This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1dkf
From Proteopedia
(New page: 200px<br /> <applet load="1dkf" size="450" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" caption="1dkf, resolution 2.50Å" /> '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE O...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:1dkf.gif|left|200px]]<br /> | + | [[Image:1dkf.gif|left|200px]]<br /><applet load="1dkf" size="350" color="white" frame="true" align="right" spinBox="true" |
| - | <applet load="1dkf" size=" | + | |
caption="1dkf, resolution 2.50Å" /> | caption="1dkf, resolution 2.50Å" /> | ||
'''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A HETERODIMERIC COMPLEX OF RAR AND RXR LIGAND-BINDING DOMAINS'''<br /> | '''CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A HETERODIMERIC COMPLEX OF RAR AND RXR LIGAND-BINDING DOMAINS'''<br /> | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| - | The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains | + | The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. |
==Disease== | ==Disease== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
==About this Structure== | ==About this Structure== | ||
| - | 1DKF is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus] with BMS and OLA as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligands ligands]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http:// | + | 1DKF is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protein_complex Protein complex] structure of sequences from [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_sapiens Homo sapiens] and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mus_musculus Mus musculus] with <scene name='pdbligand=BMS:'>BMS</scene> and <scene name='pdbligand=OLA:'>OLA</scene> as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ligands ligands]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1DKF OCA]. |
==Reference== | ==Reference== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
[[Category: Gronemeyer, H.]] | [[Category: Gronemeyer, H.]] | ||
[[Category: Moras, D.]] | [[Category: Moras, D.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: SPINE, Structural | + | [[Category: SPINE, Structural Proteomics in Europe.]] |
[[Category: Vivat, V.]] | [[Category: Vivat, V.]] | ||
| - | [[Category: Wurtz, J | + | [[Category: Wurtz, J M.]] |
[[Category: BMS]] | [[Category: BMS]] | ||
[[Category: OLA]] | [[Category: OLA]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
[[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | [[Category: structural proteomics in europe]] | ||
| - | ''Page seeded by [http:// | + | ''Page seeded by [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca OCA ] on Thu Feb 21 12:17:29 2008'' |
Revision as of 10:17, 21 February 2008
|
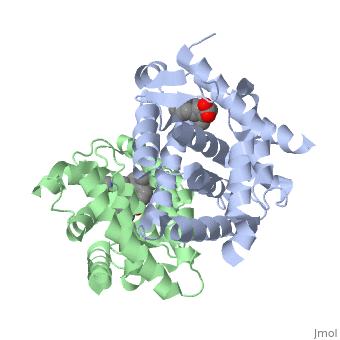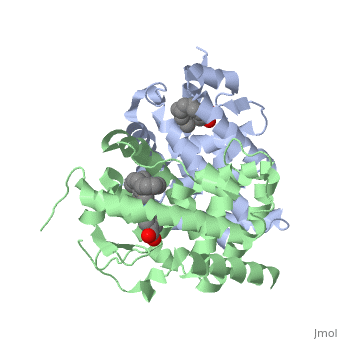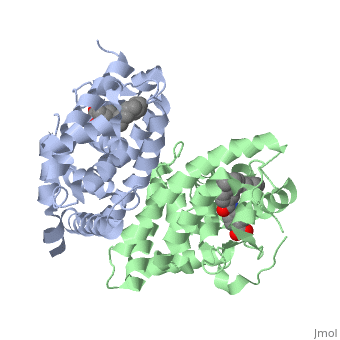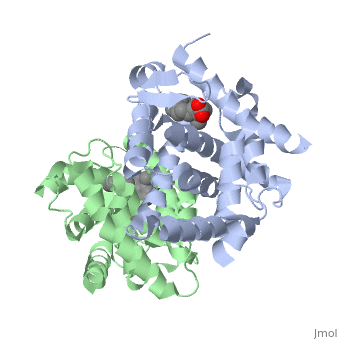
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A HETERODIMERIC COMPLEX OF RAR AND RXR LIGAND-BINDING DOMAINS
Contents |
Overview
The crystal structure of a heterodimer between the ligand-binding domains (LBDs) of the human RARalpha bound to a selective antagonist and the constitutively active mouse RXRalphaF318A mutant shows that, pushed by a bulky extension of the ligand, RARalpha helix H12 adopts an antagonist position. The unexpected presence of a fatty acid in the ligand-binding pocket of RXRalpha(F318A is likely to account for its apparent "constitutivity." Specific conformational changes suggest the structural basis of pure and partial antagonism. The RAR-RXR heterodimer interface is similar to that observed in most nuclear receptor (NR) homodimers. A correlative analysis of 3D structures and sequences provides a novel view on dimerization among members of the nuclear receptor superfamily.
Disease
Known disease associated with this structure: Leukemia, acute promyelocytic OMIM:[180240]
About this Structure
1DKF is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Homo sapiens and Mus musculus with and as ligands. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.
Reference
Crystal structure of a heterodimeric complex of RAR and RXR ligand-binding domains., Bourguet W, Vivat V, Wurtz JM, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D, Mol Cell. 2000 Feb;5(2):289-98. PMID:10882070
Page seeded by OCA on Thu Feb 21 12:17:29 2008
Categories: Homo sapiens | Mus musculus | Protein complex | Bourguet, W. | Chambon, P. | Gronemeyer, H. | Moras, D. | SPINE, Structural Proteomics in Europe. | Vivat, V. | Wurtz, J M. | BMS | OLA | Helical sandwich | Heterodimer | Hormone/growth factor receptor | Protein-ligand complex | Spine | Structural genomics | Structural proteomics in europe