User:Cristiane Custodio Ross Matheus/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
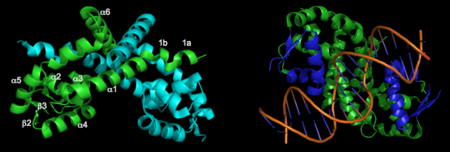
<StructureSection load='1ZB9' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Organic Hydroperoxide Resistance Protein (PDB code [[1ZB9]]).'> | <StructureSection load='1ZB9' size='450' side='right' scene='' caption='Organic Hydroperoxide Resistance Protein (PDB code [[1ZB9]]).'> | ||
| - | == | + | ==introduction== |
'''OhrR''' plays a critical role in sensing of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenic bacteria Xanthomonas campestris. Under normal cellular conditions, dimeric OhrR protein is bound to DNA to repress expression of ohr, which encodes organic hydroperoxide resistance protein. When the reactive oxygen species organic hydroperoxide (OHR) is present in the cell, it oxidizes a reactive cysteine in OhrR, resulting in a conformational change that causes the dissocation of OhrR from ohr and subsequent clearance of OHR by OHR. This dissociation occurs because the oxidation of this reactive cysteine results in the formation of an interprotein cysteine bond between each of two units. | '''OhrR''' plays a critical role in sensing of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenic bacteria Xanthomonas campestris. Under normal cellular conditions, dimeric OhrR protein is bound to DNA to repress expression of ohr, which encodes organic hydroperoxide resistance protein. When the reactive oxygen species organic hydroperoxide (OHR) is present in the cell, it oxidizes a reactive cysteine in OhrR, resulting in a conformational change that causes the dissocation of OhrR from ohr and subsequent clearance of OHR by OHR. This dissociation occurs because the oxidation of this reactive cysteine results in the formation of an interprotein cysteine bond between each of two units. | ||
Revision as of 23:27, 6 December 2021
| |||||||||||