Growth factors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
'''IL-36''' acts on naïve CD4+ T cells.<br /> | '''IL-36''' acts on naïve CD4+ T cells.<br /> | ||
''' IL-37''' has a role in inhibiting both innate and adaptive immune responses.<br /> | ''' IL-37''' has a role in inhibiting both innate and adaptive immune responses.<br /> | ||
| - | *[[Neurotrophin]] | ||
| - | *[[High affinity nerve growth factor receptor]] | ||
| - | '''TrkA'''. Trk stands for Topomyosin-Related Kinase. TrkA ligand - nerve growth factor activates the receptor by stabilizing homodimer formation which initiates transautophosphorylation. <scene name='80/805001/Cv/4'>Structure of Nerve Growth Factor Complexed with the Extracellular Domain of TrkA</scene>. An <scene name='80/805001/Cv/7'>Arg residue</scene>, conserved in all neutrophins, forms the most important binding determinant between TrkA and its ligand - nerve growth factor - which forms the active homodimer of the receptor. <scene name='80/805001/Cv/6'>All interactions between TrkA chain A and NGF</scene>. | ||
| - | *[[Tyrosine kinase receptor|Tyrosine kinase receptor TrkA]] | ||
| - | TRK-A contains an extracellular ligand binding domain (LBD), a transmembrane helix and an intracellular region which contains the kinase domain. The kinase domain ([[4yne]]) contains the tripeptide DFG which flips out in TRK-A inactivated form. <scene name='83/839914/Cv/7'>Inhibitor binding site</scene> ([[4yne]]). The structure of the complex of TRK-A with the phenylpyrrolidine derivative shows the inhibitor forming hydrogen bonds to Met620 and Lys572 residues and π-π interactions of it with Phe617 and Phe 698. | ||
| - | |||
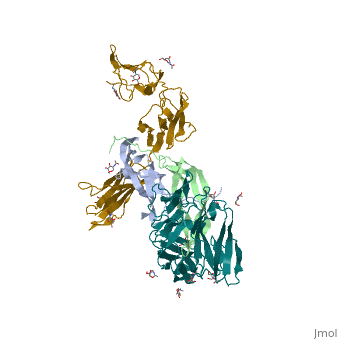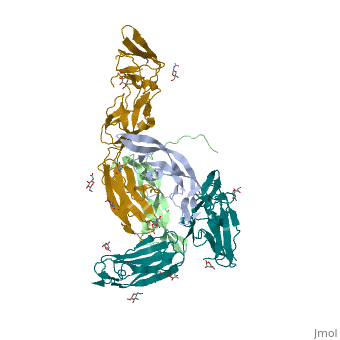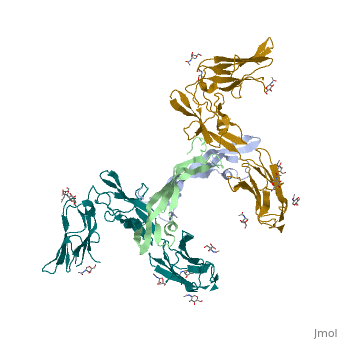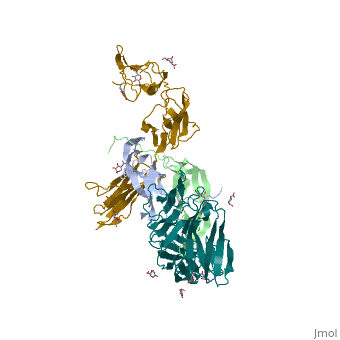
| - | The <scene name='83/839914/Cv/4'>complex between TRK-A and the nerve growth factor</scene> ([[2ifg]]) is a 2:2 dimer. The C-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain interacts with the NGF. The extracellular domain of TRK-A contains <scene name='83/839914/Cv/5'>3 Leu-rich regions</scene> flanked by <scene name='83/839914/Cv/6'>Cys-rich regions</scene> (in yellow), 2 immunoglobulin-like domains and the nerve growth factor (NGF) binding domain. | ||
*[[Neurotrophin|Neurotrophin & its receptor]] | *[[Neurotrophin|Neurotrophin & its receptor]] | ||
The complex between NT3 and p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) shows a <scene name='80/805035/Cv/2'>homodimer of NT3 with two symmetrically arranged p75NTR molecules</scene>. There are 3 sites of interactions between NT3 and p75NTR - site 1, site 2 and site 3. | The complex between NT3 and p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) shows a <scene name='80/805035/Cv/2'>homodimer of NT3 with two symmetrically arranged p75NTR molecules</scene>. There are 3 sites of interactions between NT3 and p75NTR - site 1, site 2 and site 3. | ||
| Line 109: | Line 102: | ||
<scene name='80/805035/Cv/4'>Site 2</scene>. | <scene name='80/805035/Cv/4'>Site 2</scene>. | ||
| - | <scene name='80/805035/Cv/5'>Site 3</scene>. | + | <scene name='80/805035/Cv/5'>Site 3</scene>. |
| + | |||
| + | [[High affinity nerve growth factor receptor]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''TrkA'''. Trk stands for Topomyosin-Related Kinase. TrkA ligand - nerve growth factor activates the receptor by stabilizing homodimer formation which initiates transautophosphorylation. <scene name='80/805001/Cv/4'>Structure of Nerve Growth Factor Complexed with the Extracellular Domain of TrkA</scene>. An <scene name='80/805001/Cv/7'>Arg residue</scene>, conserved in all neutrophins, forms the most important binding determinant between TrkA and its ligand - nerve growth factor - which forms the active homodimer of the receptor. <scene name='80/805001/Cv/6'>All interactions between TrkA chain A and NGF</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Tyrosine kinase receptor|Tyrosine kinase receptor TrkA]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | TRK-A contains an extracellular ligand binding domain (LBD), a transmembrane helix and an intracellular region which contains the kinase domain. The kinase domain ([[4yne]]) contains the tripeptide DFG which flips out in TRK-A inactivated form. <scene name='83/839914/Cv/7'>Inhibitor binding site</scene> ([[4yne]]). The structure of the complex of TRK-A with the phenylpyrrolidine derivative shows the inhibitor forming hydrogen bonds to Met620 and Lys572 residues and π-π interactions of it with Phe617 and Phe 698. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='83/839914/Cv/4'>complex between TRK-A and the nerve growth factor</scene> ([[2ifg]]) is a 2:2 dimer. The C-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain interacts with the NGF. The extracellular domain of TRK-A contains <scene name='83/839914/Cv/5'>3 Leu-rich regions</scene> flanked by <scene name='83/839914/Cv/6'>Cys-rich regions</scene> (in yellow), 2 immunoglobulin-like domains and the nerve growth factor (NGF) binding domain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='80/805008/Cv/6'>Structure of the TrkB-d5:NT-4/5 Complex, comprising one homodimer of NT-4/5 bound to two monomers of TrkB-d5</scene>. TrkB and neutrotrophin-4/5 interact via a <scene name='80/805008/Cv/7'>specificity interaction site</scene> and via a <scene name='80/805008/Cv/8'>conserved interaction site</scene>. | ||
| - | *[[TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor]] | ||
| - | <scene name='80/805008/Cv/6'>Structure of the TrkB-d5:NT-4/5 Complex, comprising one homodimer of NT-4/5 bound to two monomers of TrkB-d5</scene>. TrkB and neutrotrophin-4/5 interact via a <scene name='80/805008/Cv/7'>specificity interaction site</scene> and via a <scene name='80/805008/Cv/8'>conserved interaction site</scene> | ||
*[[Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors]]. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor belongs to [[Receptor tyrosine kinases]], class III. | *[[Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors]]. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor belongs to [[Receptor tyrosine kinases]], class III. | ||
*[[Renalase]] (RNLS) – Anti-apoptotic survival factor | *[[Renalase]] (RNLS) – Anti-apoptotic survival factor | ||
Revision as of 12:58, 4 August 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mohedas AH, Wang Y, Sanvitale CE, Canning P, Choi S, Xing X, Bullock AN, Cuny GD, Yu PB. Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants. J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7900-15. doi: 10.1021/jm501177w. Epub 2014 Sep 4. PMID:25101911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm501177w
- ↑ Lee JH, Chang KZ, Patel V, Jeffery CJ. Crystal structure of rabbit phosphoglucose isomerase complexed with its substrate D-fructose 6-phosphate. Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 3;40(26):7799-805. PMID:11425306
- ↑ Felix J, De Munck S, Verstraete K, Meuris L, Callewaert N, Elegheert J, Savvides SN. Structure and Assembly Mechanism of the Signaling Complex Mediated by Human CSF-1. Structure. 2015 Jul 21. pii: S0969-2126(15)00272-5. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019. PMID:26235028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.019
- ↑ Zhang C, Ibrahim PN, Zhang J, Burton EA, Habets G, Zhang Y, Powell B, West BL, Matusow B, Tsang G, Shellooe R, Carias H, Nguyen H, Marimuthu A, Zhang KY, Oh A, Bremer R, Hurt CR, Artis DR, Wu G, Nespi M, Spevak W, Lin P, Nolop K, Hirth P, Tesch GH, Bollag G. Design and pharmacology of a highly specific dual FMS and KIT kinase inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 14. PMID:23493555 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219457110
- ↑ Egea J, Klein R. Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007 May;17(5):230-8. Epub 2007 Apr 8. PMID:17420126 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2007.03.004
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120
- ↑ Davis TL, Walker JR, Allali-Hassani A, Parker SA, Turk BE, Dhe-Paganon S. Structural recognition of an optimized substrate for the ephrin family of receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS J. 2009 Aug;276(16):4395-404. PMID:19678838 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07147.x
- ↑ Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 May 26. PMID:20505120
- ↑ Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B, Zhan H, Osslund TD, Chirino AJ, Zhang J, Finer-Moore J, Elliott S, Sitney K, Katz BA, Matthews DJ, Wendoloski JJ, Egrie J, Stroud RM. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature. 1998 Oct 1;395(6701):511-6. PMID:9774108 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/26773
- ↑ Syed RS, Reid SW, Li C, Cheetham JC, Aoki KH, Liu B, Zhan H, Osslund TD, Chirino AJ, Zhang J, Finer-Moore J, Elliott S, Sitney K, Katz BA, Matthews DJ, Wendoloski JJ, Egrie J, Stroud RM. Efficiency of signalling through cytokine receptors depends critically on receptor orientation. Nature. 1998 Oct 1;395(6701):511-6. PMID:9774108 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/26773
- ↑ Kulahin N, Kiselyov V, Kochoyan A, Kristensen O, Kastrup JS, Berezin V, Bock E, Gajhede M. Dimerization effect of sucrose octasulfate on rat FGF1. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2008 Jun 1;64(Pt, 6):448-52. Epub 2008 May 16. PMID:18540049 doi:10.1107/S174430910801066X
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Schiering N, Knapp S, Marconi M, Flocco MM, Cui J, Perego R, Rusconi L, Cristiani C. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor c-Met and its complex with the microbial alkaloid K-252a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12654-9. Epub 2003 Oct 14. PMID:14559966 doi:10.1073/pnas.1734128100
- ↑ Hung IC, Chang SS, Chang PC, Lee CC, Chen CY. Memory enhancement by traditional Chinese medicine? J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2012 Dec 19. PMID:23249175 doi:10.1080/07391102.2012.741052
- ↑ Dinarello CA. Biology of interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Feb;2(2):108-15. PMID:3277884