Glucocorticoids
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
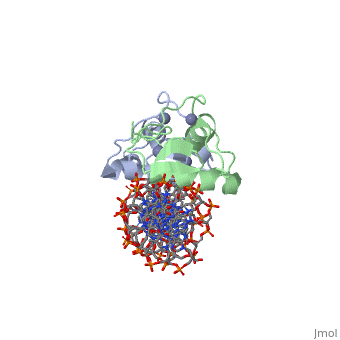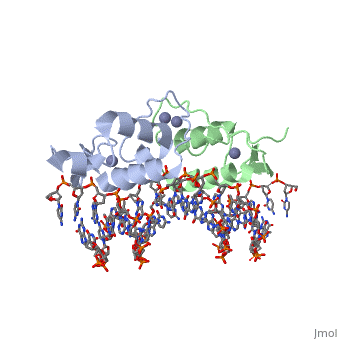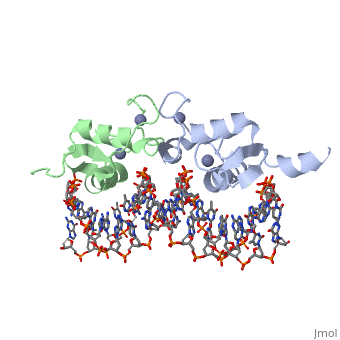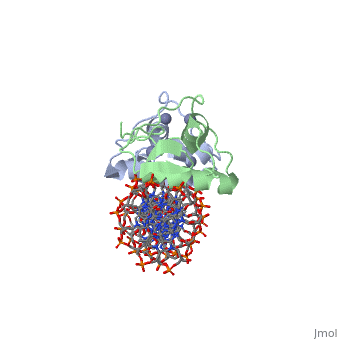
<StructureSection load='3g6r' size='350' side='right' caption='Rat glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain dimer complex with DNA and Zn+2 ions (grey) (PDB entry [[3g6r]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3g6r' size='350' side='right' caption='Rat glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain dimer complex with DNA and Zn+2 ions (grey) (PDB entry [[3g6r]])' scene=''> | ||
*[[Glucocorticoid receptor]] | *[[Glucocorticoid receptor]] | ||
| - | *[[Forkhead box proteins]] (FOX) are transcription factors involved in regulation of gene expression.<ref>PMID:17889656</ref>. '''FOXO1''' activation contributes to '''glucocorticoid'''-induced beta cell death<ref>PMID:23435785</ref>. | + | *[[Forkhead box proteins]] (FOX) are transcription factors involved in regulation of gene expression.<ref>PMID:17889656</ref>. '''FOXO1''' activation contributes to '''glucocorticoid'''-induced beta cell death<ref>PMID:23435785</ref>. FOX contain a DNA-binding motif (DBD) of 80-100 amino acids having a winged-helix shape. |
| + | **<scene name='47/479231/Cv/5'>Human FoxO1 DNA-binding domain with DNA, Ca+2 and Cl- ions</scene>. | ||
| + | **<scene name='47/479231/Cv/6'>Ca coordination site</scene>. Water molecules shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | **<scene name='47/479231/Cv/7'>Cl coordination site</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
*[[Nuclear receptor coactivator]] (NCOA) is a protein recruited by nuclear receptors in order to enhance or repress DNA transcription. NCOA is involved in coactivation with transcription factors<ref>PMID:9121485</ref>. '''NCOA1''' shows histone acetyltransferase activity and is required for '''steroid hormone''' response. '''NCOA2''' is a DNA transcription coactivator with '''glucocorticoid''' receptor. | *[[Nuclear receptor coactivator]] (NCOA) is a protein recruited by nuclear receptors in order to enhance or repress DNA transcription. NCOA is involved in coactivation with transcription factors<ref>PMID:9121485</ref>. '''NCOA1''' shows histone acetyltransferase activity and is required for '''steroid hormone''' response. '''NCOA2''' is a DNA transcription coactivator with '''glucocorticoid''' receptor. | ||
| - | *[[Thioredoxin Reductase]] (TrxR) is an enzyme which reduces thioredoxin using NADPH<ref>PMID:11012661</ref>. Mutations in TrxR-2 are associated with familial '''glucocorticoid''' deficiency<ref>PMID:24601690</ref>. | + | **<scene name='49/494427/Cv/7'>NCOA/STAT6 transactivator domain LXXLL peptide interactions</scene>. |
| - | *Microsomal [[Prostaglandin E synthase]] (PGES) converts cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived prostaglandin to PGE2. It is membrane-associated and belongs to the microsomal glutathione S-transferase family. PGES is preferentially linked with the inducible COX-2<ref>PMID:12432931</ref> . PGES is induced by proinflammatory stimuli and down-regulated by anti-inflammatory '''glucocorticoids'''<ref>PMID:16336776</ref>. | + | **<scene name='49/494427/Cv/8'>1st Iod coordination site</scene>. |
| + | **<scene name='49/494427/Cv/9'>2nd Iod coordination site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | **<scene name='49/494427/Cv/10'>3th and 4th Iod coordination sites</scene>. | ||
| + | **<scene name='49/494427/Cv/11'>5th Iod coordination site</scene>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Thioredoxin Reductase]] (TrxR) is an enzyme which reduces thioredoxin using NADPH<ref>PMID:11012661</ref>. Mutations in TrxR-2 are associated with familial '''glucocorticoid''' deficiency<ref>PMID:24601690</ref>. Thioredoxin Reductase (TrxR) is an enzyme which reduces thioredoxin using NADPH<ref>PMID:11012661</ref>. '''TrxR-2''' is mitochondrial. For more details see [[User:Sarah Abdalla/Thioredoxin Reductase]]. TrxR and Trx form an <scene name='43/433123/Cv/6'>intramolecular Cys-Cys bond</scene><ref>PMID:21750537</ref>. <scene name='43/433123/Cv/7'>FAD binding site</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Microsomal [[Prostaglandin E synthase]] (PGES) converts cyclooxygenase (COX)-derived prostaglandin to PGE2. It is membrane-associated and belongs to the microsomal glutathione S-transferase family. PGES is preferentially linked with the inducible COX-2<ref>PMID:12432931</ref> . PGES is induced by proinflammatory stimuli and down-regulated by anti-inflammatory '''glucocorticoids'''<ref>PMID:16336776</ref>. Microsomal ''Prostaglandin E synthase'' <scene name='77/778890/Cv/2'>is membrane-associated</scene> (coordinates are from [http://opm.phar.umich.edu/protein.php?extrapdb=4yl0 OPM database]. The <scene name='77/778890/Cv/6'>anti-inflammatory inhibitor binds to PGES in a pocket above the glutathione and interacts with various side-chains of a helix</scene><ref>PMID:25961169</ref>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 11:06, 7 November 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tuteja G, Kaestner KH. SnapShot: forkhead transcription factors I. Cell. 2007 Sep 21;130(6):1160. PMID:17889656 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.005
- ↑ Kaiser G, Gerst F, Michael D, Berchtold S, Friedrich B, Strutz-Seebohm N, Lang F, Haring HU, Ullrich S. Regulation of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) by protein kinase B and glucocorticoids: different mechanisms of induction of beta cell death in vitro. Diabetologia. 2013 Jul;56(7):1587-95. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2863-7. Epub 2013, Feb 23. PMID:23435785 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2863-7
- ↑ Horwitz KB, Jackson TA, Bain DL, Richer JK, Takimoto GS, Tung L. Nuclear receptor coactivators and corepressors. Mol Endocrinol. 1996 Oct;10(10):1167-77. PMID:9121485 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/mend.10.10.9121485
- ↑ Arner ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Oct;267(20):6102-9. PMID:11012661
- ↑ Prasad R, Chan LF, Hughes CR, Kaski JP, Kowalczyk JC, Savage MO, Peters CJ, Nathwani N, Clark AJ, Storr HL, Metherell LA. Thioredoxin Reductase 2 (TXNRD2) mutation associated with familial glucocorticoid deficiency (FGD). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Aug;99(8):E1556-63. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3844. Epub, 2014 Mar 6. PMID:24601690 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-3844
- ↑ Arner ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000 Oct;267(20):6102-9. PMID:11012661
- ↑ Fritz-Wolf K, Kehr S, Stumpf M, Rahlfs S, Becker K. Crystal structure of the human thioredoxin reductase-thioredoxin complex. Nat Commun. 2011 Jul 12;2:383. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1382. PMID:21750537 doi:10.1038/ncomms1382
- ↑ Murakami M, Nakatani Y, Tanioka T, Kudo I. Prostaglandin E synthase. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002 Aug;68-69:383-99. PMID:12432931
- ↑ Kudo I, Murakami M. Prostaglandin E synthase, a terminal enzyme for prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Nov 30;38(6):633-8. PMID:16336776
- ↑ Luz JG, Antonysamy S, Kuklish SL, Condon B, Lee MR, Allison D, Yu XP, Chandrasekhar S, Backer R, Zhang A, Russell M, Chang SS, Harvey A, Sloan AV, Fisher MJ. Crystal Structures of mPGES-1 Inhibitor Complexes Form a Basis for the Rational Design of Potent Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics. J Med Chem. 2015 May 20. PMID:25961169 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00330