User:Haylie Moehlenkamp/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Disease=== | ===Disease=== | ||
==Alzheimer's Disease== | ==Alzheimer's Disease== | ||
| - | Alzheimer's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular plaques that cause interferences with memory retrieval. These plaques are made up of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides which are products of the cleavage of human Amyloid Precursor Protein (hAPP) | + | Alzheimer's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular plaques that cause interferences with memory retrieval. These plaques are made up of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides which are products of the cleavage of human Amyloid Precursor Protein (hAPP) <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">doi:10.4155/fmc.15.161</ref>. Within the cells, there is an accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">doi:10.4155/fmc.15.161</ref>. Research has shown that the concentration of cholesterol within cells can affect the production of Aβ <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">doi:10.4155/fmc.15.161</ref>. As the concentration of cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons increases, hAPP is downregulated <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">doi:10.4155/fmc.15.161</ref>. Inhibition of ACAT1 would lead to higher concentrations of cholesterol in the cells, signaling downregulation of hAPP. Less hAPP available decreases the amount of Aβ peptides being produced and decreases the available Aβ peptides that could form the extracellular plaques associated with Alzheimer's Disease <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">doi:10.4155/fmc.15.161</ref>. |
===Relevance=== | ===Relevance=== | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 30 March 2021
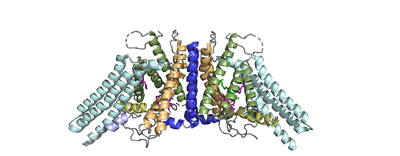
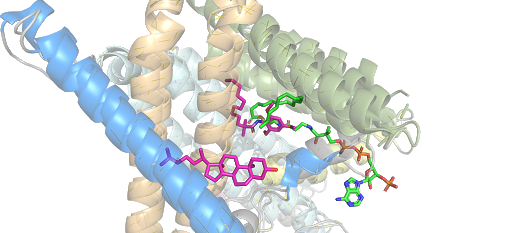
ACAT
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Chang TY, Chang CC, Bryleva E, Rogers MA, Murphy SR. Neuronal cholesterol esterification by ACAT1 in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):261-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.305. PMID:20101629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iub.305
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
Haylie Moehlenkamp Tori Templin Megan Fleshman