Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
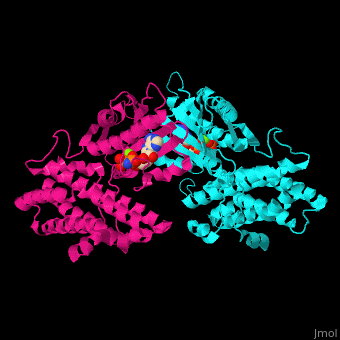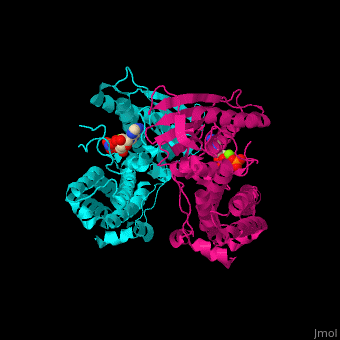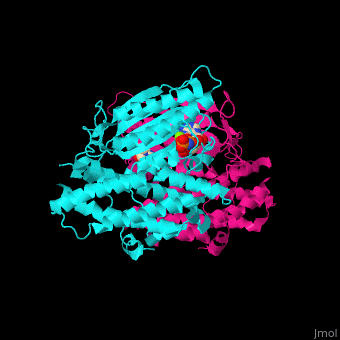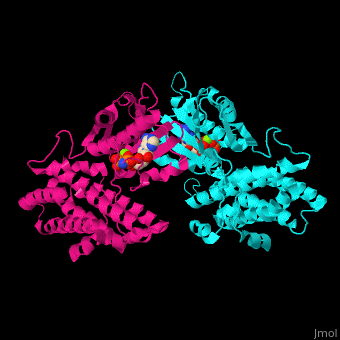
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 4 dimer complex with AMPPNP and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB entry [[2e0a]])' scene='48/485629/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isozyme 4 dimer complex with AMPPNP and Mg+2 ion (green) (PDB entry [[2e0a]])' scene='48/485629/Cv/1'> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase''' (PDK) is part of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This complex is located in the mitochondria and converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA as part of the citric acid cycle. PDK phosphphorylates serine residues on pyruvate dehydrogenase using ATP. There are 4 isozymes of PDK. The isozymes differ in length, activity and phosphorylation sites<ref>PMID:11486000</ref>. PDK1 is abundant in heart cells. PDK2 is abundant in mitochondria. PDK3 is abundant in testis. PDK4 is abundant in muscle and heart. | '''Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase''' (PDK) is part of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. This complex is located in the mitochondria and converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA as part of the citric acid cycle. PDK phosphphorylates serine residues on pyruvate dehydrogenase using ATP. There are 4 isozymes of PDK. The isozymes differ in length, activity and phosphorylation sites<ref>PMID:11486000</ref>. PDK1 is abundant in heart cells. PDK2 is abundant in mitochondria. PDK3 is abundant in testis. PDK4 is abundant in muscle and heart. | ||
Revision as of 07:29, 14 October 2020
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
Updated on 14-October-2020
References
- ↑ Korotchkina LG, Patel MS. Site specificity of four pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoenzymes toward the three phosphorylation sites of human pyruvate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 5;276(40):37223-9. Epub 2001 Aug 2. PMID:11486000 doi:10.1074/jbc.M103069200
- ↑ Roche TE, Hiromasa Y. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase regulatory mechanisms and inhibition in treating diabetes, heart ischemia, and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Apr;64(7-8):830-49. PMID:17310282 doi:10.1007/s00018-007-6380-z
- ↑ Sutendra G, Michelakis ED. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase as a novel therapeutic target in oncology. Front Oncol. 2013 Mar 7;3:38. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00038. eCollection 2013. PMID:23471124 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2013.00038
- ↑ Kukimoto-Niino M, Tokmakov A, Terada T, Ohbayashi N, Fujimoto T, Gomi S, Shiromizu I, Kawamoto M, Matsusue T, Shirouzu M, Yokoyama S. Inhibitor-bound structures of human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2011 Sep;67(Pt 9):763-73. doi:, 10.1107/S090744491102405X. Epub 2011 Aug 9. PMID:21904029 doi:10.1107/S090744491102405X