This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1db1
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /> <applet load="1db1" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1db1, resolution 1.8Å" /> '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1db1.gif|left|200px]]<br /> | + | [[Image:1db1.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1db1" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
| - | <applet load="1db1" size=" | + | |
caption="1db1, resolution 1.8Å" /> | caption="1db1, resolution 1.8Å" /> | ||
'''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR RECEPTOR FOR VITAMIN D COMPLEXED TO VITAMIN D'''<br /> | '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR RECEPTOR FOR VITAMIN D COMPLEXED TO VITAMIN D'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | The action of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is mediated by its nuclear | + | The action of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is mediated by its nuclear receptor (VDR), a ligand-dependent transcription regulator. We report the 1.8 A resolution crystal structure of the complex between a VDR ligand-binding domain (LBD) construct lacking the highly variable VDR-specific insertion domain and vitamin D. The construct exhibits the same binding affinity for vitamin D and transactivation ability as the wild-type protein, showing that the N-terminal part of the LBD is essential for its structural and functional integrity while the large insertion peptide is dispensable. The structure reveals the active conformation of the bound ligand and allows understanding of the different binding properties of some synthetic analogs. |
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1DB1 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] with VDX as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1DB1 is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_protein Single protein] structure of sequence from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] with <scene name='pdbligand=VDX:'>VDX</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligand ligand]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1DB1 OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
[[Category: Moras, D.]] | [[Category: Moras, D.]] | ||
[[Category: Rochel, N.]] | [[Category: Rochel, N.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Wurtz, J | + | [[Category: Wurtz, J M.]] |
[[Category: VDX]] | [[Category: VDX]] | ||
[[Category: complex]] | [[Category: complex]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 12:14:47 2008'' |
Revision as of 10:14, 21 February 2008
|
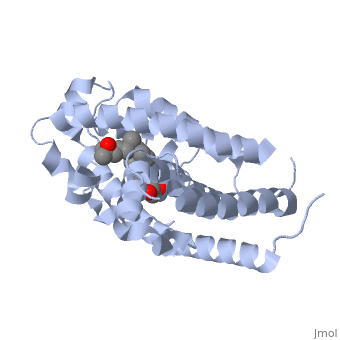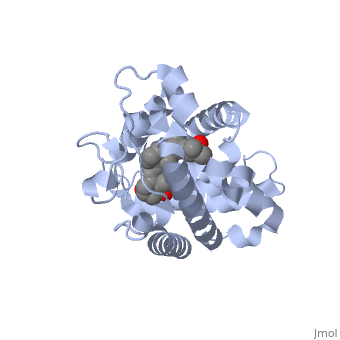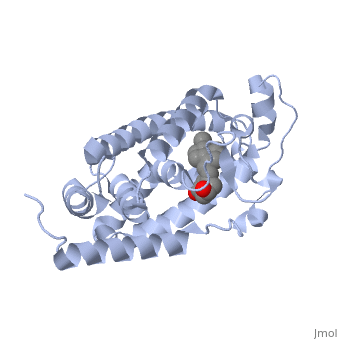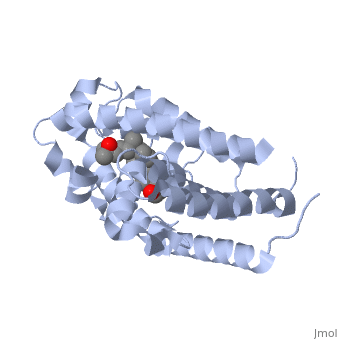
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEAR RECEPTOR FOR VITAMIN D COMPLEXED TO VITAMIN D
Contents |
Overview
The action of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is mediated by its nuclear receptor (VDR), a ligand-dependent transcription regulator. We report the 1.8 A resolution crystal structure of the complex between a VDR ligand-binding domain (LBD) construct lacking the highly variable VDR-specific insertion domain and vitamin D. The construct exhibits the same binding affinity for vitamin D and transactivation ability as the wild-type protein, showing that the N-terminal part of the LBD is essential for its structural and functional integrity while the large insertion peptide is dispensable. The structure reveals the active conformation of the bound ligand and allows understanding of the different binding properties of some synthetic analogs.
Disease
Known diseases associated with this structure: Osteoporosis, involutional, 166710 (1) OMIM:[601769], Rickets, vitamin D-resistant, type IIA OMIM:[601769]
About this Structure
1DB1 is a Single protein structure of sequence from Homo sapiens with as ligand. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
The crystal structure of the nuclear receptor for vitamin D bound to its natural ligand., Rochel N, Wurtz JM, Mitschler A, Klaholz B, Moras D, Mol Cell. 2000 Jan;5(1):173-9. PMID:10678179
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 12:14:47 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Single protein | Klaholz, B. | Mitschler, A. | Moras, D. | Rochel, N. | Wurtz, J M. | VDX | Complex