User:Maria Carolina Boer Copstein/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
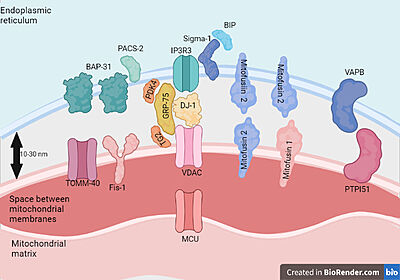
Human VDAC1 (hVDAC1) adopts a β-barrel architecture composed of 19 <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1_helix/3'>β-strands</scene> with strands β1 and β19 being in parallel connformation and an <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1_helix/2'>α-helix</scene> located horizontally midway within the pore. N-terminal region of VDAC1, consisting of 25 amino acids,lies inside the channel pore and possesses different degrees of α-helical content in each of the three proposed structures.Various studies using purified rat liver , brain mitochondria or recombinant human VDAC1 have reported that both soluble purified and membrane-embedded VDAC1 can assemble into <scene name='89/896608/Olig/1'>dimers</scene>, trimers, tetramers and higher oligomeric states. VDAC1 oligomerization was also demonstrated in VDAC1-reconstituted liposomes.VDAC1 oligomerization involves several different interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions between β‐strands, hydrophilic interactions between loop regions and one of the β‐strands, and protein–lipid interactions. | Human VDAC1 (hVDAC1) adopts a β-barrel architecture composed of 19 <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1_helix/3'>β-strands</scene> with strands β1 and β19 being in parallel connformation and an <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1_helix/2'>α-helix</scene> located horizontally midway within the pore. N-terminal region of VDAC1, consisting of 25 amino acids,lies inside the channel pore and possesses different degrees of α-helical content in each of the three proposed structures.Various studies using purified rat liver , brain mitochondria or recombinant human VDAC1 have reported that both soluble purified and membrane-embedded VDAC1 can assemble into <scene name='89/896608/Olig/1'>dimers</scene>, trimers, tetramers and higher oligomeric states. VDAC1 oligomerization was also demonstrated in VDAC1-reconstituted liposomes.VDAC1 oligomerization involves several different interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions between β‐strands, hydrophilic interactions between loop regions and one of the β‐strands, and protein–lipid interactions. | ||
| - | + | Return to <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1/3'>Ball and sticks structure</scene> or <scene name='89/896608/Vdac1/1'>cartoon</scene> structure | |
Revision as of 08:15, 13 December 2021
| |||||||||||
References
Magri Andrea ,Messina Angela, “Interactions of VDAC with Proteins Involved in Neurodegenerative Aggregation: An Opportunity for Advancement on Therapeutic Molecules”, Current Medicinal Chemistry 2017; 24(40) . https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170601073920
Hosaka T, Okazaki M, Kimura-Someya T, et al. Crystal structural characterization reveals novel oligomeric interactions of human voltage-dependent anion channel 1. Protein Sci. 2017;26(9):1749-1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121218
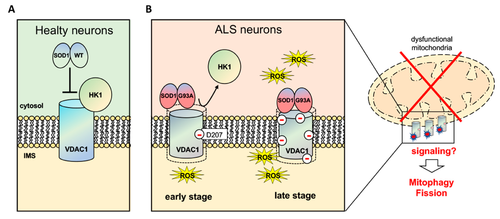
Pittalà, M.G.G.; Reina, S.; Cubisino, S.A.M.; Cucina, A.; Formicola, B.; Cunsolo, V.; Foti, S.; Saletti, R.; Messina, A. Post-Translational Modification Analysis of VDAC1 in ALS-SOD1 Model Cells Reveals Specific Asparagine and Glutamine Deamidation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121218