We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Megan Leaman/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='6VYI' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='Human Diacylglycerol O-Transferase 1 6VYI' scene=’His415 in Active Site’> | <StructureSection load='6VYI' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='Human Diacylglycerol O-Transferase 1 6VYI' scene=’His415 in Active Site’> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
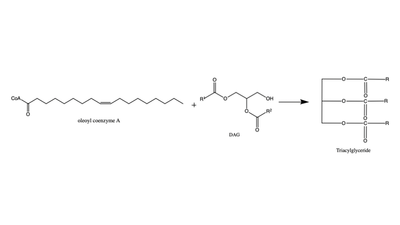
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:presentation1.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1: Reaction of oleoyl-CoA with DAG to produce a triglyceride]] |
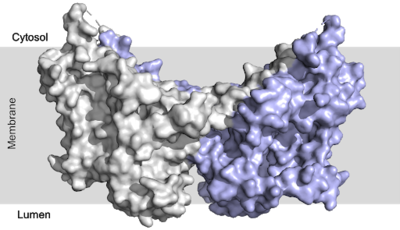
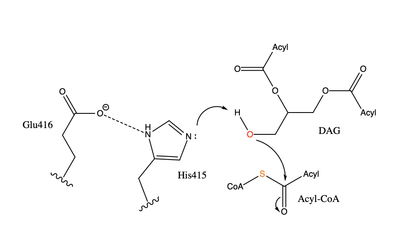
There are two families of DGAT proteins each with their own distinct cellular functions via synthesis of triacylglycerides from oleoyl-CoA. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) catalyzes the final and only committed step of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triacylclygerol synthesis] (Fig. 1). <ref name="Cases">PMID:9789033</ref> It does this by using diacylglycerol (DAG) and oleoyl CoA as substrates. DGAT1 is located in the membrane of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endoplasmic_reticulum endoplasmic reticulum] and is important for metabolism through its uptake of diacylglycerides and synthesis of triacylglicerides (Fig. 2). <ref name="Sui">PMID:32433611</ref> This metabolism is involved in intestinal fat absorption, lipoprotein assembly, lactation, and adipose tissue formation <ref name="Yen">PMID:18757836</ref>. | There are two families of DGAT proteins each with their own distinct cellular functions via synthesis of triacylglycerides from oleoyl-CoA. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) catalyzes the final and only committed step of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triacylclygerol synthesis] (Fig. 1). <ref name="Cases">PMID:9789033</ref> It does this by using diacylglycerol (DAG) and oleoyl CoA as substrates. DGAT1 is located in the membrane of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endoplasmic_reticulum endoplasmic reticulum] and is important for metabolism through its uptake of diacylglycerides and synthesis of triacylglicerides (Fig. 2). <ref name="Sui">PMID:32433611</ref> This metabolism is involved in intestinal fat absorption, lipoprotein assembly, lactation, and adipose tissue formation <ref name="Yen">PMID:18757836</ref>. | ||
[[Image:dgat with domains.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 2: DGAT1 with cytosolic, transmembrane, and luminal domains]] | [[Image:dgat with domains.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 2: DGAT1 with cytosolic, transmembrane, and luminal domains]] | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 27 April 2021
Human Diacylglycerol O-Transferase 1
| |||||||||||
References
[1] [10] [11] [12] [9] [13] [2] [4] [3]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cases S, Smith SJ, Zheng YW, Myers HM, Lear SR, Sande E, Novak S, Collins C, Welch CB, Lusis AJ, Erickson SK, Farese RV Jr. Identification of a gene encoding an acyl CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase, a key enzyme in triacylglycerol synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 27;95(22):13018-23. PMID:9789033
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Yen CL, Stone SJ, Koliwad S, Harris C, Farese RV Jr. Thematic review series: glycerolipids. DGAT enzymes and triacylglycerol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 2008 Nov;49(11):2283-301. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800018-JLR200. Epub 2008, Aug 29. PMID:18757836 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1194/jlr.R800018-JLR200
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
- ↑ Caldo, K., Acedo, J. Z., Panigrahi, R., Vederas, J. C., Weselake, R. J., & Lemieux, M. J. (2017). Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 Is Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain in Response to Allosteric Effectors. Plant physiology, 175(2), 667–680. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00934
- ↑ Denison, H., Nilsson, C., Löfgren, L., Himmelmann, A., Mårtensson, G., Knutsson, M., Al-Shurbaji, A., Tornqvist, H., & Eriksson, J. W. (2014). Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibition with AZD7687 alters lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut with intolerable side effects: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 16(4), 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12221
- ↑ Cao, J., Zhou, Y., Peng, H., Huang, X., Stahler, S., Suri, V., Qadri, A., Gareski, T., Jones, J., Hahm, S., Perreault, M., McKew, J., Shi, M., Xu, X., Tobin, J. F., & Gimeno, R. E. (2011). Targeting Acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) with small molecule inhibitors for the treatment of metabolic diseases. The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(48), 41838–41851. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.245456
- ↑ Haas, J. T., Winter, H. S., Lim, E., Kirby, A., Blumenstiel, B., DeFelice, M., Gabriel, S., Jalas, C., Branski, D., Grueter, C. A., Toporovski, M. S., Walther, T. C., Daly, M. J., & Farese, R. V., Jr (2012). DGAT1 mutation is linked to a congenital diarrheal disorder. The Journal of clinical investigation, 122(12), 4680–4684. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64873
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Gluchowski, N. L., Chitraju, C., Picoraro, J. A., Mejhert, N., Pinto, S., Xin, W., Kamin, D. S., Winter, H. S., Chung, W. K., Walther, T. C., & Farese, R. V., Jr (2017). Identification and characterization of a novel DGAT1 missense mutation associated with congenital diarrhea. Journal of lipid research, 58(6), 1230–1237. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.P075119
- ↑ Caldo, K., Acedo, J. Z., Panigrahi, R., Vederas, J. C., Weselake, R. J., & Lemieux, M. J. (2017). Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 1 Is Regulated by Its N-Terminal Domain in Response to Allosteric Effectors. Plant physiology, 175(2), 667–680. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00934
- ↑ Cao, J., Zhou, Y., Peng, H., Huang, X., Stahler, S., Suri, V., Qadri, A., Gareski, T., Jones, J., Hahm, S., Perreault, M., McKew, J., Shi, M., Xu, X., Tobin, J. F., & Gimeno, R. E. (2011). Targeting Acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) with small molecule inhibitors for the treatment of metabolic diseases. The Journal of biological chemistry, 286(48), 41838–41851. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.245456
- ↑ Denison, H., Nilsson, C., Löfgren, L., Himmelmann, A., Mårtensson, G., Knutsson, M., Al-Shurbaji, A., Tornqvist, H., & Eriksson, J. W. (2014). Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibition with AZD7687 alters lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut with intolerable side effects: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 16(4), 334–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12221
- ↑ Haas, J. T., Winter, H. S., Lim, E., Kirby, A., Blumenstiel, B., DeFelice, M., Gabriel, S., Jalas, C., Branski, D., Grueter, C. A., Toporovski, M. S., Walther, T. C., Daly, M. J., & Farese, R. V., Jr (2012). DGAT1 mutation is linked to a congenital diarrheal disorder. The Journal of clinical investigation, 122(12), 4680–4684. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64873
Student Contributors
- Megan Leaman
- Grace Hall
- Karina Latsko