Introduction
Histone Methylation
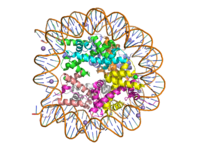
Figure 1: Human nucleosome particle, pbd code: 5y0c
Histone proteins aid in the packing of DNA for the purpose of compacting the genome in the nucleus of the cell and regulating physical accessibility of genes for transcription. The nucleosome (Figure 1) itself is an octamer complex of the core histone proteins H2a, H2b, H3, and H4. Approximately 145-157 DNA base pairs wind around a histone core and the DNA linking the core particles are bound by Histones H1 and H5.[1] Modifications to histone core proteins can affect the accessibility of transcription factors to the genome, either promoting or inhibiting transcription. Some of these modifications include methylation/demethylation, acetylation/deacetylation, and ubiquitination/deubiquitination.[2]
Histone methylation is associated with both gene activation and silencing. The factors influencing the specific outcome are the methylation site, residue type (Lys or Arg) and the extent (mono-, di- or tri-methylation).[3] Sites known for gene activation are Lys-4, Lys-36, and Lys-79 on H3; whereas, methylation at Lys-9 and Lys-27 on H3 and Lys-20 on H4 are known for transcriptional repression or silencing.[4] Typically, methylation of some of these sites are found on both active and inactive genes. Some tumor related genes such as p53 are site specifically methylated to promote their biological function [4], whereas hypomethylation of CpG island sequences is linked to tumor genesis.[2]
Sidechain methylation of basic amino acids in histone proteins is accomplished by the Histone Methyltransferase class of enzymes. In all but one instance, the many enzymes that are lysine substrate specific contain the structural protein domain known as the SET domain. Generally, these enzymes use S-adenosyl methionine to methylate lysine in the H3, H4 and H2a core proteins. One enzyme in this family is the , which adds a methyl group to Lys4 of the H3 protein. This histone modification results in the formation of euchromatin and gene transcription.[5], [3]
Lysine Methyltransferase (KMT) Structure
The structure of human histone methyltransferase SET7/9 was determined by x-ray diffraction at 1.75Å resolution. In this structure, a 10-residue peptide representing histone H3 was co-crystallized with SET7/9 and its co-factor product, S-adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) [5]. Here, the histone H3 peptide is methylated at lysine four, representing the product of the reaction.
Overall Structure
The SET7/9 enzyme structure sequentially consists of a N-terminal domain (177-193), followed by the characteristic SET domain () which itself ends with a specific C-terminal segment (344-366). The enzyme is best characterized as having alpha+beta folding topology as it consists of a mixture of both α-helix and β-sheet, but without any significant repeating pattern [5]. The helical composition includes three , with two residing in the SET domain and one in the C-terminal segment. The α-helices in the SET domain are two turns in length while the C-terminal helix is by far the largest with four turns. There are also two in the SET domain which are each one turn. There are 21 total found in both the N-terminal and the SET domains. The β-strands are primarily anti-parallel and multiple β-strands are connected by Type 1 and Type 2 .
The N-terminal Domain

Figure 2: Clustal alignment of N-terminal sequences corresponding to residues 117-184 of human SET7/9
Though a highly conserved region (Figure 2), the of SET7/9 is notably far from the active site and has not been shown to be involved in enzyme activity or participate in substrate binding.[6] With deletion of the N-terminal domain, studies have shown this modification does not affect SET7/9 activity.[5] Though not essential for catalytic activity, the N-terminal domain may interact with other small molecules or proteins to act as an allosteric regulator region to the C-terminal domain.[6]
The Active Site
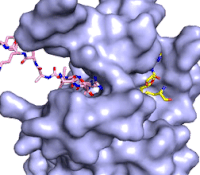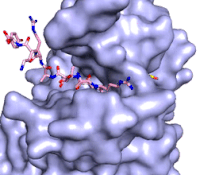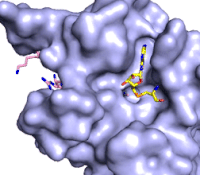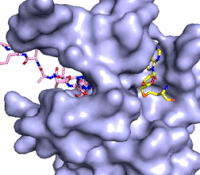
Figure 3: Gif-image of histone substrate (pink sticks) bound on one side of SET7/9 with the lysine target in the active site channel approaching S-adenosyl homocysteine (yellow sticks) bound on the opposite surface. The video was made using PyMOL, then converted to gif format using EZgif.
The active site and binding pocket of KMT contain residues that optimize catalytic function and stability. First, the lysine of the substrate histone enters the active site via the comprised of Tyr335 and Tyr337. The substrate lysine can be seen reaching through this channel to the SAM co-factor which is bound on the opposite face of the SET domain (Figure 3). With the histone substrate bound, the alkyl groups of the lysine sidechain are stabilized by tyrosine residues in the , and polar residues are stabilized by hydrogen bonding interactions on the protein surface. Of note are the several interactions between SET7/9 and the Arg2 of the histone H3 peptide, including a hydrophobic interaction between Trp260 and the alkyl groups of the Arg2 side chain, and hydrogen bonds between Asp256 and Arg258 and Arg2 of the substrate. The itself contains the cofactor S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) which donates the methyl group in the reaction.
[5] In the active site scene, the structures depict the post-reaction result, where the Lys has been methylated and SAM has been converted to S-adenosyl homocysteine (SAH).
The methylation reaction (Figure 4) is activated by several hydrogen bond interactions between active site residues and the substrate lysine. Specifically, the Tyr305 hydroxyl and the mainchain carbonyl oxygen of both Ala295 and Gly292 coordinate a buried water molecule that in turn coordinates a hydrogen of the lysine substrate. Additionally, the hydroxyl of Tyr245 also hydrogen bonds to the lysine substrate. These interactions enhance the nucleophilic nature of the amine nitrogen so that subsequent attack of the SAM methyl group carbon becomes favorable. Attack is further facilitated as the donor methyl is bound to a positively charged sulfur which will make a good leaving group when demthylated. Once the methyl group is transferred to the amine, the charge on the sulfur is resolved and thus SAM is converted to SAH.[5]
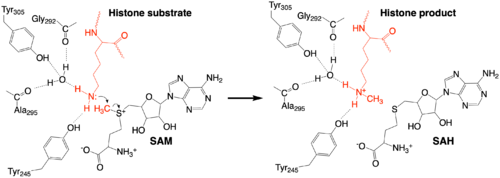
Figure 4: The proposed KMT Mechanism. The lysine substrate and transferred methyl group are in red.
The C-Terminal Domain
The C-terminal domain of lysine methyltransferase consists of a β-hairpin and α-helix that serve as a 'cap' for the SET domain. The overall structure of the provides various interactions that facilitate binding of substrate to the SET domain (residues 193-344).[5] Hydrophobic interactions between the C-terminal domain and the SET domain are mainly responsible in forming the access channel for the substrate and assist in deprotonation of the lysine. Residues 337-349 create a pro-gly rich that stabilizes the orientation of two tyrosine residues, Tyr 335 and Tyr337, that form the lysine access channel. Furthermore, there is substantial hydrophobic packing of the C-terminal helix against the SET domain using . These interactions position the indole ring of Trp352 in the C-terminal helix to as well as allowing Glu356 to hydrogen bond with N6 of the adenine ring.[5]
Inhibitors
SET7/9’s structure and function has been studied extensively because of its role in transcription [7]. In the past few years it has been identified to methylate genes involved in multiple diseases; making it a potential candidate for drug inhibition.[8] Two compounds that have been found to inhibit SET7/9 in certain cells in vitro are Sinefungin and Cyproheptadine. Each inhibitor acts on the catalytic center of SET7/9, however their mechanisms of inhibition and possible medical relevancies differ greatly.
Sinefungin
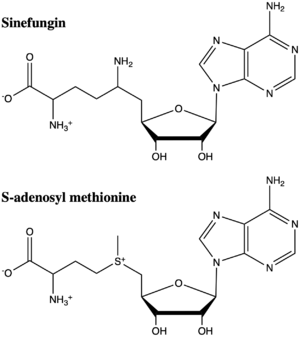
Figure 5: The structure of SAM and Sinefungin. The amine group of sinefungin potentially makes two hydrogen bonds to active site residues in the SET domain.
Sinefungin is a potent methyltransferase inhibitor that is a natural nucleoside isolated from the
"Streptomyces" species.
[8] Also referred to as adenosyl-ornithine, it is the delta (5’ adenosyl) derivative of
ornithine and a
structural analog of SAM (Figure 5). Sinefugin is unique because it binds in the cofactor pocket rather than where the substrate binds like a typical competitive inhibitor. The amine group of sinefungin potentially makes two hydrogen bonds to the main chain carbonyls of Arg265 and His293. As a result, sinefungin is potentially binds with a higher affinity than SAM due to the formation of these two additional hydrogen bonds, which are not possible with the SAM methyl group.
In some renal disease patients treated using peritoneal dialysis, a condition called peritoneal fibrosis develops which reduces how effectively fluid is removed.[9] Sinefungin has been used to inhibit the SET7/9 enzyme to treat peritoneal fibrosis in mice and has been tested against human peritoneal mesothelial cells.[8] SET7/9 is effective in treating in peritoneal fibrosis because it mono-methylates H3K4, which activates the transcription of fibrosis related genes. The administration of Sinefungin to mice resulted in decreased levels of mono-methylated H3K4 protein (H3K4me1), as well as suppressed peritoneal cell density and thickening. This decrease suggests that the methylation of H3K4 was inhibited by Sinefungin, and furthermore that inhibiting SET7/9 might have the potential to ameliorate peritoneal fibrosis.
Cyproheptadine
Another inhibitor of SET7/9 is cyproheptadine, a clinically-approved anti-allergy drug that was originally developed as histamine (H1) and serotonin (5-HT2A) receptor antagonist.[7] The structure of bound with the SAM co-factor was determined by X-ray diffraction at 2.0Å resolution (PDB:5ayf). Unlike Sinefungin, which mimics the SAM co-factor, cyproheptadine is a traditional inhibitor that competes with the histone peptide substrate for the peptide-binding site. When cyproheptadine binds to the substrate site, the methylated nitrogen of the piperdine ring forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl of Thr266 as well as stacking with Tyr335. The binding of cyproheptadine to the catalytic site displaces residue Tyr337, an important residue for the formation of the lysine access channel and unresolved in the inhibited structure. This movement subsequently causes a conformational change of the rendering it disordered in the structure, and shifts the position of the C-terminal helix.[7]
With the revelation of its inhibitory effects on SET7/9, cyproheptadine was used in vitro to treat MCF-7 breast cancer cells. SET7/9's non-histone activities include the methylation of the estrogen receptor α (ERα), a nuclear receptor and a transcription factor responsible for estrogen-responsive gene regulation. The expression and transcriptional activity of ERα is involved in the carcinogenesis of 70% of breast cancers, making it a major target for hormone therapy. Researchers found that treating the MCF-7 cells with cyproheptadine decreased ERα's expression and transcriptional activity which therefore inhibited the estrogen-dependent cell growth. These findings suggest that cyproheptadine could possibly be repurposed to breast cancer therapy in the future.[7]
References
- ↑ DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lu, D. Epigenetic modification enzymes: catalytic mechanisms and inhibitors, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2013 May. 3(3):141-9 DOI:10.1016/j.apsb.2013.04.007
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dong X, Weng Z. The correlation between histone modifications and gene expression. Epigenomics. 2013 Apr;5(2):113-6. doi: 10.2217/epi.13.13. PMID:23566087 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/epi.13.13
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Del Rizzo PA, Trievel RC. Substrate and product specificities of SET domain methyltransferases. Epigenetics. 2011 Sep 1;6(9):1059-67. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.9.16069. Epub 2011 Sep, 1. PMID:21847010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.9.16069
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kwon T, Chang JH, Kwak E, Lee CW, Joachimiak A, Kim YC, Lee J, Cho Y. Mechanism of histone lysine methyl transfer revealed by the structure of SET7/9-AdoMet. EMBO J. 2003 Jan 15;22(2):292-303. PMID:12514135 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg025
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Takemoto Y, Ito A, Niwa H, Okamura M, Fujiwara T, Hirano T, Handa N, Umehara T, Sonoda T, Ogawa K, Tariq M, Nishino N, Dan S, Kagechika H, Yamori T, Yokoyama S, Yoshida M. Identification of Cyproheptadine as an Inhibitor of SET Domain Containing Lysine Methyltransferase 7/9 (Set7/9) That Regulates Estrogen-Dependent Transcription. J Med Chem. 2016 Apr 28;59(8):3650-60. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01732. Epub, 2016 Apr 18. PMID:27088648 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01732
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Tamura R, Doi S, Nakashima A, Sasaki K, Maeda K, Ueno T, Masaki T. Inhibition of the H3K4 methyltransferase SET7/9 ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis. PLoS One. 2018 May 3;13(5):e0196844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196844., eCollection 2018. PMID:29723250 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196844
- ↑ Williams JD, Craig KJ, Topley N, Von Ruhland C, Fallon M, Newman GR, Mackenzie RK, Williams GT. Morphologic changes in the peritoneal membrane of patients with renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002 Feb;13(2):470-9. PMID:11805177





