzadegan T, Shankley N P, Barrett T D, Rabinowitz M H. Benzimidazole-2-pyrazole HIF Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Inhibitors as Oral Erythropoietin Secretagogues. ACS Medicinal Chemical Letters. 2010 Oct 5.</ref> For more detalis see [[Molecular Playground/Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain (PHD) Enzyme]]. | <ref>Rosen M D, Venkatesan H, Peltier H M, Bembenek S D, Kanelakis K C, Zhao L X, Leonard B E, Hocutt F M, Wu X, Palomino H L, Brondtetter T I, Haugh P V, Cagnon L, Yan W, Liotta L A, Young A, Mirzadegan T, Shankley N P, Barrett T D, Rabinowitz M H. Benzimidazole-2-pyrazole HIF Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Inhibitors as Oral Erythropoietin Secretagogues. ACS Medicinal Chemical Letters. 2010 Oct 5.</ref> For more detalis see [[Molecular Playground/Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain (PHD) Enzyme]]. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of prolyl hydroxylase domain == | == 3D Structures of prolyl hydroxylase domain == | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | [[ | + | *Prolyl hydroxylase domain containing Mn |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5l9r]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain residues 181-426 (mutant) + Mn + 2OG - human<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[3hqr]], [[5l9b]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain (mutant) + Mn + HIF 1 α C terminal + 2OG<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5l9v]], [[5la9]], [[5las]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain (mutant) + Mn + HIF NODD domain + 2OG<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[4bqw]], [[4bqx]], [[4bqy]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Mn + quinolin derivative<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[6st3]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Mn + pyrimidin derivative<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[6yvt]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Mn + pyridin derivative<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[6qgv]], [[5a3u]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Mn + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5ox6]], [[6ox5]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Mn + drug<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[5lat]], [[5lb6]], [[5lbb]], [[5lbc]], [[5lbe]], [[5lbf]], [[4uwd]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain (mutant) + Mn + quinolin derivative<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | **[[4h6j]] – hPHD Pasb domain 238-348 (mutant) + aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (mutant)<br /> |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | [[ | + | *Prolyl hydroxylase domain containing other metal ions |
| - | [[ | + | |
| + | **[[2y33]] – hPHD2 catalytic domain residues 181-426 + Zn + quinolin derivative – human<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ouh]], [[3oui]], [[5v18]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4kbz]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain (mutant) + Fe + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4jzr]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Ni + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3ouj]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + 2OG<br /> | ||
| + | **[[3hqu]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + HIF 1 α C terminal + quinolin derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[2hbt]], [[2hbu]], [[2g19]], [[2g1m]], [[2y34]], [[4bqi]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + quinolin derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5v18]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + pyridin derivative<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5v1b]] - hPHD1 catalytic domain + Fe + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nmq]] - hPHD2 catalytic domain + Fe + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 09:05, 7 October 2020
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of prolyl hydroxylase domain
Updated on 07-October-2020
References
- ↑ Stolze IP, Mole DR, Ratcliffe PJ. Regulation of HIF: prolyl hydroxylases. Novartis Found Symp. 2006;272:15-25; discussion 25-36. PMID:16686427
- ↑ Rosen M D, Venkatesan H, Peltier H M, Bembenek S D, Kanelakis K C, Zhao L X, Leonard B E, Hocutt F M, Wu X, Palomino H L, Brondtetter T I, Haugh P V, Cagnon L, Yan W, Liotta L A, Young A, Mirzadegan T, Shankley N P, Barrett T D, Rabinowitz M H. Benzimidazole-2-pyrazole HIF Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Inhibitors as Oral Erythropoietin Secretagogues. ACS Medicinal Chemical Letters. 2010 Oct 5.
Created with the participation of Andrew Winslow.