This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Maggie Stopa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
=Lipoprotein Lipase LPL= | =Lipoprotein Lipase LPL= | ||
<StructureSection load='6ob0' size='350' side='right' caption='Lipoprotein Lipase PDB' scene='87/877513/Original_scene/1'> | <StructureSection load='6ob0' size='350' side='right' caption='Lipoprotein Lipase PDB' scene='87/877513/Original_scene/1'> | ||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
==Structural Overview== | ==Structural Overview== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is assumed to only be active as a <scene name='87/877513/Lpl_dimer/ | + | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is assumed to only be active as a <scene name='87/877513/Lpl_dimer/2'>homodimer</scene>, however, previous studies have argued that the lipase can be active in its monomeric form. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6442593/) The N-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is known to consist of an alpha/beta hydrolase domain, which is composed of six alpha helices and ten beta-strands. This domain creates an <scene name='87/877513/Alpha-beta_hydrolase_domain/1'>alpha/beta hydrolase fold</scene>. The C-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is composed of twelve beta strands which form a “<scene name='87/877513/Barrel_domain/3'>barrel domain</scene>”. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
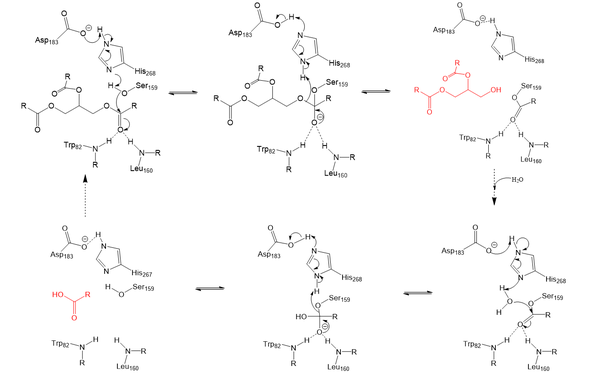
Lipoprotein Lipase functions to catalyze the hydrolysis of one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ester ester bond] of triglycerides. It does this by utilizing a simple [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_hydrolase serine hydrolase] mechanism, in which it uses a <scene name='87/877513/Catalytic_triad/3'>catalytic triad</scene> composed of Asp183, His268, and Ser159 to catalyze the hydrolysis. His268 serves as a base catalyst by deprotonation of Ser159, which can then serve as the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophile]. The transition state of the catalysis is stabilized by the <scene name='87/877516/Oxyanion_hole_master/1'>oxyanion hole</scene> composed of Trp82 and Leu160. The hydrolysis results in the formation of one free fatty acid and a glycerol with two fatty acid tails. | Lipoprotein Lipase functions to catalyze the hydrolysis of one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ester ester bond] of triglycerides. It does this by utilizing a simple [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_hydrolase serine hydrolase] mechanism, in which it uses a <scene name='87/877513/Catalytic_triad/3'>catalytic triad</scene> composed of Asp183, His268, and Ser159 to catalyze the hydrolysis. His268 serves as a base catalyst by deprotonation of Ser159, which can then serve as the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophile]. The transition state of the catalysis is stabilized by the <scene name='87/877516/Oxyanion_hole_master/1'>oxyanion hole</scene> composed of Trp82 and Leu160. The hydrolysis results in the formation of one free fatty acid and a glycerol with two fatty acid tails. | ||
| - | [[Image:LPL_final_Mechanism.png| | + | [[Image:LPL_final_Mechanism.png|600 px|center|thumb|Serine hydrolase mechanism utilized by LPL to catalyze the breakdown of one ester bond of a triglyceride. Compounds colored red are the products of the hydrolysis.]] |
| - | + | ||
== Relevance & Disease == | == Relevance & Disease == | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Original look: <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> | Original look: <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> | ||
| - | GPI/LPL interface: <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface/1'>hydrophobic interface</scene> | + | GPI/LPL interface (w/labels): <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface-labeled/1'>hydrophobic interface</scene> |
| - | Calcium ion stabilization:<scene name='87/877513/ | + | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Calcium ion stabilization:<scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization_-labeled/1'>calcium ion stabilization</scene> | ||
<scene name='87/877514/Lipid_binding_and_lid/1'>lipid binding region</scene> | <scene name='87/877514/Lipid_binding_and_lid/1'>lipid binding region</scene> | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface-labeled/1'>hydrophobic interface</scene> | ||
| - | Lid: <scene name='87/877514/Lid_region_final/1'>Lid Region</scene> | + | |
| - | < | + | Lid: <scene name='87/877514/Lid_region_final/1'>Lid Region</scene> |
| - | < | + | |
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Davies”>PMID:20620994</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Beigneux”>PMID:30850549</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name=”Mead”>PMID:12483461</ref> (LPL GENERAL REFERENCE) | ||
| + | <ref name=”Eckel”>PMID:2648155</ref> (LPL GENERAL REFERENCE BOOK IF NEEDED) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Student Contributors== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Giselle Flores | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dustin Soe | ||
| + | |||
| + | Maggie Stopa | ||
Revision as of 21:42, 23 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase LPL
| |||||||||||