| Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are transcription factors responsible of the cellular adaptation to hypoxia, which is a condition of low oxygen availability. Among the genes regulated by HIF, we can find those involved in erythropoiesis, angiogenesis and metabolism.
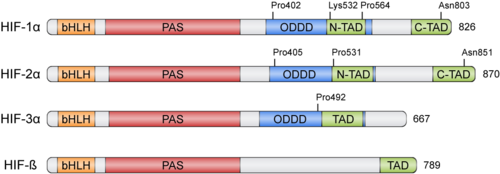
HIFs were discovered more than 30 years ago thanks to the Erythropoietin (EPO) gene, an hormone that is transcribed in hypoxic conditions and stimulates erythrocyte proliferation[3]. EPO presents an upstream Hypoxia Response Element (HRE) that resulted to be bound by HIF [4]. HIFs form part of the basic helix-loop-helix-Per-ARNT-Sim (bHLH-PAS) family of proteins[5]. Active HIFs are achieved by heterodimerization of a constitutively expressed subunit and an oxygen-regulated subunit, which can be HIF-1α or its paralogs and HIF-3α (Table 1.). HIF-β is also known as the aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (ARNT)[6]. Their structure can contain the following domains from the N-terminus to the C-terminus:
- basic Helix-Loop-Helix (): essential for heterodimer formation and DNA binding to HRE
- Per-Arnt-Sim ('): their surface forms the key core of the heterodimer.
- Oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD): mediates oxygen-regulated stability in the α subunits. This domain contains two Proline residues susceptible of hydroxylation and one Lysine that can be acetylated
- N-terminal and C-terminal transactivating domains (N-TAD and C-TAD): bind different coactivators to promote gene expression, such as p300/CBP[7]. HIF-3α lacks one of the TAD domains.
| Member
| Gene
| Protein
|
| HIF-1α | HIF1A | hypoxia-inducible factor 1, α subunit
|
| HIF-2α | EPAS1 | endothelial PAS domain protein 1
|
| HIF-3α | HIF3A | hypoxia-inducible factor 3, α subunit
|
| HIF-1β | ARNT | aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator
|
| HIF-2β | ARNT2 | aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2
|
| HIF-3β | ARNT3 | aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 3
|
Table 1: Members of the HIF family
Physiological Function
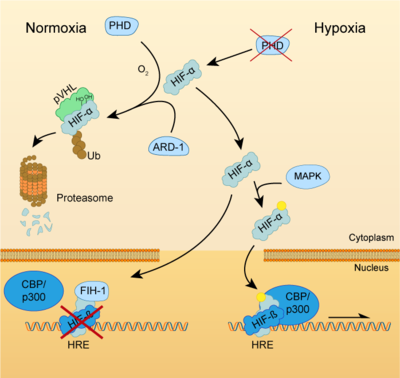
Both HIF-α and β subunits are constitutively and ubiquitously expressed in almost every single cell, although some isoforms may be predominant in some specific tissues[8]. For example, HIF-2α is mostly expressed in the endothelium, kidney, lung, heart and small intestine . While HIF-β protein levels in the cell are constant, HIF-α has a short half-life (~ 5 mins) and is highly regulated by oxygen through its ODDD domain. With normal oxygen levels (normoxia), HIF-α protein levels are rapidly degraded, resulting in essentially no detectable HIF-α protein. However, in hypoxic conditions HIF-α becomes stabilized and is translocated from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, where it dimerizes with HIF-β and the HIF complex formed becomes transcriptionally active. More than 100 genes with varying functions have been described to be transcribed by the action of HIF. Moreover, HIF regulates up to 2% of all human genes in arterial endothelial cells, either directly or indirectly[9]. In response to hypoxia, the capacity of red blood cells to transport oxygen is upregulated by the expression of genes like EPO, essential in erythropoiesis, and genes involved in iron metabolism. In addition, a large number of genes involved in different steps of angiogenesis have been shown to increase by hypoxia challenge, being the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) among them. VEGF directly recruits endothelial cells into hypoxic areas to generate new blood vessels by stimulating their proliferation. Furthermore, HIF complexes have been shown to induce pro-survival factors such as Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 (IGF2) and Transforming Growth Factor-α (TGF-α), which in turn enhances expression of HIFα itself.
Regulation of HIF-α subunits is achieved by pos-translational modifications such as hydroxylation, ubiquitination, acetylation and phosphorylation. De novo synthesized cytoplasmic HIF-α is rapidly hydroxylated on Pro402 and Pro564 (in HIF-1α) or Pro405 and Pro531 (in HIF-2α) by a family of Prolyl Hydroxylases (PHD) that recognize the consensus sequence LXXLAP . These PHD require an oxygen molecule that will be splitted to catalyze the hydroxylation of the target prolines[10]. Once the two proline residues of HIF-α are converted to hydroxyproline, the Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (pVHL) will recognize it. pVHL acts as the substrate recognition component of a complex with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that will then polyubiquitinate HIF-1α on Lysine 532 for proteasomal degradation[11]. In hypoxic conditions, PHDs will be inactive due to the lack of oxygen, so HIF-α can escape proteasomal degradation and translocate to the nucleus to active gene expression. Additional modifications can also modulate HIF-α properties: acetylation of Lys532 by Arrest-Defective-1 (ARD1) favors the interaction of HIF-1α with pVHL[12]; hydroxylation of Asn803 or 851 within the C-CAD domain (in HIF-1α or HIF-2α, respectively) by Factor Inhibiting HIF-1 (FIH-1) prevents interaction with p300/CBP, thus inhibiting transcription[13]. Furthermore, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) pathway seems to be able to phosphorylate HIF-α in response to growth factors. This phosphorylation would increase HIF complex transcriptional activity rather than affecting its stability or DNA-binding ability[14].
Clinical Significance
METER FRASE INTRODUCTORIA AQUI
HIF activators
Due to the protective role of HIF, therapies based on small-molecules that stabilize HIF-α have attracted a lot of attention. In pathologies such as ischemia or stroke, HIF activation could help to reduce the damage done by the lack of oxygen and restore tissue functionality. This objective can be achieved by two different ways: inhibition of HIF-PHD pathway or without the inhibition of PHDs [15].
HIF-1α Upregulation via Inhibition of PHD Pathway
This group includes the majority of HIF-1α upregulators. PHDs inhibition can be achieved through different interventions:
Iron chelators and competitors
Iron chelators reduce the number of free iron (Fe2+) by binding tightly to it. In this way, PHD enzymes do not have enough available iron to carry out the hydroxylation reaction and the expression of HIF-1α is upregulated. Also, iron competitors such as Co2+ or Mn2+ can be used [16]. Deferoxamine (DFO) and mimosine were the first iron chelators to mediate HIF-1α neuroprotection. Pre-treatment with DFO protected neurons from oxidative stress-induced death by inhibiting PHDs, therefore increasing mRNA and protein expression of both HIF-1α and its controlled genes [17]. 2,2-dipyridyl (DP) is a liposoluble iron chelator that upregulates HIF-1α expression. Treatment with this drug decreased expansion of tissue damage after ischemia and protected neurons and endothelial cells by decreasing the amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [18].
2-oxoglutarate analogs
2-oxoglutarate is also a required co-substrate for the hydroxylation reaction by PHDs. So, compounds such as hydroxybenzenes or their analogous can inhibit PHD action to stabilize HIF-1α an allow gene expression of its targets. Dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG) is a cell permeable ester that prevents HIF-1α degradation and increases VEGF levels in ischemic neurons. Studies in animal stroke models showed reduced ischemic injury in neurons and a lower degree of damage [19].
Alternative mechanism of action
Instead of sequestering Fe2+ ions or mimicking 2-oxoglutarate binding, some molecules can bind directly into the active site of PHDs. FG-4497 is a PHD inhibitor that stabilizes HIF-1α and upregulates VEGF and EPO in murine cell lines. It has also been shown to enhance cell survival following oxygen-glucose deprivation. Indeed, intraperitoneal administration of FG-4497 can reduce infarct size[20]. On the other hand, Folic acid (FA) can directly inhibit PHD2, FIH-1 and pVHL. Post-ischemic in vivo treatments showed that FA upregulated HIF-1α and its target genes[21].
HIF-1α Upregulation Without the Inhibition of PHDs
These kinds of molecules have been recently discovered. They can upregulate HIF-1α in different ways:
- MiR-335 is a microRNA that directly regulates HIF-1α. Treatment with this microRNA decreased infarct volume in rat models when administered early after ischemia induction, but inhibition of miR-335 in later phases surprisingly had beneficial effects. This could be due to the biphasic nature of HIF-1α[22].
- Proteasome inhibitors such as MG-132 can stabilize HIF-1α, with better prognosis when combined with DMOG. Other proteasome inhibitors, like epoxomicin or Bsc2118[23], are also able to reduce infarct size and promote cell survival in ischemic conditions, being even more effective than PHDs inhibitors[24].
HIF inhibitors
Given the significant role of the dysregulation of the HIF pathway in several diseases, numerous efforts have been devoted to the development of inhibitors that target the HIF pathway. There are two major categories of the HIF inhibitors: direct HIF inhibitors which affect the expression or function of the HIF molecules, and indirect HIF inhibitors which regulate other molecules in upstream or downstream pathways and affect the transcription, translation or degradation of the factor, ultimately altering the HIF signal as one of the targets.
Indirect HIF inhibitors
Inhibitors of HIF mRNA expression
EZN-2968 is an RNA antagonist composed of a third-generation oligonucleotide, a technology that specifically binds and inhibits the expression of HIF-1α mRNA. It has shown potent (IC50 = 1–5 nM) and selective inhibition of HIF-1α mRNA and protein expression in both normoxia and hypoxia [25]. Preclinical studies both in vitro and in vivo in xenograft prostate cancer mice showed promising results [25], while a Phase II trial was inconclusive due to premature closure [26].
Inhibitors of HIF protein translation
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: PI3K/Akt/mTOR plays a major role in the upregulation of HIF-1 several human cancer cell lines, mainly by increasing the rate of HIF-1α protein translation. Although the process by which this pathway regulates HIF protein translation is still poorly understood, several mTOR inhibitors, such as temsirolimus and everolimus, which are two FDA approved agents for the treatment of different types of cancer, have shown to inhibit HIF-1α.
- Camptothecin analogues (CPTs): CPTs analogues are used as chemotherapeutic agents that induce the formation of Topoisomerase I-DNA cleavage complexes, which in the presence of DNA replication generate double strand DNA breaks and cytotoxicity. Among the CPTs is Topotecan, a chemotherapeutic agent that has been approved for the treatment of ovarian cancer, cervical cancer and non-small cell lung carcinoma. This agent act as a HIF inhibitor by blocking HIF-1α protein accumulation and transcriptional activity in a topoisomerase I-dependent manner[27].
- Steroidal HIF inhibitors: 2-Methoxyestradiol (2ME2 or panzem) is a natural metabolite of estradiol that inhibits HIF-1α translation and transcriptional activity. Although the specific mechanism by 2ME2 and its synthetic analogues inhibit HIF is unknown, these compounds bind to the colchicine binding site of tubulin and cause the disruption of tumor interphase microtubules, which results in repression of HIF-1α at translation level [28]. 2ME2 and its synthetic analogues have shown antitumoral activity in preclinical models as well as favorable oral bioavailability, metabolic stability and safety profiles [29]. Unfortunately, 2ME2 has been evaluated in several clinical trials both alone and in combination with other drugs and has shown limited efficacy in the treatment of different types of cancer.
Inhibitors of HIF stabilization
- HSP90 inhibitors: The binding of HSP90 to HIF-1α promotes HIF-1α activity by blocking the pVHL-independent proteasomal degradation and also by helping HIF-1α heterodimers acquire the appropriate conformation to recruit p300 and consequently initiate HIF transactivation. The first HSP90 inhibitor identified was the natural product geldanamycin, a benzoquinone ansamyzine antibiotic that inhibits HSP90 by competing with its ATP binding site. Several HSP90 inhibitors have been developed since, and despite their promising results in preclinical studies, they have demonstrated limited efficacy during clinical trials [30].
- Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi): Histone deacetylases mediate the removal of acetyl groups from target proteins, regulating their function[31]. Treatment with HDACi results in the hyperacetylation of histones and other target proteins such as the chaperone HSP90, leading to a loss of activity. It was recently described that this HSP90 inhibition by an HDACi such as Vorinostat leads to an alteration in HIF-1α signaling by interfering with its ability to translocate to the nucleus[32], although other mechanisms of alteration of HIF-1α signalling by HDAC1 have been proposed[33]. Vorinostat and Romidepsin have been recently approved for the treatment of cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), and these and others are currently being evaluated for the treatment of various tumors, both alone and in combination with other agents[34].
Direct HIF inhibitors
Inhibitors of HIF-1 dimerization
- PT2385 and PT2399 are recently discovered small molecules and selective HIF-2α inhibitors that bind to the HIF-1β hydrophobic pocket and allosterically block its dimerization with HIF-2α (see below).
- Acriflavine is a mixture of trypaflavin (3,6-diamino-10-methylacridinium chloride) and proflavine (3,6-diaminoacridine), which has trypanocidal, antibacterial, and antiviral activities. Acriflavine is also a HIF inhibitor that acts through inhibition of HIF-1 dimerization by binding to the PAS-B subdomain of HIF-1α and HIF-2α[35]. This agent has demonstrated highly promising antitumor activity against a wide spectrum of cancers, including colorectal, hepatocellular, and ovarian cancer cell lines, and more recently in malignant brain cancer both in vitro and in vivo[36]. Its promising safety profile and characteristic ability of binding to both HIF-1α and HIF-2α subunits makes it a promising candidate for clinical evaluation.
Inhibitors of HIF-1 transcriptional activity
- Cardenolides are natural steroids with 25–26 carbon atoms and a five or six-membered lactone ring at C-17. Among them, Digoxin is a widely used cardiac glycoside that has been in clinical use for the treatment of heart failure for many years. This compound also shows HIF-1 inhibitory activity, which has demonstrated efficiency to block tumor growth, invasion, vascularization and metastasis of breast cancer (among other cancer types) both ex vivo and in vivo assays[37]. Digoxin was well tolerated by patients of prostate cancer in a phase II clinical trial and has been evaluated both alone and in combination with other therapies for other types of cancer. It has also demonstrated great efficacy as an inhibitor of pathological angiogenesis in a murine model of ischemic retinopathy[38].
- Chetomin is an antimicrobial dithioketopiperazine fungal metabolite which acts as a HIF-1 inhibitor by blocking its transcriptional co-activation pathway. Chetomin binds to the CH1 domain of the co-activator p300/CBP and disrupts its tertiary structure, thus hindering its interaction with HIF-1 and lowering its transactivation. This compound exhibited antitumoral activity both in vitro and in vivo in a murine model of prostate cancer[39], however, the usefulness of this HIF inhibitor is limited by its toxicity.
- Bortemozib is the first proteasome inhibitor that has been approved by the FDA, in this case for the treatment of multiple myeloma. It has more recently been identified as an HIF-1 inhibitor which simulates the interaction between the C-TAD domain of HIF-1 and FIH target site, thus enhancing FIH mediated repression of p300 recruitment and lowering HIF transactivation[40].
Inhibitors of HIF-1/DNA binding
Echinomycin is a natural cyclic peptide that belongs to the quinoxaline antibiotic family. It also acts as a HIF-1 inhibitor by specifically binding to the core of its recognition sequence, impeding HIF-1 to bind to its target DNA sequence[41]. Although it demonstrated antitumor activity in preclinical studies, no significant antitumoral activity was observed in clinical trials[42].
References
- ↑ Ke Q, Costa M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;70(5):1469-80. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.027029. Epub 2006 Aug, 3. PMID:16887934 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/mol.106.027029
- ↑ Wu D, Potluri N, Lu J, Kim Y, Rastinejad F. Structural integration in hypoxia-inducible factors. Nature. 2015 Aug 5. doi: 10.1038/nature14883. PMID:26245371 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14883
- ↑ Goldberg MA, Dunning SP, Bunn HF. Regulation of the erythropoietin gene: evidence that the oxygen sensor is a heme protein. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1412-5. doi: 10.1126/science.2849206. PMID:2849206 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.2849206
- ↑ Semenza GL, Nejfelt MK, Chi SM, Antonarakis SE. Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3' to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5680-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5680. PMID:2062846 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.13.5680
- ↑ Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5510-4. PMID:7539918
- ↑ Reyes H, Reisz-Porszasz S, Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1193-5. PMID:1317062
- ↑ Dames SA, Martinez-Yamout M, De Guzman RN, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. Structural basis for Hif-1 alpha /CBP recognition in the cellular hypoxic response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 16;99(8):5271-6. PMID:11959977 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082121399
- ↑ Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J. HIF-1 and HIF-2 transcription factors--similar but not identical. Mol Cells. 2010 May;29(5):435-42. doi: 10.1007/s10059-010-0067-2. Epub 2010 Apr, 12. PMID:20396958 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0067-2
- ↑ Manalo DJ, Rowan A, Lavoie T, Natarajan L, Kelly BD, Ye SQ, Garcia JG, Semenza GL. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by HIF-1. Blood. 2005 Jan 15;105(2):659-69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2958. Epub 2004 Sep , 16. PMID:15374877 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2958
- ↑ Bruick RK, McKnight SL. A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science. 2001 Nov 9;294(5545):1337-40. doi: 10.1126/science.1066373. Epub 2001, Oct 11. PMID:11598268 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1066373
- ↑ Kamura T, Sato S, Iwai K, Czyzyk-Krzeska M, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. Activation of HIF1alpha ubiquitination by a reconstituted von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Sep 12;97(19):10430-5. PMID:10973499 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.190332597
- ↑ Jeong JW, Bae MK, Ahn MY, Kim SH, Sohn TK, Bae MH, Yoo MA, Song EJ, Lee KJ, Kim KW. Regulation and destabilization of HIF-1alpha by ARD1-mediated acetylation. Cell. 2002 Nov 27;111(5):709-20. PMID:12464182
- ↑ Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ, Whitelaw ML. Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain a hypoxic switch. Science. 2002 Feb 1;295(5556):858-61. doi: 10.1126/science.1068592. PMID:11823643 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1068592
- ↑ Richard DE, Berra E, Gothie E, Roux D, Pouyssegur J. p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases phosphorylate hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and enhance the transcriptional activity of HIF-1. J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 12;274(46):32631-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.46.32631. PMID:10551817 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.46.32631
- ↑ Davis CK, Jain SA, Bae ON, Majid A, Rajanikant GK. Hypoxia Mimetic Agents for Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jan 8;6:175. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00175. eCollection, 2018. PMID:30671433 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00175
- ↑ Davis CK, Jain SA, Bae ON, Majid A, Rajanikant GK. Hypoxia Mimetic Agents for Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jan 8;6:175. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00175. eCollection, 2018. PMID:30671433 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2018.00175
- ↑ Zaman K, Ryu H, Hall D, O'Donovan K, Lin KI, Miller MP, Marquis JC, Baraban JM, Semenza GL, Ratan RR. Protection from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cortical neuronal cultures by iron chelators is associated with enhanced DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and ATF-1/CREB and increased expression of glycolytic enzymes, p21(waf1/cip1), and erythropoietin. J Neurosci. 1999 Nov 15;19(22):9821-30. PMID:10559391
- ↑ Demougeot C, Van Hoecke M, Bertrand N, Prigent-Tessier A, Mossiat C, Beley A, Marie C. Cytoprotective efficacy and mechanisms of the liposoluble iron chelator 2,2'-dipyridyl in the rat photothrombotic ischemic stroke model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Dec;311(3):1080-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.072744. Epub , 2004 Jul 27. PMID:15280435 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.072744
- ↑ Nagel S, Papadakis M, Chen R, Hoyte LC, Brooks KJ, Gallichan D, Sibson NR, Pugh C, Buchan AM. Neuroprotection by dimethyloxalylglycine following permanent and transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Jan;31(1):132-43. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.60. Epub, 2010 Apr 21. PMID:20407463 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2010.60
- ↑ Reischl S, Li L, Walkinshaw G, Flippin LA, Marti HH, Kunze R. Inhibition of HIF prolyl-4-hydroxylases by FG-4497 reduces brain tissue injury and edema formation during ischemic stroke. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 7;9(1):e84767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084767. eCollection , 2014. PMID:24409307 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084767
- ↑ Davis CK, Nampoothiri SS, Rajanikant GK. Folic Acid Exerts Post-Ischemic Neuroprotection In Vitro Through HIF-1alpha Stabilization. Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Nov;55(11):8328-8345. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0982-3. Epub, 2018 Mar 14. PMID:29542054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0982-3
- ↑ Liu FJ, Kaur P, Karolina DS, Sepramaniam S, Armugam A, Wong PT, Jeyaseelan K. MiR-335 Regulates Hif-1alpha to Reduce Cell Death in Both Mouse Cell Line and Rat Ischemic Models. PLoS One. 2015 Jun 1;10(6):e0128432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128432., eCollection 2015. PMID:26030758 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128432
- ↑ Doeppner TR, Mlynarczuk-Bialy I, Kuckelkorn U, Kaltwasser B, Herz J, Hasan MR, Hermann DM, Bahr M. The novel proteasome inhibitor BSc2118 protects against cerebral ischaemia through HIF1A accumulation and enhanced angioneurogenesis. Brain. 2012 Nov;135(Pt 11):3282-97. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws269. PMID:23169919 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws269
- ↑ Badawi Y, Shi H. Relative Contribution of Prolyl Hydroxylase-Dependent and -Independent Degradation of HIF-1alpha by Proteasomal Pathways in Cerebral Ischemia. Front Neurosci. 2017 May 17;11:239. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00239. eCollection, 2017. PMID:28566998 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00239
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Greenberger LM, Horak ID, Filpula D, Sapra P, Westergaard M, Frydenlund HF, Albaek C, Schroder H, Orum H. A RNA antagonist of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, EZN-2968, inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Nov;7(11):3598-608. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0510., Epub 2008 Oct 30. PMID:18974394 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0510
- ↑ Jeong W, Rapisarda A, Park SR, Kinders RJ, Chen A, Melillo G, Turkbey B, Steinberg SM, Choyke P, Doroshow JH, Kummar S. Pilot trial of EZN-2968, an antisense oligonucleotide inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha), in patients with refractory solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;73(2):343-8. doi: 10.1007/s00280-013-2362-z., Epub 2013 Nov 30. PMID:24292632 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2362-z
- ↑ Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O, Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G. Topoisomerase I-mediated inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: mechanism and therapeutic implications. Cancer Res. 2004 Feb 15;64(4):1475-82. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3139. PMID:14983893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3139
- ↑ Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Johnson MS, Willard MT, Zhong H, Simons JW, Giannakakou P. 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell. 2003 Apr;3(4):363-75. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00077-1. PMID:12726862 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00077-1
- ↑ Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Johnson MS, Willard MT, Zhong H, Simons JW, Giannakakou P. 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell. 2003 Apr;3(4):363-75. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00077-1. PMID:12726862 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00077-1
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/https
- ↑ Turtoi A, Peixoto P, Castronovo V, Bellahcene A. Histone deacetylases and cancer-associated angiogenesis: current understanding of the biology and clinical perspectives. Crit Rev Oncog. 2015;20(1-2):119-37. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423. PMID:25746107 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423
- ↑ Zhang C, Yang C, Feldman MJ, Wang H, Pang Y, Maggio DM, Zhu D, Nesvick CL, Dmitriev P, Bullova P, Chittiboina P, Brady RO, Pacak K, Zhuang Z. Vorinostat suppresses hypoxia signaling by modulating nuclear translocation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha. Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(34):56110-56125. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18125., eCollection 2017 Aug 22. PMID:28915577 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18125
- ↑ Turtoi A, Peixoto P, Castronovo V, Bellahcene A. Histone deacetylases and cancer-associated angiogenesis: current understanding of the biology and clinical perspectives. Crit Rev Oncog. 2015;20(1-2):119-37. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423. PMID:25746107 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423
- ↑ Turtoi A, Peixoto P, Castronovo V, Bellahcene A. Histone deacetylases and cancer-associated angiogenesis: current understanding of the biology and clinical perspectives. Crit Rev Oncog. 2015;20(1-2):119-37. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423. PMID:25746107 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1615/critrevoncog.2014012423
- ↑ Lee K, Zhang H, Qian DZ, Rey S, Liu JO, Semenza GL. Acriflavine inhibits HIF-1 dimerization, tumor growth, and vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 20;106(42):17910-5. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0909353106. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID:19805192 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909353106
- ↑ Mangraviti A, Raghavan T, Volpin F, Skuli N, Gullotti D, Zhou J, Asnaghi L, Sankey E, Liu A, Wang Y, Lee DH, Gorelick N, Serra R, Peters M, Schriefer D, Delaspre F, Rodriguez FJ, Eberhart CG, Brem H, Olivi A, Tyler B. HIF-1alpha- Targeting Acriflavine Provides Long Term Survival and Radiological Tumor Response in Brain Cancer Therapy. Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 2;7(1):14978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14990-w. PMID:29097800 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14990-w
- ↑ Zhang H, Qian DZ, Tan YS, Lee K, Gao P, Ren YR, Rey S, Hammers H, Chang D, Pili R, Dang CV, Liu JO, Semenza GL. Digoxin and other cardiac glycosides inhibit HIF-1alpha synthesis and block tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 16;105(50):19579-86. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0809763105. Epub 2008 Nov 19. PMID:19020076 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809763105
- ↑ Yoshida T, Zhang H, Iwase T, Shen J, Semenza GL, Campochiaro PA. Digoxin inhibits retinal ischemia-induced HIF-1alpha expression and ocular neovascularization. FASEB J. 2010 Jun;24(6):1759-67. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-145664. Epub 2010 Jan 11. PMID:20065104 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-145664
- ↑ Reece KM, Richardson ED, Cook KM, Campbell TJ, Pisle ST, Holly AJ, Venzon DJ, Liewehr DJ, Chau CH, Price DK, Figg WD. Epidithiodiketopiperazines (ETPs) exhibit in vitro antiangiogenic and in vivo antitumor activity by disrupting the HIF-1alpha/p300 complex in a preclinical model of prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 2014 Apr 28;13:91. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-91. PMID:24775564 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-91
- ↑ Befani CD, Vlachostergios PJ, Hatzidaki E, Patrikidou A, Bonanou S, Simos G, Papandreou CN, Liakos P. Bortezomib represses HIF-1alpha protein expression and nuclear accumulation by inhibiting both PI3K/Akt/TOR and MAPK pathways in prostate cancer cells. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Jan;90(1):45-54. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0805-8. Epub 2011, Sep 10. PMID:21909688 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0805-8
- ↑ Kong D, Park EJ, Stephen AG, Calvani M, Cardellina JH, Monks A, Fisher RJ, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G. Echinomycin, a small-molecule inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 DNA-binding activity. Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 1;65(19):9047-55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1235. PMID:16204079 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1235
- ↑ Kong D, Park EJ, Stephen AG, Calvani M, Cardellina JH, Monks A, Fisher RJ, Shoemaker RH, Melillo G. Echinomycin, a small-molecule inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 DNA-binding activity. Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 1;65(19):9047-55. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1235. PMID:16204079 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1235
|