User:Hannah Wright/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
GPIHBP1’s LU domain interacts with LPL’s C-terminal domain via <scene name='87/877603/Lpl_gpihb1_interaction/3'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. This is largely due to the hydrophobic effect and stabilization. The acidic N-terminal domain of GPIHBP1 (residues 21–61) is disordered and not visible in the structure, which is presumably due to dynamic interaction with the large basic patch on the LPL. | GPIHBP1’s LU domain interacts with LPL’s C-terminal domain via <scene name='87/877603/Lpl_gpihb1_interaction/3'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. This is largely due to the hydrophobic effect and stabilization. The acidic N-terminal domain of GPIHBP1 (residues 21–61) is disordered and not visible in the structure, which is presumably due to dynamic interaction with the large basic patch on the LPL. | ||
====Calcium Ion Coordination==== | ====Calcium Ion Coordination==== | ||
| - | The calcium ion has been shown to convert inactive LPL to the active dimer form. The calcium ion is coordinated by residues A194, R197, S199, D201, and D202. Mutations in the | + | The <scene name='87/877636/Calcium_ion_coordination/1'>calcium ion</scene> has been shown to convert inactive LPL to the active dimer form. The calcium ion is coordinated by residues A194, R197, S199, D201, and D202. Mutations in the coordinating residues can give rise to detrimental metabolic diseases. The crystal structures of LPL revealed that the carboxylic acid side chain of D201 significantly aids in the coordination of LPL with the calcium ion. If D201 is mutated to a valine, for example, LPL can no longer fold correctly, and thus, LPL secretion from cells is inhibited due to the loss of the carboxylic acid side chain <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
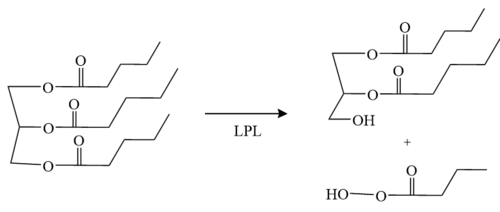
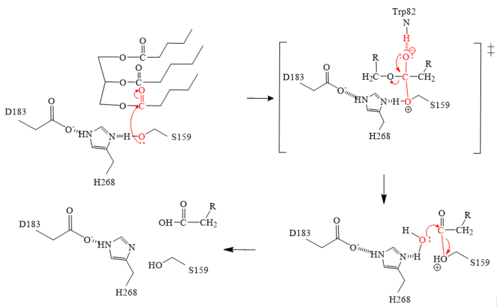
| - | The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_4_20/2'>active site</scene> of LPL is composed of multiple pieces. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_hphob_fixed/9'>hydrophobic entry</scene> to the binding site outlines the general structure and provides considerable stability to the active site. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_lid_region_fixed/5'>lid region</scene> is also an important component of the active site, occupying residues 243-266, which is vital for the recognition of substrates. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_w_catalytic_residu/6'>catalytic residues</scene> are H268, S159, and D183 (also known as the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad#:~:text=A%20catalytic%20triad%20is%20a,lipases%20and%20%CE%B2%2Dlactamases) catalytic triad] which catalyze the reaction of the typical substrate of LPL, triglycerides. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxyanion_hole#:~:text=An%20oxyanion%20hole%20is%20a,amides%20or%20positively%20charged%20residues oxyanion hole], consisting of residues L160 | + | The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_4_20/2'>active site</scene> of LPL is composed of multiple pieces. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_hphob_fixed/9'>hydrophobic entry</scene> to the binding site outlines the general structure and provides considerable stability to the active site. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_lid_region_fixed/5'>lid region</scene> is also an important component of the active site, occupying residues 243-266, which is vital for the recognition of substrates. The <scene name='87/878236/Active_site_w_catalytic_residu/6'>catalytic residues</scene> are H268, S159, and D183 (also known as the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Catalytic_triad#:~:text=A%20catalytic%20triad%20is%20a,lipases%20and%20%CE%B2%2Dlactamases) catalytic triad] which catalyze the reaction of the typical substrate of LPL, triglycerides. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxyanion_hole#:~:text=An%20oxyanion%20hole%20is%20a,amides%20or%20positively%20charged%20residues oxyanion hole], consisting of residues <scene name='87/877636/Activesite_oxyanionhole/3'>L160 and W82</scene>, aids in the stability of the transition state of substrates. The main chain nitrogens stabilize the tetrahedral intermediate <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
====Mechanism==== | ====Mechanism==== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
===Mutations=== | ===Mutations=== | ||
====D201V==== | ====D201V==== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877636/D201_mutation/11'>D201V</scene> is a mutation that is found to cause [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia]. Chylomicronemia is when the body cannot break down lipids properly. This leads to their build-up in the body causing high levels of triglycerides in the body. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspartic_acid carboxyl side chain of aspartate] 201 is one of the coordination sites for the calcium ion of LPL. The mutation to hydrophobic [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Valine valine] means the loss of this coordination site<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. This mutation adversely affects the folding of LPL and thus affects the secretion of LPL, overall decreasing the activity of LPL<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | + | <scene name='87/877636/D201_mutation/11'>D201V</scene> is a mutation that is found to cause [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia]. Chylomicronemia is when the body cannot break down lipids properly. This leads to their build-up in the body causing high levels of triglycerides in the body <ref name="Falko">PMID:30183397</ref>. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspartic_acid carboxyl side chain of aspartate] 201 is one of the coordination sites for the calcium ion of LPL. The mutation to hydrophobic [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Valine valine] means the loss of this coordination site<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. This mutation adversely affects the folding of LPL and thus affects the secretion of LPL, overall decreasing the activity of LPL<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
====M404R==== | ====M404R==== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877636/M404r_1/3'>M404R</scene> is a mutation found within LPL that caused [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia] in patients. The hydrophobic [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methionine methionine] is mutated to the larger and charged side chain of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine arginine]. Originally it was thought to impact LPL secretion from cells. It was found that the M404R does not affect LPL secretion <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. M404R interacts with the hydrophobic pocket of GPIHBP1’s finger 3 of its 3 fingered domain (V121, E122, T124, V126). The large, charged arginine repelled the hydrophobic pocket and does not fit well. This prevents proper binding and formation of the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | + | <scene name='87/877636/M404r_1/3'>M404R</scene> is a mutation found within LPL that caused [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia] in patients <ref name="Falko">PMID:30183397</ref>. The hydrophobic [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methionine methionine] is mutated to the larger and charged side chain of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine arginine]. Originally it was thought to impact LPL secretion from cells. It was found that the M404R does not affect LPL secretion <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. M404R interacts with the hydrophobic pocket of GPIHBP1’s finger 3 of its 3 fingered domain (V121, E122, T124, V126). The large, charged arginine repelled the hydrophobic pocket and does not fit well. This prevents proper binding and formation of the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
Revision as of 01:10, 27 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) complexed with GPIHBP1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Birrane G, Beigneux AP, Dwyer B, Strack-Logue B, Kristensen KK, Francone OL, Fong LG, Mertens HDT, Pan CQ, Ploug M, Young SG, Meiyappan M. Structure of the lipoprotein lipase-GPIHBP1 complex that mediates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 17. pii: 1817984116. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1817984116. PMID:30559189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817984116
- ↑ Arora R, Nimonkar AV, Baird D, Wang C, Chiu CH, Horton PA, Hanrahan S, Cubbon R, Weldon S, Tschantz WR, Mueller S, Brunner R, Lehr P, Meier P, Ottl J, Voznesensky A, Pandey P, Smith TM, Stojanovic A, Flyer A, Benson TE, Romanowski MJ, Trauger JW. Structure of lipoprotein lipase in complex with GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 21;116(21):10360-10365. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1820171116. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID:31072929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820171116
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Falko JM. Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome: A Clinical Guide For Endocrinologists. Endocr Pract. 2018 Aug;24(8):756-763. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0157. PMID:30183397 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4158/EP-2018-0157
Student/Contributors
- Ashrey Burley
- Allison Welz
- Hannah Wright