User:Haylie Moehlenkamp/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
==Other Diseases== | ==Other Diseases== | ||
ACAT is also involved in diseases such as Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases due to the accumulation of Aβ plaques in the brain. After research on glioma, prostate, pancreatic, leukemia, and breast cancers, it has been noted that ACAT plays a role in the progression of cancer over time. Recently, Ayyagari et al. found that there was a significant increase in ACAT-1 expression in ovarian cancer cell lines <ref name="Ayyagari"> doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228024</ref>. ACAT-2 is believed to be upregulated in Nephrotic Syndrome (NS) which can lead to cardiovascular disease and renal diseases <ref name="Vaziri"> doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F</ref>. Because of ACAT's activity in tissues such as the aorta, intestine, and liver, it plays a role in Atherosclerosis <ref name="Willner"> doi:10.1073/pnas.0336398100</ref>. Studies have shown that the inhibition of ACAT-2 can slow the progression of Atherosclerosis <ref name="Willner"> doi:10.1073/pnas.0336398100</ref>. | ACAT is also involved in diseases such as Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases due to the accumulation of Aβ plaques in the brain. After research on glioma, prostate, pancreatic, leukemia, and breast cancers, it has been noted that ACAT plays a role in the progression of cancer over time. Recently, Ayyagari et al. found that there was a significant increase in ACAT-1 expression in ovarian cancer cell lines <ref name="Ayyagari"> doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228024</ref>. ACAT-2 is believed to be upregulated in Nephrotic Syndrome (NS) which can lead to cardiovascular disease and renal diseases <ref name="Vaziri"> doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F</ref>. Because of ACAT's activity in tissues such as the aorta, intestine, and liver, it plays a role in Atherosclerosis <ref name="Willner"> doi:10.1073/pnas.0336398100</ref>. Studies have shown that the inhibition of ACAT-2 can slow the progression of Atherosclerosis <ref name="Willner"> doi:10.1073/pnas.0336398100</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==Mutations== | ||
| - | Within ACAT, at codon 265 a change from serine to leucine renders the enzyme inactive <ref name="Cao"> doi:10.1074/jbc.271.24.14642</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 19:14, 6 April 2021
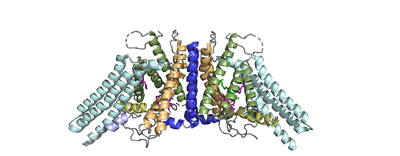
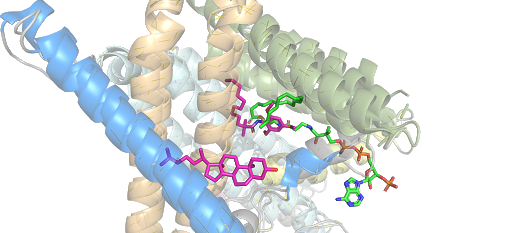
ACAT
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Chang TY, Chang CC, Bryleva E, Rogers MA, Murphy SR. Neuronal cholesterol esterification by ACAT1 in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):261-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.305. PMID:20101629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iub.305
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Shibuya Y, Chang CC, Chang TY. ACAT1/SOAT1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(18):2451-67. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.161. Epub 2015 Dec 15. PMID:26669800 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.161
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
- ↑ Vaziri ND, Liang KH. Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibition ameliorates proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase, SRB-1, and low-denisty lipoprotein receptor deficiencies in nephrotic syndrome. Circulation. 2004 Jul 27;110(4):419-25. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F. , Epub 2004 Jul 19. PMID:15262831 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Willner EL, Tow B, Buhman KK, Wilson M, Sanan DA, Rudel LL, Farese RV Jr. Deficiency of acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 prevents atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 4;100(3):1262-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0336398100., Epub 2003 Jan 21. PMID:12538880 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0336398100
Student Contributors
Haylie Moehlenkamp Tori Templin Megan Fleshman