Fel d 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
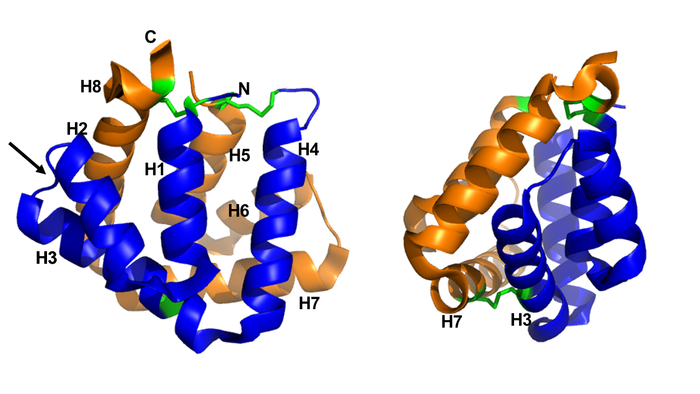
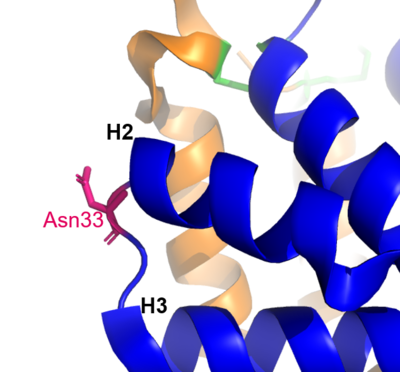
Figure 1 shows the general structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two different orientations, rotated 90° around the vertical axis. Chains 1 and 2 correspond to the orange and blue helices respectively. The three disulfide bridges connecting chains 1 and 2 are shown in green. An arrow indicates the unique [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycosylation#N-linked_glycosylation glycosylation] site at residue Asn33 (N33) and in Figure 2 it is possible to visualize the residue Asn33 in pink<ref name="[1]"/>. | Figure 1 shows the general structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two different orientations, rotated 90° around the vertical axis. Chains 1 and 2 correspond to the orange and blue helices respectively. The three disulfide bridges connecting chains 1 and 2 are shown in green. An arrow indicates the unique [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycosylation#N-linked_glycosylation glycosylation] site at residue Asn33 (N33) and in Figure 2 it is possible to visualize the residue Asn33 in pink<ref name="[1]"/>. | ||
| - | [[Image:Monomero e monomero 90.PNG | thumb | center | | + | [[Image:Monomero e monomero 90.PNG | thumb | center | 700px | '''Figure 1.''' General structure of a Fel d 1 monomer, shown in two distinct orientations, rotated 90° about the vertical axis. (Source: PyMOL 2.5.2)]] |
[[Image:N33.png | thumb | center | 400px | '''Figure 2.''' Residue Asn33 in pink. (Source: PyMOL 2.5.2)]] | [[Image:N33.png | thumb | center | 400px | '''Figure 2.''' Residue Asn33 in pink. (Source: PyMOL 2.5.2)]] | ||
| + | |||
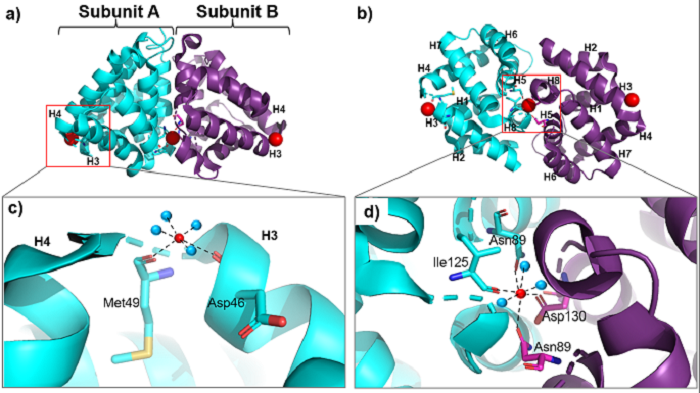
In the Fel d 1 tetramer, three Ca<sup>2+</sup> binding sites were identified<ref name="[4]"/>, as in Figure 3, where the Ca<sup>2+</sup> are indicated as red balls. Two Ca<sup>2+</sup> binding sites are equivalent and are found symmetrically located on either side of the dimer and the third is found within the dimerization interface (Figure 3 (a) and (b)). The Ca<sup>2+</sup> equivalents bind to the carbonyl groups of Asp46 and Met49 residues, as well as to four and three water molecules in the A and B subunits, respectively, (Figure 3 (c)) and the Ca<sup>2+</sup> located at the dimerization interface binds to the [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe-srv/pdbechem/atom/show?cid=IAS&name=OD1 OD1] atoms of residues Asn89 (in subunit A), Asn89 (B) and Asp130 (B), as well as to the carbonyl group of residue Ile125 (A) and three molecules of water (Figure 3 (d))<ref name="[2]">KAISER, Liselotte; VELICKOVIC, Tanja Cirkovic; BADIA-MARTINEZ, Daniel; ADEDOYIN, Justus; THUNBERG, Sarah; HALLÉN, Dan; BERNDT, Kurt; GRÖNLUND, Hans; GAFVELIN, Guro; HAGE, Marianne van; ACHOUR, Adnane. Structural Characterization of the Tetrameric form of the Major Cat Allergen Fel d 1. Journal of Molecular Biology, [s. l.], v. 370, ed. 4, p. 714-727, 2007. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.074.</ref>. | In the Fel d 1 tetramer, three Ca<sup>2+</sup> binding sites were identified<ref name="[4]"/>, as in Figure 3, where the Ca<sup>2+</sup> are indicated as red balls. Two Ca<sup>2+</sup> binding sites are equivalent and are found symmetrically located on either side of the dimer and the third is found within the dimerization interface (Figure 3 (a) and (b)). The Ca<sup>2+</sup> equivalents bind to the carbonyl groups of Asp46 and Met49 residues, as well as to four and three water molecules in the A and B subunits, respectively, (Figure 3 (c)) and the Ca<sup>2+</sup> located at the dimerization interface binds to the [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe-srv/pdbechem/atom/show?cid=IAS&name=OD1 OD1] atoms of residues Asn89 (in subunit A), Asn89 (B) and Asp130 (B), as well as to the carbonyl group of residue Ile125 (A) and three molecules of water (Figure 3 (d))<ref name="[2]">KAISER, Liselotte; VELICKOVIC, Tanja Cirkovic; BADIA-MARTINEZ, Daniel; ADEDOYIN, Justus; THUNBERG, Sarah; HALLÉN, Dan; BERNDT, Kurt; GRÖNLUND, Hans; GAFVELIN, Guro; HAGE, Marianne van; ACHOUR, Adnane. Structural Characterization of the Tetrameric form of the Major Cat Allergen Fel d 1. Journal of Molecular Biology, [s. l.], v. 370, ed. 4, p. 714-727, 2007. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.074.</ref>. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
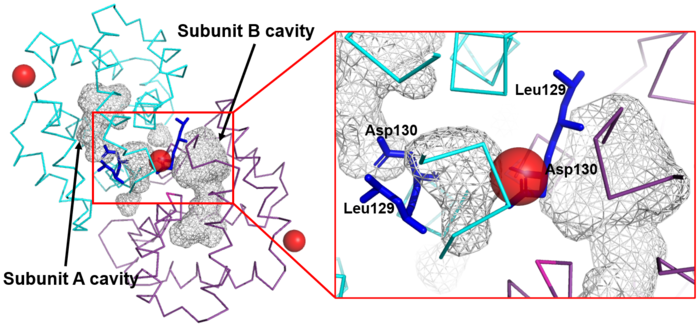
The Fel d 1 quaternary structure reports two cavities in the A and B subunits of 350 and 730 Å<sup>3</sup>, respectively, where the difference in size between the two cavities is a direct result of the conformational change within the region corresponding to residues 121– 131. This size difference is related to the conformation of residues Leu129 and Asp130, which point to opposite uptake, in subunit A they point to the cavity and in subunit B they point to a dimerization interface. Furthermore, the Ca<sup>2+</sup> from the dimerization interface does not interact with the side chain of the Asp130 from the A subunit, projecting itself, then into its cavity, while the Asp130 side chain of the B subunit interacts with Ca<sup>2+</sup>. Such cavities have 3 and 7 water molecules, respectively. All of this can be seen in Figure 4<ref name="[2]"/>. | The Fel d 1 quaternary structure reports two cavities in the A and B subunits of 350 and 730 Å<sup>3</sup>, respectively, where the difference in size between the two cavities is a direct result of the conformational change within the region corresponding to residues 121– 131. This size difference is related to the conformation of residues Leu129 and Asp130, which point to opposite uptake, in subunit A they point to the cavity and in subunit B they point to a dimerization interface. Furthermore, the Ca<sup>2+</sup> from the dimerization interface does not interact with the side chain of the Asp130 from the A subunit, projecting itself, then into its cavity, while the Asp130 side chain of the B subunit interacts with Ca<sup>2+</sup>. Such cavities have 3 and 7 water molecules, respectively. All of this can be seen in Figure 4<ref name="[2]"/>. | ||
| - | [[Image:Cavidades e Zoom.png | thumb | center | | + | [[Image:Cavidades e Zoom.png | thumb | center | 700px | '''Figure 4.''' Shape of the cavities (in gray) directly governed by the conformation of Leu129 and Asp130 residues. The Asp130 side chain (underlined) does not interact with Ca<sup>2+</sup> and projects into the cavity in the A subunit (in cyan), while the Asp130 side chain (B subunit) binds to Ca<sup>2+</sup>. These conformations can be seen in ampliation. The Ca<sup>2+</sup> ions are also indicated like red balls. (Source: PyMOL 2.5.2)]] |
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
[https://acaai.org/allergies/management-treatment/allergy-immunotherapy/ Immunotherapy], or allergy vaccination, which is based on repeated subcutaneous injections of cat hair extracts has been shown to be effective in the curative treatment of allergy. However, in addition to being a time-consuming treatment, it can cause serious side effects such as asthma attacks and anaphylactic shock <ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | [https://acaai.org/allergies/management-treatment/allergy-immunotherapy/ Immunotherapy], or allergy vaccination, which is based on repeated subcutaneous injections of cat hair extracts has been shown to be effective in the curative treatment of allergy. However, in addition to being a time-consuming treatment, it can cause serious side effects such as asthma attacks and anaphylactic shock <ref name="[1]"/><ref name="[4]"/>. | ||
| - | Additionally, to add to the immunotherapy treatment, there is a cat food supplemented with anti-Fel d 1 IgY, which significantly reduces active Fel d 1 levels. | + | Additionally, to add to the immunotherapy treatment, there is a cat food supplemented with anti-Fel d 1 IgY, which significantly reduces active Fel d 1 levels <ref name="[3]"/>. |
== '''References''' == | == '''References''' == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 8 December 2021
Fel d 1: The major cat allergen
| |||||||||||