Sandbox Reserved 1712
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
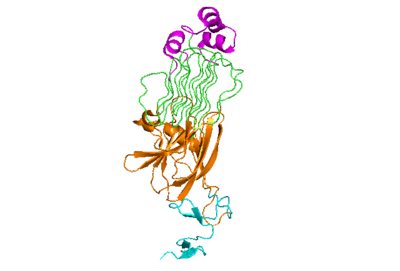
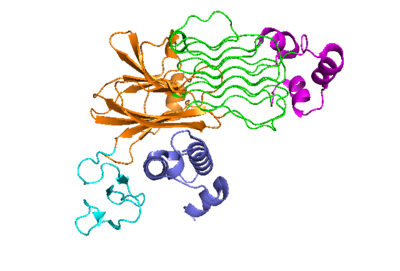
| + | The active state of the kinase is when two monomers have completed a conformational change and moved across the membrane to form a dimer. | ||
[[Image:Prote_ALK_Monomer_White.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1]] | [[Image:Prote_ALK_Monomer_White.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1]] | ||
[[Image:Proteo_ALK-ALKAL_Monomer_White.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 2]] | [[Image:Proteo_ALK-ALKAL_Monomer_White.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 2]] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
== Relevance & Role in the body == | == Relevance & Role in the body == | ||
<ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7</ref> | <ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7</ref> | ||
| - | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | The active state of the kinase is when two monomers have completed a conformational change and moved across the membrane to form a <scene name='90/904317/Dimer_full_colored/3'>dimer</scene>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 02:17, 28 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
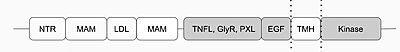
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ De Munck S, Provost M, Kurikawa M, Omori I, Mukohyama J, Felix J, Bloch Y, Abdel-Wahab O, Bazan JF, Yoshimi A, Savvides SN. Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors. Nature. 2021 Oct 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. PMID:34646012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5
- ↑ Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7