User:Brianna Avery/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
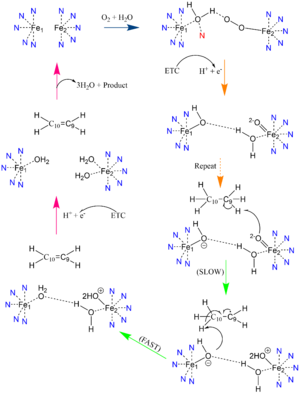
| - | Palmitoyl and Stearoyl CoA are substrates of SCD1. These substrates enter the hydrophobic V-shaped tunnel inside SCD1. Hydrogens are removed at the C9, then C10 to introduce the double bond through a desaturation mechanism. [[Image:Better_SCD_mech_pic.png|300 px|right|thumb|Proposed mechanism of SCD1 based off Shen et al. 2020 <ref name="Shen" />. Nitrogens colored blue represent the Histine stabilization of the di-iron complex while the red nitrogen is the water-stabilizing asparagine | + | Palmitoyl and Stearoyl CoA are substrates of SCD1. These substrates enter the hydrophobic V-shaped tunnel inside SCD1. Hydrogens are removed at the C9, then C10 to introduce the double bond through a desaturation mechanism. [[Image:Better_SCD_mech_pic.png|300 px|right|thumb|Proposed mechanism of SCD1 based off Shen et al. 2020 <ref name="Shen" />. Nitrogens colored blue represent the Histine stabilization of the di-iron complex while the red nitrogen is the water-stabilizing asparagine.]] |
====Desaturation Mechanism==== | ====Desaturation Mechanism==== | ||
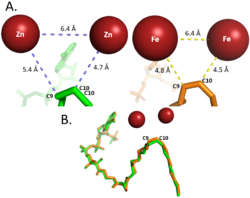
| - | Due to the novel coordination of histidine residues and lack of presence of a stable oxo-bridge, the mechanism of desaturase activity for SCD1 is unknown. For typical desaturases, the elements involved in catalysis include the di-metal center, metal-bound water and oxygen, electrons from an Electron Transport Chain, and the acyl-CoA substrate. For the proposed mechanism, catalysis occurs in four phases: the binding of water and oxygen to the di-metal complex using Asn261, the nucleophilic activation of the water/oxygen using the ETC, the interaction of the complex with the substrate, and the recovery of the enzyme. The rate-limiting step of the mechanism is the primary elimination reaction on the substrate due to the nucleophilic attack occurring on an already stable C9-C10 sigma bond. | + | Due to the novel coordination of histidine residues and lack of presence of a stable oxo-bridge, the mechanism of desaturase activity for SCD1 is unknown. For typical desaturases, the elements involved in catalysis include the di-metal center, metal-bound water and oxygen, electrons from an Electron Transport Chain, and the acyl-CoA substrate. For the proposed mechanism, catalysis occurs in four phases: the binding of water and oxygen to the di-metal complex using Asn261 (blue arrow), the nucleophilic activation of the water/oxygen using the ETC (orange arrows), the interaction of the complex with the substrate (green arrows), and the recovery of the enzyme (pink arrows). The rate-limiting step of the mechanism is the primary elimination reaction on the substrate due to the nucleophilic attack occurring on an already stable C9-C10 sigma bond. |
====Product Conversion and Release==== | ====Product Conversion and Release==== | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 26 April 2021
Desaturation of Fatty Stearoyl-CoA by SCD1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Tracz-Gaszewska Z, Dobrzyn P. Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 as a Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 5;11(7). pii: cancers11070948. doi:, 10.3390/cancers11070948. PMID:31284458 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070948
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
- ↑ Wang H, Klein MG, Zou H, Lane W, Snell G, Levin I, Li K, Sang BC. Crystal structure of human stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase in complex with substrate. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;22(7):581-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3049. Epub 2015 Jun , 22. PMID:26098317 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3049
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Gutierrez-Juarez R, Pocai A, Mulas C, Ono H, Bhanot S, Monia BP, Rossetti L. Critical role of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) in the onset of diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2006 Jun;116(6):1686-95. doi: 10.1172/JCI26991. PMID:16741579 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI26991
- ↑ Yokoyama S, Hosoi T, Ozawa K. Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) is a key factor mediating diabetes in MyD88-deficient mice. Gene. 2012 Apr 15;497(2):340-3. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.024. Epub 2012 Feb 3. PMID:22326531 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.024
- ↑ Ntambi JM, Miyazaki M, Stoehr JP, Lan H, Kendziorski CM, Yandell BS, Song Y, Cohen P, Friedman JM, Attie AD. Loss of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 function protects mice against adiposity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Aug 20;99(17):11482-6. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.132384699. Epub 2002 Aug 12. PMID:12177411 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.132384699
- ↑ Holder AM, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Chen H, Akcakanat A, Do KA, Fraser Symmans W, Pusztai L, Hortobagyi GN, Mills GB, Meric-Bernstam F. High stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 expression is associated with shorter survival in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(1):319-27. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2354-4. , Epub 2012 Dec 4. PMID:23208590 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2354-4
- ↑ Li J, Condello S, Thomes-Pepin J, Ma X, Xia Y, Hurley TD, Matei D, Cheng JX. Lipid Desaturation Is a Metabolic Marker and Therapeutic Target of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Mar 2;20(3):303-314.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.004., Epub 2016 Dec 29. PMID:28041894 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.004
Student Contributors
- Brianna M. Avery
- William J. Harris III
- Emily M. Royston