Growth factors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<scene name='45/450911/Cv/10'>Peptide substrate binding site</scene> ([[3fxx]]).<ref>PMID:19678838</ref> | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/10'>Peptide substrate binding site</scene> ([[3fxx]]).<ref>PMID:19678838</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Ephrin Type-A Receptor]] | ||
| + | The <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Ecto/2'>extracellular part of Eph receptors</scene> includes the N-terminal ephrin (Ligand)-binding domain (LBD), a cysteine-rich domain (CRD), and 2 fibronectin Type-III Repeats (FN3). EphA binds ephrins with <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Lbd_in/1'>its LBD</scene>. Most ephrins have a similar rigid structure which <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Ephrin_a2_opening/2'>includes four loops</scene>, AB, CD, FG, & GH. The LBD of EphA4 is said to be a “structural chameleon” able bind both A and B class ephrins. This explains why Ephrin Type-A receptors exhibit cross-class reactivity. The <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Epha4_opening/1'>overall structure of the EphA4 LBD </scene>includes four important loops, the BC, DE, GH, & JK loops. EphA4 binds the GH loop of the ephrin ligand <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Epha4_pocket/3'>within a deep pocket</scene> created by the EphA4 DE and JK loops. It is these loops, DE and JK, which undergo the greatest conformational shifts when binding either EphrinA2 or EphrinB2. <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Epha4_a2_interactions/2'>When binding EphrinA2</scene>, EphA4-Arg 162 forms a hydrogen bond with EphrinA2-Leu 138, while EphA4-Met 164 and EphA4-Leu 166 participate in hydrophobic interactions with EphrinA2-Leu 138 and EphrinA2-PHe 136. Although <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Ephrinb2_opening/1'>EphA4 binds EphrinB2</scene> in the same binding pocket, the local interactions are significantly different. Most notably, the α-helix present in the EphA4-EphrinA2 JK loop is disrupted in the EphA4-EphrinB2 structure. This is due to <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Ephrinb2_opening/2'>the steric clash</scene> that would occur between EphrinB2-Trp 122 and EphA4 Met 164. Instead, EphA4-Arg 162 and EphrinB2-Trp 122 form hydrophobic stacking interactions <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Ephrinb2_stabile/1'>among other interactions </scene> which stabilize the receptor-ligand complex. A morph of the movements EphA4 undergoes to bind EphrinA2 and EphrinB2 can be <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Morph/4'>seen here</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
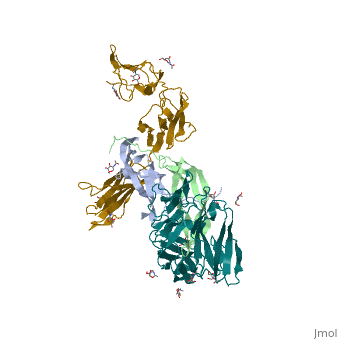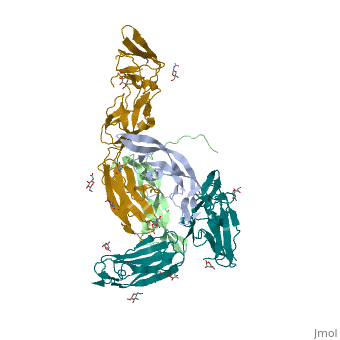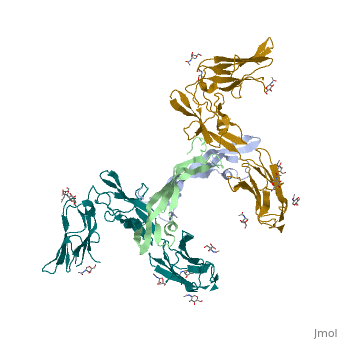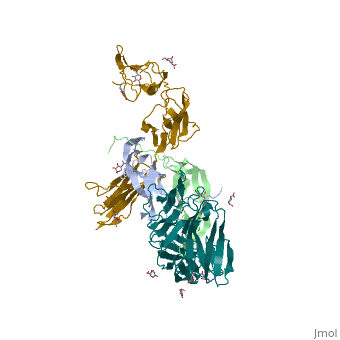
| + | Eph-Ephrin complexes form two unique heterotetrameric assemblies consisting of distinct EphA2-EphA2 interfaces. <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Dimer_out/2'>The 1st tetrameric form</scene> is generated by <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Dimer_out_int/1'>Eph-Eph interactions only within the LBD</scene>. The 2nd <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Dimer_in/3'>tetrameric form</scene> involves complex <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Dimer_in_2/2'>interactions in the LBD</scene> and in the region <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Dimer_in_3/1'>near the CRD</scene>.<ref>PMID:20505120</ref> These two heterotetramers generate a <scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Clustering/2'>continuous Eph-ephrin assembly when combined</scene> (<scene name='Ephrin_Type-A_Receptor/Clustering2/1'>Alternative Coloring</scene>). The proximity of kinase domains in an eph-ephrin tetramer, favors transphosphorylation of tyrosines in the cytoplasmic domains. Phosphorylation promotes kinase activity by orienting the activation segment of the kinase domain in a way that favors subsrate binding and subsequent signaling. | ||
*[[Erythropoietin]] and [[Erythropoietin receptor]] | *[[Erythropoietin]] and [[Erythropoietin receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 28 July 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mohedas AH, Wang Y, Sanvitale CE, Canning P, Choi S, Xing X, Bullock AN, Cuny GD, Yu PB. Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants. J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7900-15. doi: 10.1021/jm501177w. Epub 2014 Sep 4. PMID:25101911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm501177w
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
- ↑ Felix J, De Munck S, Verstraete K, Meuris L, Callewaert N, Elegheert J, Savvides SN. Structure and Assembly Mechanism of the Signaling Complex Mediated by Human CSF-1. Structure. 2015 Jul 21. pii: S0969-2126(15)00272-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019. PMID:26235028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019
- ↑ Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Zhang J, Burton EA, Habets G, Zhang Y, Powell B, West BL, Matusow B, Tsang G, Shellooe R, Carias H, Nguyen H, Marimuthu A, Zhang KY, Oh A, Bremer R, Hurt CR, Artis DR, Wu G, Nespi M, Spevak W, Lin P, Nolop K, Hirth P, Tesch GH, Bollag G. Design and pharmacology of a highly specific dual FMS and KIT kinase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 14. PMID:23493555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219457110
- ↑ Egea J, Klein R. Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007 May;17(5):230-8. Epub 2007 Apr 8. PMID:17420126 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2007.03.004
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120
- ↑ Davis TL, Walker JR, Allali-Hassani A, Parker SA, Turk BE, Dhe-Paganon S. Structural recognition of an optimized substrate for the ephrin family of receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS J. 2009 Aug;276(16):4395-404. PMID:19678838 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07147.x
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120