Introduction
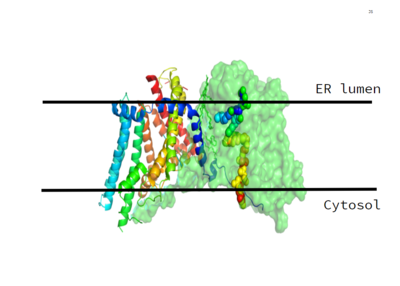
Figure 1. Location of the DGAT1 protein within the Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane (6vp0)
, or Diacylglycerol O-Acyltransferase 1, is a polytopic endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein embedded within the membrane of the Endoplasmic reticulum. DGAT1 is highly expressed in epithelial cells of the small intestine of homo sapiens. It can also be found in the liver, where it helps synthesize fats for storage, and the female mammary glands, where it produces fat in the milk. [1]
DGAT1 was originally discovered by its homology to Acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferases (ACAT) 1 and 2. The structure, catalytic mechanism of diacylglycerol acyltransferase, and how DGAT1 interacts with CoA were discovered using a Cryo-EM. The Cryo-EM map revealed that DGAT1 forms a dimer, with each subunit containing nine transmembrane helices. The N and C terminals of each helix are located on the cytosolic and luminal sides of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane respectively (Figure 1). [2]
DGAT1 makes triglycerides from a diglyceride in plasma (Figure 2). In order to do this, DGAT1 uses two substrates: a fatty acyl-CoA and a diacylglycerol substrate. The basic mechanism consists of a lone pair on a hydroxyl group of glycerol attacking the carbon of the thioester bond of CoA. This results in the breakage of the thioester bond, and the attached acyl group attaches to the glycerol, creating a triglyceride.
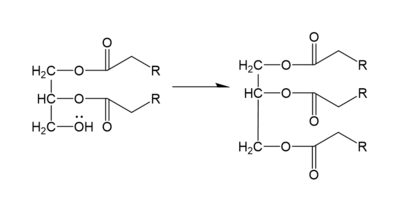
Figure 2. General schematic of DGAT1's function.
Structure
DGAT1 consists of two domains, one cytoplasmic and one luminal. The cytoplasmic domain interacts with the interior of the cell and relays signals. Each monomer of DGAT1 consists of one protein chain, one ligand, one polymer, nine that are connected with loops of varying sizes. The transmembrane helices form a large central cavity within the membrane that opens to the bilayer via a wide lateral gate. Through openings on the cytosolic and luminal sides of DGAT1, this central cavity is also accessible. The majority of the transmembrane helices present within the structure also form a concave-shaped ridge on either side of the membrane.[1]
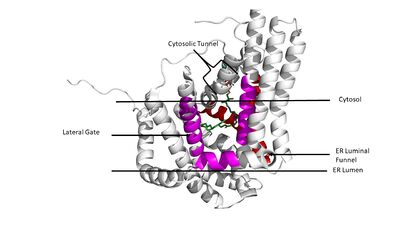
Figure 3. Shows the location of the lateral gate accessed via the ER lumen side of the membrane in pink, with the substrate acyl-CoA in the cytosolic tunnel and ER funnel (red) shown in the back in atom colors(6vp0).
The DGAT1 dimer structure is formed primarily through many hydrogen-bonding interactions between the first 20 resolved residues (His69-Gly87)(see figure 4). Hydrophobic interactions of the transmembrane helix region (Phe82-Ile98) with the other monomer also support the dimer structure formation. Additionally, there are four phospholipids present at the dimer interface that have been thought to contribute to the interactions between DGAT1 monomers. [2]
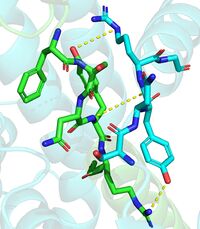
Figure 4. Shows the interactions between residues His69-Gly87. One dimmer is shown in blue and the other in green(6vyi).
Tunnels
These aspects of the domain structure are deemed as the 'MBOAT core'. Within this core, a tunnel-like region, similar to a binding pocket, is also present. Access to the active site of DGAT1 by substrates is done through the lateral gate, which lies on the ER lumen side, within the membrane. This tunnel-like region is referred to as the cytosolic, or C, tunnel. [1]
DGAT1 consists of 3 tunnels, , an , and a membrane-embedded (Figure 3). The cytosolic tunnel is the site of acyl-CoA binding, with the CoA group pointing at the cytosolic face and its acyl chain pointing towards the endoplasmic reticulum lumen. DAG then enters via the lateral gate on the luminal side of the lateral gate where it can then access the active site. The resulting product can then be released to either side of the membrane. [1]
Active Site
The active site of DGAT1 is located within the membrane, with the catalytic histidine residue (-represented in white) buried inside the central cavity. This central cavity serves as the catalytic site. The acyl-acceptor lipid substrates access the active site through the lateral gate within the membrane. The active site also contains and several nearby (including Asn378, Gln437, and Gln465) whose side chains are oriented towards the cavity center. These residues interact and create a hydrophilic channel within the active site. The His415 residue is also likely involved in catalysis, making it increasingly significant. In fact, single mutations of His415 and Asn378 terminated DGAT1 activity. This suggests that the central cavity of DGAT1 within the membrane is the catalytic site. [1]
Mechanism
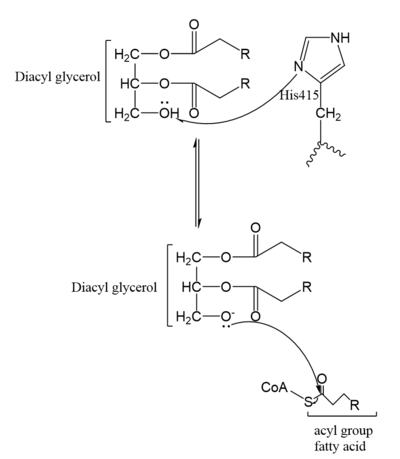
Figure 5. Mechanism for DGAT1
In the DGAT1 mechanism (Figure 4), the diglyceride serves as the nucleophile. While the acyl group of the CoA enzyme serves as the electrophile. The lone pair on the last hydroxyl group present on the glycerol of the diglyceride attacks the thioester bond of the acyl-CoA enzyme. This attack breaks the sulfur-carbon bond, a weak bond that is easily breakable. This allows the acyl group of the acyl-CoA enzyme to attach to the diglyceride, creating a triglyceride. While the CoA group then serves as the leaving group.
The cleavage site for oleoyl-CoA is within a short distance of a lipid acceptor. This revelation was made after a strong, lipid-like density in the central cavity in the cryo-EM data. Hydrophobic residues line this region and form a channel surrounding the lipid-like density. The channel itself has a bent, hydrophobic pathway that allows the binding of hydrophobic molecules. The bent architecture of this tunnel is likely how DGAT1 distinguishes acyl acceptors from other molecules, such as cholesterol. [1]
Product Release
As previously mentioned, the Acyl-CoA molecule serves as the leaving group in the DGAT1 mechanism. This occupies the cytosolic tunnel, which has a bent architecture. The CoA moiety is at the cytosolic face, while the acyl chain extends through the center towards the endoplasmic reticulum lumen. The distal end of the acyl chain oleoyl-CoA interacts with DGAT1 deep within the hydrophobic channel, which suggests that the binding of longer acyl chains helps accurately position the acyl-donor substrate for the reaction. As the acyl-CoA binds to DGAT1, small conformational changes are seen in the active site region, specifically, the His415 residue flips towards the endoplasmic reticulum-luminal side when acyl-CoA binds. This conformational change allows a new hydrogen bond to form and positions His415 near the thioester bond of the acyl-CoA. Therefore, the binding of acyl-CoA binding to DGAT1 results in small, but important, conformational changes in the active site that likely prime the enzyme for catalysis. [1]
Figure 6. Conformational Change
Image001.png
Mutations
Mutations in the DGAT1 enzyme are particularly rare. One specific mutation discovered in the DGAT1 gene leads to congenital diarrhea, electrolyte derangements, protein-losing enteropathy, and rickets. This homozygous recessive mutation does not allow for the expression of the gene causing the DGAT enzyme to not be expressed. More specifically this mutation is linked to a 3 base pair deletion at a nucleotide position that results in an in-frame deletion of a , maternally, and a C to G transversion that results in a serine to arginine substitution at , (Cheng, 2020). DGAT1 was also found to be a positive regulator in Glioblastoma tumor growth. Inhibition of DGAT1 in glioblastoma cells was found to induce slight apoptosis by increasing fat catabolism and oxidative stress, (Cheng, 2020).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
Student Contributors
- Justin Smith
- Eloi Bigirimana
- Leanne Price






