User:Cristiane Custodio Ross Matheus/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Ohr''' is a thiol dependent antioxidant enzyme that belongs to the Ohr/OsmC family, present in bacteria and fungi, and which has the function of protecting these microorganisms from oxidative stress. It is evident, therefore, that this protein plays a central role in bacterial defense against oxidants from the host's reaction to infection. With the progress of studies on this compound it was found that Ohr are the essential actors in the decomposition of hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrite, that is, it has these compounds as its main substrate, not presenting much efficiency in the decomposition of other types of oxidants. Within this context it is important to point out that although similar to peroxiredoxins the Ohr are not seen as such. Peroxiredoxins are nothing more than proteins that also have antioxidant action but have a structure both primary and tertiary, quite different from Ohr enzymes.. Another important point to be raised is the relevance of ohr studies for the creation of new drugs, since it is an enzyme whose structure is characteristic only of bacteria and fungi, not presenting similar structure in animals and plants. Some examples of pathogenic bacteria expressing Ohr proteins are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae and Xylella fastidiosa. It is important to note that this protein varies according to the microorganism studied, having differences in its regulation and expression, and the focus of this page is the Ohr protein of Xylella Fastidiosa. | '''Ohr''' is a thiol dependent antioxidant enzyme that belongs to the Ohr/OsmC family, present in bacteria and fungi, and which has the function of protecting these microorganisms from oxidative stress. It is evident, therefore, that this protein plays a central role in bacterial defense against oxidants from the host's reaction to infection. With the progress of studies on this compound it was found that Ohr are the essential actors in the decomposition of hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrite, that is, it has these compounds as its main substrate, not presenting much efficiency in the decomposition of other types of oxidants. Within this context it is important to point out that although similar to peroxiredoxins the Ohr are not seen as such. Peroxiredoxins are nothing more than proteins that also have antioxidant action but have a structure both primary and tertiary, quite different from Ohr enzymes.. Another important point to be raised is the relevance of ohr studies for the creation of new drugs, since it is an enzyme whose structure is characteristic only of bacteria and fungi, not presenting similar structure in animals and plants. Some examples of pathogenic bacteria expressing Ohr proteins are Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio cholerae and Xylella fastidiosa. It is important to note that this protein varies according to the microorganism studied, having differences in its regulation and expression, and the focus of this page is the Ohr protein of Xylella Fastidiosa. | ||
==Organic Hydroperoxide Resistance Protein from Xylella fastidiosa (Ohr)== | ==Organic Hydroperoxide Resistance Protein from Xylella fastidiosa (Ohr)== | ||
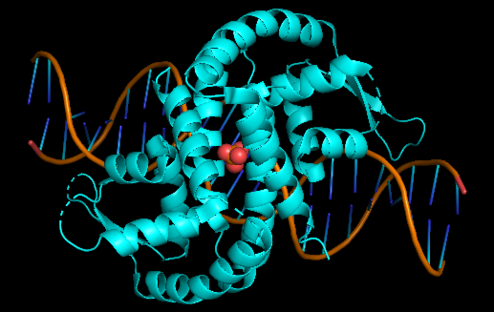
| - | Xylella fastidiosa is a gram - negative bacterium, restricted colonizer of plant xylem, known to cause diseases in several monocotyledons and dicotyledons of great economic importance. Addressing the pathogen-host relationship, it was possible to observe that the plant releases reactive oxygen species that function as microbicide agents. Among the ROS produced are fatty acid hydroperoxides, generated from an oxidation reaction catalyzed by lipoxygenase enzymes. To defend itself from this oxidative attack Xylella produces the Enzyme Ohr. Within this topic it was observed that in a situation of increased stress there is no increase in the amount of enzyme, concluding that in this bacterium there is no regulatory mechanism as for most OM so that have the Ohr gene | + | '''Xylella fastidiosa''' is a gram - negative bacterium, restricted colonizer of plant xylem, known to cause diseases in several monocotyledons and dicotyledons of great economic importance. Addressing the pathogen-host relationship, it was possible to observe that the plant releases reactive oxygen species that function as microbicide agents. Among the ROS produced are fatty acid hydroperoxides, generated from an oxidation reaction catalyzed by lipoxygenase enzymes. To defend itself from this oxidative attack Xylella produces the Enzyme Ohr. Within this topic it was observed that in a situation of increased stress there is no increase in the amount of enzyme, concluding that in this bacterium there is no regulatory mechanism as for most OM so that have the Ohr gene |
[[Image:OHRR_(2).png|left|494px]]<br /> | [[Image:OHRR_(2).png|left|494px]]<br /> | ||
==Ohr gene regulation== | ==Ohr gene regulation== | ||
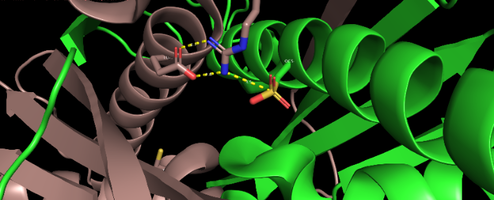
| - | OhrR is a transcriptional factor characterized by being a repressive protein and the main regulatory factor of the Ohr gene in most microorganisms. This protein is found on the promoter of the Ohr gene and has its structure altered when oxidized when it comes into contact with hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrites. With the change of conformation generated by the oxidation of OhrR occurs its detachment from the promoter of the gene, making it more accessible to RNA polymerase, resulting in an overexpression of the Ohr gene. In addition to OhrR were also found in some microorganisms different regulatory means for the Ohr gene. An example is positive regulation by the alternative sigma factor, present in some microorganisms | + | '''OhrR''' is a transcriptional factor characterized by being a repressive protein and the main regulatory factor of the Ohr gene in most microorganisms. This protein is found on the promoter of the Ohr gene and has its structure altered when oxidized when it comes into contact with hydroperoxides of fatty acids and peroxynitrites. With the change of conformation generated by the oxidation of OhrR occurs its detachment from the promoter of the gene, making it more accessible to RNA polymerase, resulting in an overexpression of the Ohr gene. In addition to OhrR were also found in some microorganisms different regulatory means for the Ohr gene. An example is positive regulation by the alternative sigma factor, present in some microorganisms |
[[Image:Screenshot 20211212-110409~2.png|right|494px]]<br /> | [[Image:Screenshot 20211212-110409~2.png|right|494px]]<br /> | ||
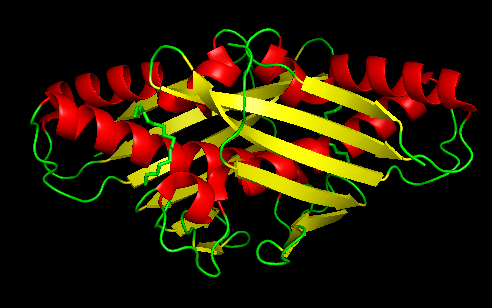
==Structural features== | ==Structural features== | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 12 December 2021
| |||||||||||
References
<CUSSIOL, Jose Renato Rosa. Caracterização funcional de uma nova proteína antioxidante: Ohr (Organic Hidroperoxide Resistance Protein). Vias de redução e expressão em Xylella fastidiosa. 2010. 218 f. Tese (Doutorado) - Curso de Biociências, Departamento de Biologia Evolutiva e Genética, Usp, São Paulo, 2010. Disponível em: https://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/41/41131/tde-21072010-161740/publico/Jose_Renato_Cussiol_versao_completa.pdf. Acesso em: 13 nov. 2021./>