Sandbox GGC1
From Proteopedia
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
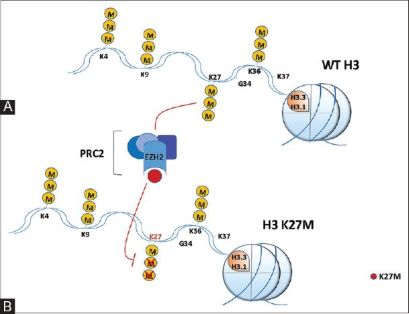
There have been studies that have identified mutations encoding a K27M substitution and there have also been mutations that encoded | There have been studies that have identified mutations encoding a K27M substitution and there have also been mutations that encoded | ||
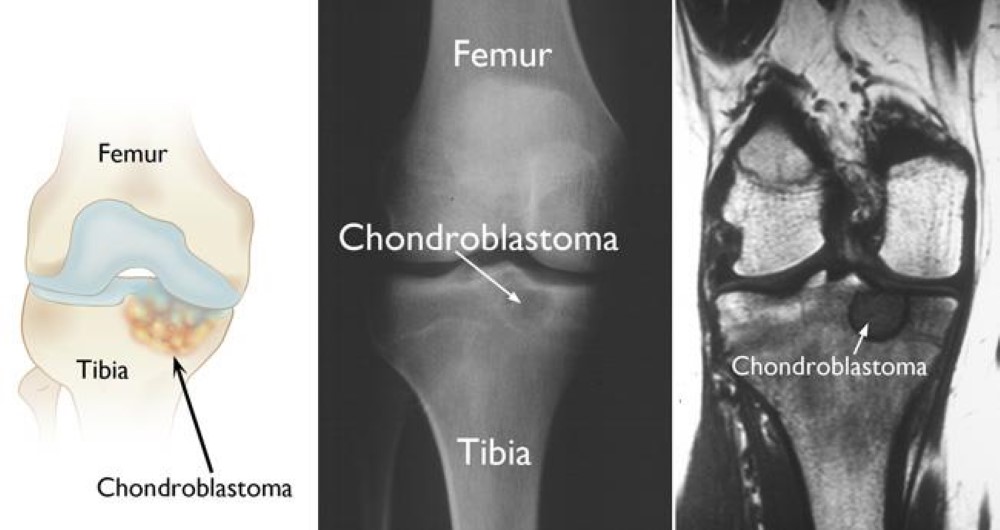
GLY 34 to ARG or VAL called the G34R/V substitution. K27M tumors are present in ex: spinal cord, thalamus, pons, brainstem and G34R/V tumors are shown in the cerebral hemispheres. There are mutations in H3.3 that are found in different types of bone tumors like [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4446520/ chrondroblastoma] for example and giant cell tumors of the bone. [https://cancerdiscovery.aacrjournals.org/content/3/12/1329.1 Chondroblastoma]arises in children and in young adults in the cartilage of the growth plates of the long bones and is most typically benign. | GLY 34 to ARG or VAL called the G34R/V substitution. K27M tumors are present in ex: spinal cord, thalamus, pons, brainstem and G34R/V tumors are shown in the cerebral hemispheres. There are mutations in H3.3 that are found in different types of bone tumors like [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4446520/ chrondroblastoma] for example and giant cell tumors of the bone. [https://cancerdiscovery.aacrjournals.org/content/3/12/1329.1 Chondroblastoma]arises in children and in young adults in the cartilage of the growth plates of the long bones and is most typically benign. | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Glioma_2018_1_4_117_240231_f1.jpg]] | [[Image:Glioma_2018_1_4_117_240231_f1.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 16 November 2020
Histone H3.3
| |||||||||||
References
1. Arimura, Y.; Shirayama, K.; Horikoshi, N.; Fujita, R.; Taguchi, H.; Kagawa, W.; Fukagawa, T.; Almouzni, G.; Kurumizaka, H. Crystal structure and stable property of the cancer-associated heterotypic nucleosome containing CENP-A and H3.3. https://www.nature.com/articles/srep07115 (accessed Nov 1, 2020).
2. Cancer Discovery Science Writers. Histone H3.3 Mutations Are Cancer Type-Specific. https://cancerdiscovery.aacrjournals.org/content/3/12/1329.1 (accessed Nov 14, 2020).
3. Gianno, F.; Antonelli, M.; Ferretti2018, E.; Massimino, M.; Arcella, A.; Giangaspero, F. Pediatric high-grade glioma: A heterogeneous group of neoplasms with different molecular drivers.  (accessed Nov 16, 2020).
(accessed Nov 16, 2020).
4. Kallappagoudar, S.; Yadav, R. K.; Lowe, B. R.; Partridge, J. F. Histone H3 mutations--a special role for H3.3 in tumorigenesis? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4446520/ (accessed Nov 1, 2020).
5. Morell, N.; Rajani, R. Chondroblastoma - OrthoInfo - AAOS. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/chondroblastoma (accessed Nov 16, 2020).
6.panelRuiGuo111LijuanZheng111Juw WonPark2RuituLv1HaoChen1FangfangJiao1WenqiXu1ShirongMu3HongWen45JinsongQiu6ZhentianWang1PengyuanYang1FeizhenWu1JingyiHui3XiangdongFu6XiaobingShi4512Yujiang GenoShi7812YiXing212…YangShi891012, A. links open overlay; RuiGuo111; 1; 11; LijuanZheng111; Juw WonPark2; 2; RuituLv1; HaoChen1; FangfangJiao1; WenqiXu1; ShirongMu3; 3; HongWen45; 4; 5; JinsongQiu6; 6; ZhentianWang1; PengyuanYang1; FeizhenWu1; JingyiHui3; XiangdongFu6; XiaobingShi4512; 12; Yujiang GenoShi7812; 7; 8; YiXing212; YangShi891012; 9; 10; Highlights•BS69/ZMYND11 binds H3.3K36me3 and colocalizes with H3.3K36me3 in gene bodies•BS69 directly interacts with EFTUD2; SummaryBS69 (also called ZMYND11) contains tandemly arranged PHD. BS69/ZMYND11 Reads and Connects Histone H3.3 Lysine 36 Trimethylation-Decorated Chromatin to Regulated Pre-mRNA Processing. https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S1097276514006777?token=A4FD3B8CDE2F310EA514C66E96DC4489F79C8EA96F6FC878DCD4BFC066FA809C2E83C8A9B57353A53915171AD2491D4C (accessed Nov 16, 2020).
7. UniProt ConsortiumEuropean Bioinformatics InstituteProtein Information ResourceSIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Histone H3.3. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P84243 (accessed Nov 1, 2020).
8.Yuen, B. T. K.; Knoepfler, P. S. Histone H3.3 mutations: a variant path to cancer. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3882088/ (accessed Nov 16, 2020).