We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC17
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
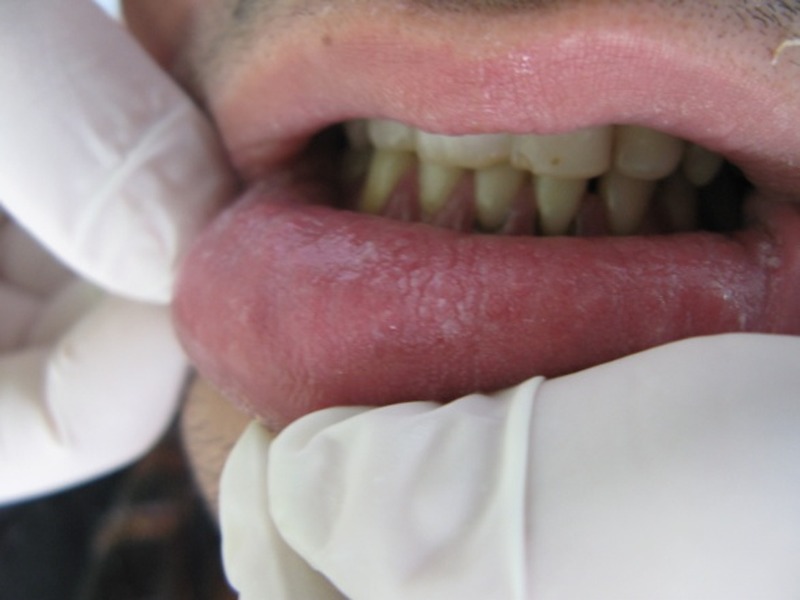
The disease that Keratin 4 causes is called white sponge nevus. White sponge nevus is an autosomal dominant disease which is caused by a mutation of a certain keratin gene. White sponge nevus is going to be a main componenet for a group of inherited diseases that are going to provide a white bilateral, keratinized apperance typically appearing on the buccal mucosa. [[Image:joddd-3-70-g001.jpg]] White sponge nevus lesions on the inside of the lips.<ref>PMID: 23230487</ref> | The disease that Keratin 4 causes is called white sponge nevus. White sponge nevus is an autosomal dominant disease which is caused by a mutation of a certain keratin gene. White sponge nevus is going to be a main componenet for a group of inherited diseases that are going to provide a white bilateral, keratinized apperance typically appearing on the buccal mucosa. [[Image:joddd-3-70-g001.jpg]] White sponge nevus lesions on the inside of the lips.<ref>PMID: 23230487</ref> | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | The two way parallel beta-sheet is where the C-terminal strand of one monomer is being positioned and anti-parallel to the N-terminal strand of the main adjacent monomer and this arrangement is not seen so far in any of the homologous structures. This is the <scene name='87/874949/00rainbow_ribbon/1'>Keratin 4 protein</scene>. | + | The two way parallel beta-sheet is where the C-terminal strand of one monomer is being positioned and anti-parallel to the N-terminal strand of the main adjacent monomer and this arrangement is not seen so far in any of the homologous structures. This is the <scene name='87/874949/00rainbow_ribbon/1'>Keratin 4 protein</scene>. The C-terminal strand is comprimised of residues from 485-642 that have been identified to essentially bind to Keratin 4. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 28 April 2021
Keratin 4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Samen U, Eikmanns BJ, Reinscheid DJ, Borges F. The surface protein Srr-1 of Streptococcus agalactiae binds human keratin 4 and promotes adherence to epithelial HEp-2 cells. Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5405-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00717-07. Epub 2007 Aug, 20. PMID:17709412 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00717-07
- ↑ Moore PS, Hierholzer J, DeWitt W, Gouan K, Djore D, Lippeveld T, Plikaytis B, Broome CV. Respiratory viruses and mycoplasma as cofactors for epidemic group A meningococcal meningitis. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1271-5. PMID:2117679
- ↑ Aghbali A, Pouralibaba F, Eslami H, Pakdel F, Jamali Z. White sponge nevus: a case report. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2009 Spring;3(2):70-2. doi:, 10.5681/joddd.2009.017. Epub 2009 Jun 5. PMID:23230487 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5681/joddd.2009.017