We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1wki
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
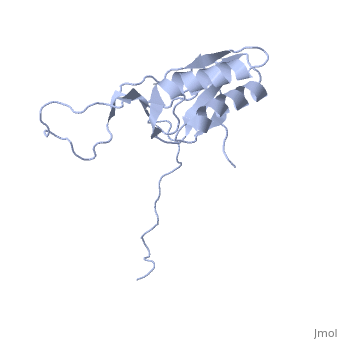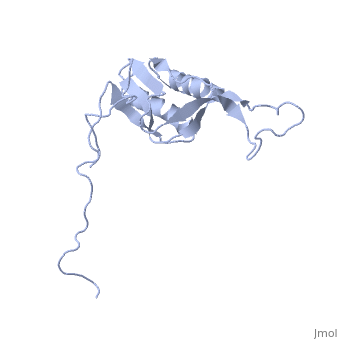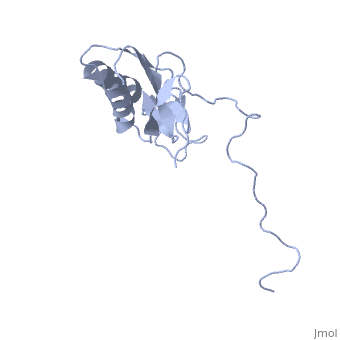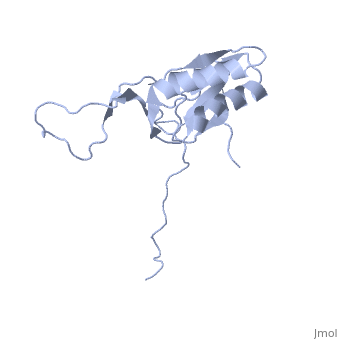
==solution structure of ribosomal protein L16 from thermus thermophilus HB8== | ==solution structure of ribosomal protein L16 from thermus thermophilus HB8== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1wki' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1wki | + | <StructureSection load='1wki' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1wki]]' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1wki]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1wki]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermus_thermophilus_HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1WKI OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1WKI FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1wki FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1wki OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1wki PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1wki RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1wki PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1wki ProSAT], [https://www.topsan.org/Proteins/RSGI/1wki TOPSAN]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [ | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/RL16_THET8 RL16_THET8] This protein binds directly to 23S rRNA. Interacts with the A site tRNA.[HAMAP-Rule:MF_01342] |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1wki ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1wki ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | Ribosomal protein L16 is an essential component of the bacterial ribosome. It organizes the architecture of aminoacyl tRNA binding site in the ribosome 50S subunit. The three-dimensional structure of L16 from Thermus thermophilus HB8 was determined by NMR. In solution, L16 forms an alpha+beta sandwich structure combined with two additional beta sheets located at the loop regions connecting the two layers. The terminal regions and a central loop region did not show any specific secondary structure. The structured part of L16 could be superimposed well on the C(alpha) model of L16 determined in the crystal structure of the ribosome 50S subunit. By overlaying the L16 solution structure onto the coordinates of the ribosome crystal structure, we constructed the combined model that represents the ribosome-bound state of L16 in the detailed structure. The model showed that L16 possesses residues in contact with helices 38, 39, 42, 43 and 89 of 23S rRNA and helix 4 of 5S rRNA. This suggests its broad effect on the ribosome architecture. Comparison of L16 with the L10e protein, which is the archaeal counterpart, showed that they share a common fold, but differ in some regions of functional importance, especially in the N-terminal region. All known mutation sites in L16 that confer resistance to avilamycin and evernimicin were positioned so that their side-chains were exposed to solvent in the internal cavity of the ribosome. This suggests the direct participation of L16 as a part of the binding site for antibiotics. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Solution structure of ribosomal protein L16 from Thermus thermophilus HB8.,Nishimura M, Yoshida T, Shirouzu M, Terada T, Kuramitsu S, Yokoyama S, Ohkubo T, Kobayashi Y J Mol Biol. 2004 Dec 10;344(5):1369-83. PMID:15561149<ref>PMID:15561149</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.<br> | ||
| - | </div> | ||
| - | <div class="pdbe-citations 1wki" style="background-color:#fffaf0;"></div> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Ribosomal protein L16|Ribosomal protein L16]] | *[[Ribosomal protein L16|Ribosomal protein L16]] | ||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
[[Category: Large Structures]] | [[Category: Large Structures]] | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Thermus thermophilus HB8]] |
| - | [[Category: Kobayashi | + | [[Category: Kobayashi Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Kuramitsu | + | [[Category: Kuramitsu S]] |
| - | [[Category: Nishimura | + | [[Category: Nishimura M]] |
| - | [[Category: Ohkubo | + | [[Category: Ohkubo T]] |
| - | + | [[Category: Shirouzu M]] | |
| - | [[Category: Shirouzu | + | [[Category: Terada T]] |
| - | [[Category: Terada | + | [[Category: Yokoyama S]] |
| - | [[Category: Yokoyama | + | [[Category: Yoshida T]] |
| - | [[Category: Yoshida | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
solution structure of ribosomal protein L16 from thermus thermophilus HB8
| |||||||||||