|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | | | |
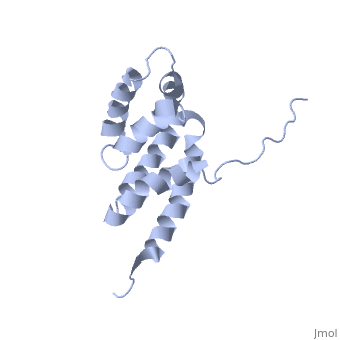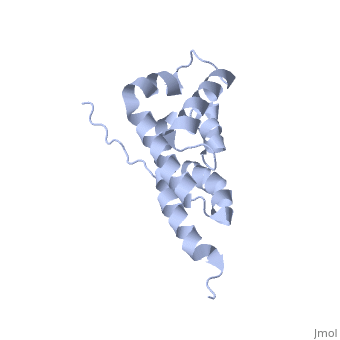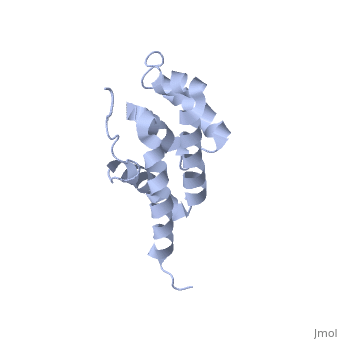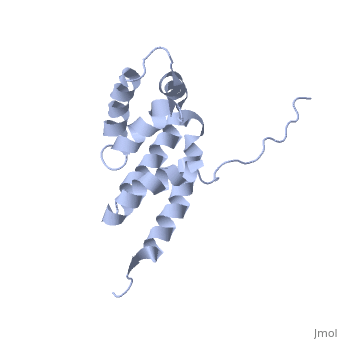
| | ==Bovine oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein N-terminal domain== | | ==Bovine oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein N-terminal domain== |
| - | <StructureSection load='2bo5' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2bo5]], [[NMR_Ensembles_of_Models | 44 NMR models]]' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='2bo5' size='340' side='right'caption='[[2bo5]]' scene=''> |
| | == Structural highlights == | | == Structural highlights == |
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2bo5]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bovin Bovin]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2BO5 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2BO5 FirstGlance]. <br> | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[2bo5]] is a 1 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bos_taurus Bos taurus]. Full experimental information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2BO5 OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2BO5 FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/H(+)-transporting_two-sector_ATPase H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase], with EC number [https://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=3.6.3.14 3.6.3.14] </span></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">Solution NMR</td></tr> |
| | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2bo5 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2bo5 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2bo5 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2bo5 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2bo5 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2bo5 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=2bo5 FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=2bo5 OCA], [https://pdbe.org/2bo5 PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=2bo5 RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/2bo5 PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=2bo5 ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
| | </table> | | </table> |
| | == Function == | | == Function == |
| - | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ATPO_BOVIN ATPO_BOVIN]] Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha(3)beta(3) subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements.
| + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ATPO_BOVIN ATPO_BOVIN] Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha(3)beta(3) subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements. |
| | == Evolutionary Conservation == | | == Evolutionary Conservation == |
| | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] |
| Line 32: |
Line 32: |
| | __TOC__ | | __TOC__ |
| | </StructureSection> | | </StructureSection> |
| - | [[Category: Bovin]] | + | [[Category: Bos taurus]] |
| | [[Category: Large Structures]] | | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Carbajo, R J]] | + | [[Category: Carbajo RJ]] |
| - | [[Category: Kellas, F A]] | + | [[Category: Kellas FA]] |
| - | [[Category: Montgomery, M G]] | + | [[Category: Montgomery MG]] |
| - | [[Category: Neuhaus, D]] | + | [[Category: Neuhaus D]] |
| - | [[Category: Runswick, M J]] | + | [[Category: Runswick MJ]] |
| - | [[Category: Walker, J E]] | + | [[Category: Walker JE]] |
| - | [[Category: Alpha-subunit]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Atp synthase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Beta-subunit]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Binding interface]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Chemical shift mapping]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Chemical shift perturbation]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hydrogen ion transport]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Hydrolase]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Ion transport]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Mitochondrion]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Oscp]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Peripheral stalk]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Protein-protein interaction]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Titration]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transit peptide]]
| + | |
| - | [[Category: Transport]]
| + | |
| Structural highlights
Function
ATPO_BOVIN Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase (F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1) - containing the extramembraneous catalytic core and F(0) - containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(0) domain and the peripheric stalk, which acts as a stator to hold the catalytic alpha(3)beta(3) subcomplex and subunit a/ATP6 static relative to the rotary elements.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check, as determined by ConSurfDB. You may read the explanation of the method and the full data available from ConSurf.
Publication Abstract from PubMed
The peripheral stalk of ATP synthase holds the alpha3beta3 catalytic subcomplex stationary against the torque of the rotating central stalk. In bovine mitochondria, the N-terminal domain of the oligomycin sensitivity conferral protein (OSCP-NT; residues 1-120) anchors one end of the peripheral stalk to the N-terminal tails of one or more alpha-subunits of the F1 subcomplex. Here we present the solution structure of OSCP-NT and an NMR titration study of its interaction with peptides representing N-terminal tails of F1 alpha-subunits. The structure comprises a bundle of six alpha-helices, and its interaction site contains adjoining hydrophobic surfaces of helices 1 and 5; residues in the region 1-8 of the alpha-subunit are essential for the interaction. The OSCP-NT is similar to the N-terminal domain of the delta-subunit from Escherichia coli ATP synthase (delta-NT), except that their surface charges differ (basic and acidic, respectively). As the charges of the adjacent crown regions in their alpha3beta3 complexes are similar, the OSCP-NT and delta-NT probably do not contact the crowns extensively. The N-terminal tails of alpha-subunit tails are probably alpha-helical, and so this interface, which is essential for the rotary mechanism of the enzyme, appears to consist of helix-helix interactions.
Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit.,Carbajo RJ, Kellas FA, Runswick MJ, Montgomery MG, Walker JE, Neuhaus D J Mol Biol. 2005 Aug 26;351(4):824-38. PMID:16045926[1]
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
References
- ↑ Carbajo RJ, Kellas FA, Runswick MJ, Montgomery MG, Walker JE, Neuhaus D. Structure of the F1-binding domain of the stator of bovine F1Fo-ATPase and how it binds an alpha-subunit. J Mol Biol. 2005 Aug 26;351(4):824-38. PMID:16045926 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.06.012
|