|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
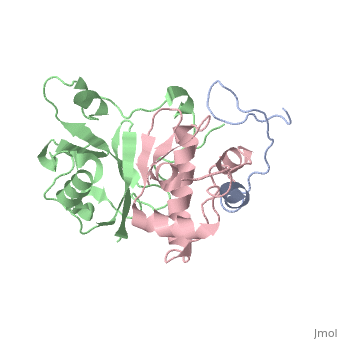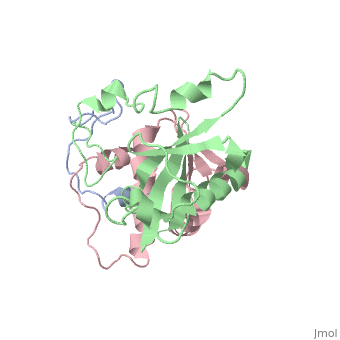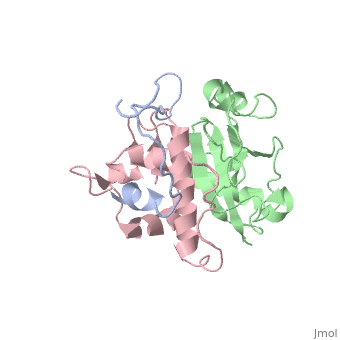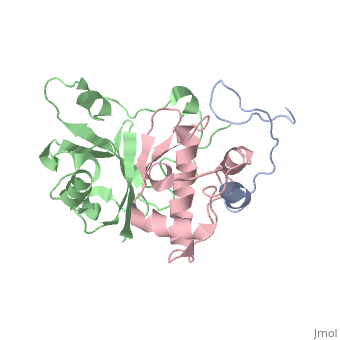
| | ==HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box and Elongin BC solution structure== | | ==HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box and Elongin BC solution structure== |
| - | <StructureSection load='2ma9' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2ma9]], [[NMR_Ensembles_of_Models | 20 NMR models]]' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2ma9' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2ma9]]' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2ma9]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hiv-1 Hiv-1] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2MA9 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2MA9 FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2ma9]] is a 3 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_immunodeficiency_virus_type_1_(NEW_YORK-5_ISOLATE) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (NEW YORK-5 ISOLATE)]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2MA9 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2MA9 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[3dcg|3dcg]]</div></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2ma9 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2ma9 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2ma9 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2ma9 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2ma9 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2ma9 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">vif ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=11698 HIV-1]), TCEB2 ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN]), TCEB1 ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr>
| + | |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2ma9 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2ma9 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2ma9 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2ma9 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2ma9 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2ma9 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | + | |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/VIF_HV1N5 VIF_HV1N5]] Counteracts the innate antiviral activity of human APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. Forms a complex with host APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G thus preventing the entry of these lethally hypermutating enzymes into progeny virions. Recruits an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex composed of elongin BC, CUL5, and RBX2 to induce polyubiquitination of APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F. In turn, they are directed to the 26S proteasome for degradation. Vif interaction with APOBEC3G also blocks its cytidine deaminase activity in a proteasome-independent manner, suggesting a dual inhibitory mechanism. May interact directly with APOBEC3G mRNA in order to inhibit its translation. Seems to play a role in viral morphology by affecting the stability of the viral nucleoprotein core. Finally, Vif also contributes to the G2 cell cycle arrest observed in HIV infected cells (By similarity).<ref>PMID:8184544</ref> <ref>PMID:14557625</ref> [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ELOC_HUMAN ELOC_HUMAN]] SIII, also known as elongin, is a general transcription elongation factor that increases the RNA polymerase II transcription elongation past template-encoded arresting sites. Subunit A is transcriptionally active and its transcription activity is strongly enhanced by binding to the dimeric complex of the SIII regulatory subunits B and C (elongin BC complex).<ref>PMID:15590694</ref> The elongin BC complex seems to be involved as an adapter protein in the proteasomal degradation of target proteins via different E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, including the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex CBC(VHL). By binding to BC-box motifs it seems to link target recruitment subunits, like VHL and members of the SOCS box family, to Cullin/RBX1 modules that activate E2 ubiquitination enzymes.<ref>PMID:15590694</ref> [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ELOB_HUMAN ELOB_HUMAN]] SIII, also known as elongin, is a general transcription elongation factor that increases the RNA polymerase II transcription elongation past template-encoded arresting sites. Subunit A is transcriptionally active and its transcription activity is strongly enhanced by binding to the dimeric complex of the SIII regulatory subunits B and C (elongin BC complex).<ref>PMID:7638163</ref> <ref>PMID:15590694</ref> The elongin BC complex seems to be involved as an adapter protein in the proteasomal degradation of target proteins via different E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, including the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex CBC(VHL). By binding to BC-box motifs it seems to link target recruitment subunits, like VHL and members of the SOCS box family, to Cullin/RBX1 modules that activate E2 ubiquitination enzymes.<ref>PMID:7638163</ref> <ref>PMID:15590694</ref>
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/VIF_HV1N5 VIF_HV1N5] Counteracts the innate antiviral activity of human APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. Forms a complex with host APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G thus preventing the entry of these lethally hypermutating enzymes into progeny virions. Recruits an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex composed of elongin BC, CUL5, and RBX2 to induce polyubiquitination of APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F. In turn, they are directed to the 26S proteasome for degradation. Vif interaction with APOBEC3G also blocks its cytidine deaminase activity in a proteasome-independent manner, suggesting a dual inhibitory mechanism. May interact directly with APOBEC3G mRNA in order to inhibit its translation. Seems to play a role in viral morphology by affecting the stability of the viral nucleoprotein core. Finally, Vif also contributes to the G2 cell cycle arrest observed in HIV infected cells (By similarity).<ref>PMID:8184544</ref> <ref>PMID:14557625</ref> |
| | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> |
| | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == |
| Line 21: |
Line 19: |
| | | | |
| | ==See Also== | | ==See Also== |
| | + | *[[Elongation factor 3D structures|Elongation factor 3D structures]] |
| | *[[Virion infectivity factor|Virion infectivity factor]] | | *[[Virion infectivity factor|Virion infectivity factor]] |
| | == References == | | == References == |
| Line 26: |
Line 25: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Hiv-1]] | + | [[Category: Homo sapiens]] |
| - | [[Category: Human]]
| + | |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Atkinson, R A]] | + | [[Category: Atkinson RA]] |
| - | [[Category: Bergeron, J R]] | + | [[Category: Bergeron JR]] |
| - | [[Category: Lu, Z]] | + | [[Category: Lu Z]] |
| - | [[Category: Malim, M H]] | + | [[Category: Malim MH]] |
| - | [[Category: Matthews, S J]] | + | [[Category: Matthews SJ]] |
| - | [[Category: Oregioni, A]] | + | [[Category: Oregioni A]] |
| - | [[Category: Sanderson, M R]] | + | [[Category: Sanderson MR]] |
| - | [[Category: Schaller, T]] | + | [[Category: Schaller T]] |
| - | [[Category: Veselkov, D A]] | + | [[Category: Veselkov DA]] |
| - | [[Category: Yang, Y]] | + | [[Category: Yang Y]] |
| - | [[Category: Elongin bc]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hiv-1 vif socs-box]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Viral protein-protein binding complex]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
VIF_HV1N5 Counteracts the innate antiviral activity of human APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G. Forms a complex with host APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G thus preventing the entry of these lethally hypermutating enzymes into progeny virions. Recruits an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex composed of elongin BC, CUL5, and RBX2 to induce polyubiquitination of APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F. In turn, they are directed to the 26S proteasome for degradation. Vif interaction with APOBEC3G also blocks its cytidine deaminase activity in a proteasome-independent manner, suggesting a dual inhibitory mechanism. May interact directly with APOBEC3G mRNA in order to inhibit its translation. Seems to play a role in viral morphology by affecting the stability of the viral nucleoprotein core. Finally, Vif also contributes to the G2 cell cycle arrest observed in HIV infected cells (By similarity).[1] [2]
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The HIV-1 viral infectivity factor (Vif) neutralizes cell-encoded antiviral APOBEC3 proteins by recruiting a cellular ElonginB (EloB)/ElonginC (EloC)/Cullin5-containing ubiquitin ligase complex, resulting in APOBEC3 ubiquitination and proteolysis. The suppressors-of-cytokine-signalling-like domain (SOCS-box) of HIV-1 Vif is essential for E3 ligase engagement, and contains a BC box as well as an unusual proline-rich motif. Here, we report the NMR solution structure of the Vif SOCS-ElonginBC (EloBC) complex. In contrast to SOCS-boxes described in other proteins, the HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box contains only one alpha-helical domain followed by a beta-sheet fold. The SOCS-box of Vif binds primarily to EloC by hydrophobic interactions. The functionally essential proline-rich motif mediates a direct but weak interaction with residues 101-104 of EloB, inducing a conformational change from an unstructured state to a structured state. The structure of the complex and biophysical studies provide detailed insight into the function of Vif's proline-rich motif and reveal novel dynamic information on the Vif-EloBC interaction.
Insight into the HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box-ElonginBC interaction.,Lu Z, Bergeron JR, Atkinson RA, Schaller T, Veselkov DA, Oregioni A, Yang Y, Matthews SJ, Malim MH, Sanderson MR Open Biol. 2013 Nov 13;3(11):130100. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130100. PMID:24225024[3]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
See Also
References
- ↑ Hoglund S, Ohagen A, Lawrence K, Gabuzda D. Role of vif during packing of the core of HIV-1. Virology. 1994 Jun;201(2):349-55. PMID:8184544 doi:http://dx.doi.org/S0042-6822(84)71300-6
- ↑ Kao S, Khan MA, Miyagi E, Plishka R, Buckler-White A, Strebel K. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vif protein reduces intracellular expression and inhibits packaging of APOBEC3G (CEM15), a cellular inhibitor of virus infectivity. J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11398-407. PMID:14557625
- ↑ Lu Z, Bergeron JR, Atkinson RA, Schaller T, Veselkov DA, Oregioni A, Yang Y, Matthews SJ, Malim MH, Sanderson MR. Insight into the HIV-1 Vif SOCS-box-ElonginBC interaction. Open Biol. 2013 Nov 13;3(11):130100. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130100. PMID:24225024 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsob.130100
|