This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Kaitlyn Roberts/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== Tunnel System === | === Tunnel System === | ||
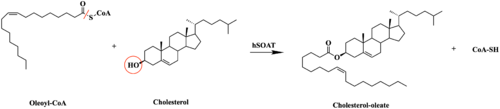
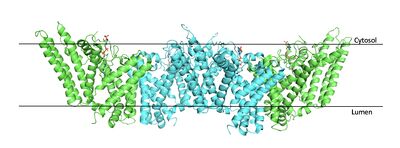
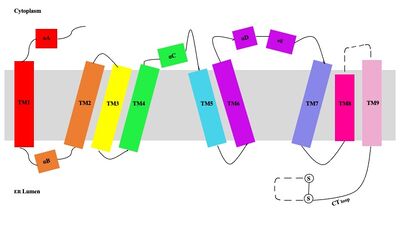
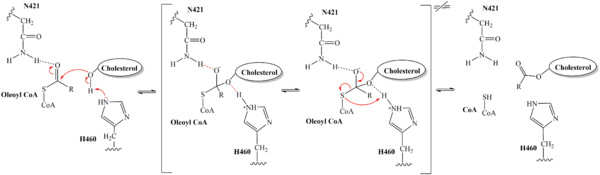
| - | A main structural element of this enzyme is the tunnel systems. [[Image:Tunnels2.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4.''' 2D layout of the SOAT tunnel system. The orientation of the tunnels shows the C tunnel opening to the cytosol and the L tunnel opening to the lumen. The T tunnel opens into the membrane, but is not quite the 90 degree shown in the 2D image.]] There are 3 main tunnels in each monomer: the cytosolic (C) tunnel opening to the cytosol, the transmembrane(T) tunnel opening to the membrane, and the lumenal (L) tunnel opens to the lumen. <ref name="Qian" /> The C tunnel opens to the cytosol of the cell and is the entrance site for the Acyl CoA into the active site. Surface representations of SOAT indicate that there are 2 alpha helices that block the entrance to the C tunnel, therefore a conformational change needs to occur to move the 2 helices so the substrate can enter the tunnel. The T tunnel opens into the membrane and is where cholesterol enters to have access to the active site. The two substrates are catalyzed by the H460 in the active site to form the cholesteryl ester. The products then leave via different pathways. The CoA-SH in the C tunnel leaves via that tunnel and is released back into the cytosol. The cholesteryl ester then leaves via either the T tunnel into the membrane or through the L tunnel into the lumen of the cell. <ref name="Qian" /> | + | A main structural element of this enzyme is the tunnel systems. [[Image:Tunnels2.jpg|350 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4.''' 2D layout of the SOAT tunnel system. The orientation of the tunnels shows the C tunnel opening to the cytosol and the L tunnel opening to the lumen. The T tunnel opens into the membrane, but is not quite the 90 degree shown in the 2D image.]] There are 3 main tunnels in each monomer: the cytosolic (C) tunnel opening to the cytosol, the transmembrane(T) tunnel opening to the membrane, and the lumenal (L) tunnel opens to the lumen. <ref name="Qian" /> The C tunnel opens to the cytosol of the cell and is the entrance site for the Acyl CoA substrate into the active site. Residues <scene name='87/877559/C_tunnel_and_measurements/6'>N415, Y433, and K445</scene> are involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with polar atoms on CoenzymeA to help stabilize the substrate within the binding pocket. It is important to note that the N415 residue in the PDB file provided is likely incorrect in orientation. We believe it should be flipped so that the hydrogens associated with the nitrogen atom are performing the stabilization shown. Surface representations of SOAT indicate that there are 2 alpha helices that block the entrance to the C tunnel, therefore a conformational change needs to occur to move the 2 helices so the substrate can enter the tunnel. The T tunnel opens into the membrane and is where cholesterol enters to have access to the active site. The two substrates are catalyzed by the H460 in the active site to form the cholesteryl ester. The products then leave via different pathways. The CoA-SH in the C tunnel leaves via that tunnel and is released back into the cytosol. The cholesteryl ester then leaves via either the T tunnel into the membrane or through the L tunnel into the lumen of the cell. <ref name="Qian" /> |
=== Active Site === | === Active Site === | ||
Revision as of 19:25, 25 April 2021
Human Sterol O-acyltransferase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bhattacharyya R, Kovacs DM. ACAT inhibition and amyloid beta reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):960-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003. , Epub 2010 Apr 14. PMID:20398792 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Huttunen HJ, Kovacs DM. ACAT as a drug target for Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2008;5(3-4):212-4. doi: 10.1159/000113705. Epub 2008 Mar 6. PMID:18322393 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000113705
- ↑ Chang C, Dong R, Miyazaki A, Sakashita N, Zhang Y, Liu J, Guo M, Li BL, Chang TY. Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) and its potential as a target for pharmaceutical intervention against atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2006 Mar;38(3):151-6. doi:, 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x. PMID:16518538 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
Student Contributors
- Kylie Pfeifer
- Stephanie Pellegrino
- Kaitlyn Roberts