|
|
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
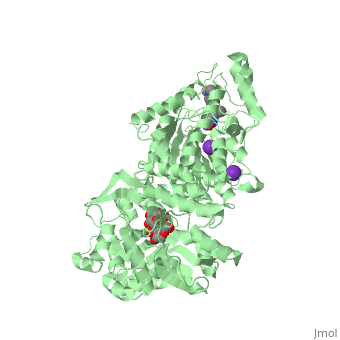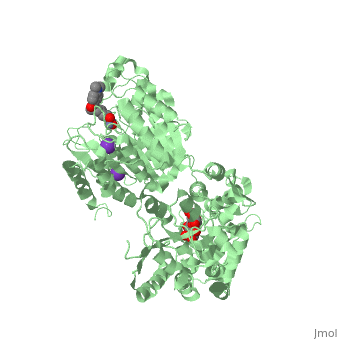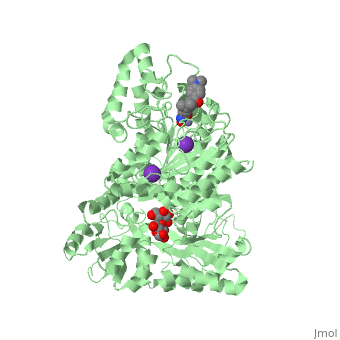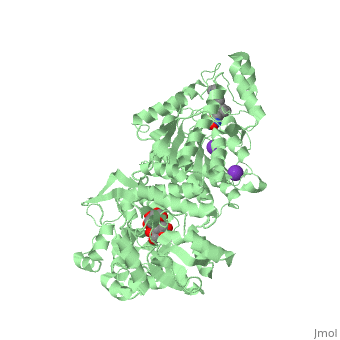
| | <StructureSection load='5edu' size='340' side='right'caption='[[5edu]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.79Å' scene=''> | | <StructureSection load='5edu' size='340' side='right'caption='[[5edu]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.79Å' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[5edu]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=5EDU OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [http://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=5EDU FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[5edu]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Escherichia_coli Escherichia coli] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=5EDU OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=5EDU FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GLC:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE'>GLC</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=K:POTASSIUM+ION'>K</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=TSN:TRICHOSTATIN+A'>TSN</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.79Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[5eef|5eef]], [[5eei|5eei]], [[5eek|5eek]], [[5eem|5eem]], [[5een|5een]], [[5ef7|5ef7]], [[5ef8|5ef8]], [[5efb|5efb]], [[5efg|5efg]], [[5efh|5efh]], [[5efj|5efj]], [[5efk|5efk]], [[5efn|5efn]]</div></td></tr> | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GLC:ALPHA-D-GLUCOSE'>GLC</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=K:POTASSIUM+ION'>K</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=PRD_900001:alpha-maltose'>PRD_900001</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=TSN:TRICHOSTATIN+A'>TSN</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=ZN:ZINC+ION'>ZN</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">HDAC6, KIAA0901, JM21 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr>
| + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=5edu FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=5edu OCA], [https://pdbe.org/5edu PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=5edu RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/5edu PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=5edu ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone_deacetylase Histone deacetylase], with EC number [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.5.1.98 3.5.1.98] </span></td></tr> | + | |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=5edu FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=5edu OCA], [http://pdbe.org/5edu PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=5edu RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/5edu PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=5edu ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/MALE_ECO57 MALE_ECO57]] Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system MalEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides (By similarity). | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/MALE_ECOLI MALE_ECOLI] Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system MalEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides.[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/HDAC6_HUMAN HDAC6_HUMAN] Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes (By similarity). Plays a central role in microtubule-dependent cell motility via deacetylation of tubulin.<ref>PMID:12024216</ref> <ref>PMID:17846173</ref> In addition to its protein deacetylase activity, plays a key role in the degradation of misfolded proteins: when misfolded proteins are too abundant to be degraded by the chaperone refolding system and the ubiquitin-proteasome, mediates the transport of misfolded proteins to a cytoplasmic juxtanuclear structure called aggresome. Probably acts as an adapter that recognizes polyubiquitinated misfolded proteins and target them to the aggresome, facilitating their clearance by autophagy.<ref>PMID:12024216</ref> <ref>PMID:17846173</ref> |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 21: |
Line 19: |
| | </div> | | </div> |
| | <div class="pdbe-citations 5edu" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | | <div class="pdbe-citations 5edu" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> |
| | + | |
| | + | ==See Also== |
| | + | *[[Histone deacetylase 3D structures|Histone deacetylase 3D structures]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Histone deacetylase]] | + | [[Category: Escherichia coli]] |
| - | [[Category: Human]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Christianson, D W]] | + | [[Category: Christianson DW]] |
| - | [[Category: Hai, Y]] | + | [[Category: Hai Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Hydrolase-hydrolase inhibitor complex]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
5edu is a 2 chain structure with sequence from Escherichia coli and Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
| | Method: | X-ray diffraction, Resolution 2.79Å |
| Ligands: | , , , , |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, ProSAT |
Function
MALE_ECOLI Involved in the high-affinity maltose membrane transport system MalEFGK. Initial receptor for the active transport of and chemotaxis toward maltooligosaccharides.HDAC6_HUMAN Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes (By similarity). Plays a central role in microtubule-dependent cell motility via deacetylation of tubulin.[1] [2] In addition to its protein deacetylase activity, plays a key role in the degradation of misfolded proteins: when misfolded proteins are too abundant to be degraded by the chaperone refolding system and the ubiquitin-proteasome, mediates the transport of misfolded proteins to a cytoplasmic juxtanuclear structure called aggresome. Probably acts as an adapter that recognizes polyubiquitinated misfolded proteins and target them to the aggresome, facilitating their clearance by autophagy.[3] [4]
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is a critical target for drug design because of its role in oncogenic transformation and cancer metastasis, and is unique among all histone deacetylases in that it contains tandem catalytic domains designated CD1 and CD2. We now report the crystal structures of CD2 from Homo sapiens HDAC6 and of CD1 and CD2 from Danio rerio HDAC6. We correlated these structures with activity measurements using 13 different substrates. The catalytic activity of CD2 from both species exhibited broad substrate specificity, whereas that of CD1 was highly specific for substrates bearing C-terminal acetyllysine residues. Crystal structures of substrate complexes yielded unprecedented snapshots of the catalytic mechanism. Additionally, crystal structures of complexes with eight different inhibitors, including belinostat and panobinostat (currently used in cancer chemotherapy), the macrocyclic tetrapeptide HC toxin, and the HDAC6-specific inhibitor N-hydroxy-4-(2-((2-hydroxyethyl)(phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)benzamide, revealed surprising new insight regarding changes in Zn2+ coordination and isozyme-specific inhibition.
Histone deacetylase 6 structure and molecular basis of catalysis and inhibition.,Hai Y, Christianson DW Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Jul 25. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2134. PMID:27454933[5]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF, Yao TP. HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 2002 May 23;417(6887):455-8. PMID:12024216 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/417455a
- ↑ Olzmann JA, Li L, Chudaev MV, Chen J, Perez FA, Palmiter RD, Chin LS. Parkin-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination targets misfolded DJ-1 to aggresomes via binding to HDAC6. J Cell Biol. 2007 Sep 10;178(6):1025-38. PMID:17846173 doi:10.1083/jcb.200611128
- ↑ Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF, Yao TP. HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature. 2002 May 23;417(6887):455-8. PMID:12024216 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/417455a
- ↑ Olzmann JA, Li L, Chudaev MV, Chen J, Perez FA, Palmiter RD, Chin LS. Parkin-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination targets misfolded DJ-1 to aggresomes via binding to HDAC6. J Cell Biol. 2007 Sep 10;178(6):1025-38. PMID:17846173 doi:10.1083/jcb.200611128
- ↑ Hai Y, Christianson DW. Histone deacetylase 6 structure and molecular basis of catalysis and inhibition. Nat Chem Biol. 2016 Jul 25. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2134. PMID:27454933 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2134
|