We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Leanne Price/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
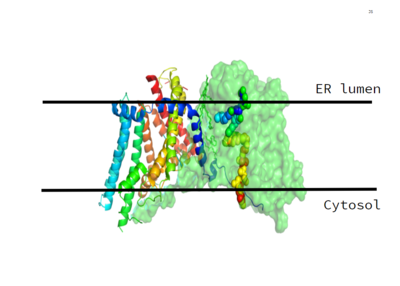
| - | The active site of DGAT is located within the membrane, with the catalytic histidine residue (<scene name='87/877601/His415/ | + | The active site of DGAT is located within the membrane, with the catalytic histidine residue (<scene name='87/877601/His415/2'>His415</scene>) buried inside the central cavity. This central cavity serves as the catalytic site. The acyl-acceptor lipid substrates access the active site through the lateral gate within the membrane. The active site also contains <scene name='87/877601/His415/1'>His415</scene> and several nearby polar residues (including Asn378, Gln437, and Gln465) whose side chains are oriented towards the cavity center. These residues interact and create a hydrophilic channel within the active site. The His415 residue is also likely involved in catalysis, making it increasingly significant. |
Revision as of 23:16, 17 March 2021
DGAT Human
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
- ↑ Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
Student Contributors
- Justin Smith
- Eloi Bigirimana
- Leanne Price