We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1712
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
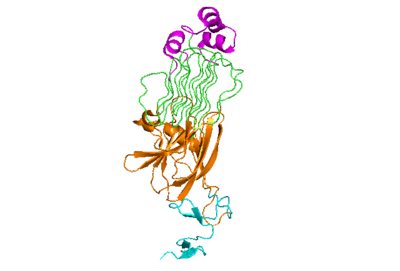
<scene name='90/904318/Alkalbindingsurfacewmembrane/1'>Binding surface of ALKAL with the membrane</scene> | <scene name='90/904318/Alkalbindingsurfacewmembrane/1'>Binding surface of ALKAL with the membrane</scene> | ||
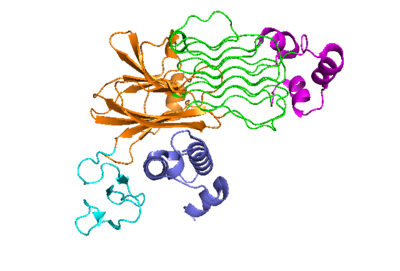
<scene name='90/904318/Alkal1membraneinteraction/2'>ALKAL's residues that interact with membrane</scene> | <scene name='90/904318/Alkal1membraneinteraction/2'>ALKAL's residues that interact with membrane</scene> | ||
| + | <ref>DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2005916</ref> | ||
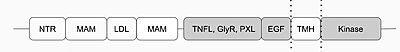
[[Image:2d_image.jpg|400 px|center|thumb|Fig.1 Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase and its domains. The region from NTR to the MAM is the Heparin Binding Domain. The TNFL-PXL are the extracellular domains and the EGF is the domain that binds the extracellular region with the extracellular region of the transmembrane. The TMH is the transmembrane domain. The kinase domain is the intracellular portion of the ALK.]] | [[Image:2d_image.jpg|400 px|center|thumb|Fig.1 Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase and its domains. The region from NTR to the MAM is the Heparin Binding Domain. The TNFL-PXL are the extracellular domains and the EGF is the domain that binds the extracellular region with the extracellular region of the transmembrane. The TMH is the transmembrane domain. The kinase domain is the intracellular portion of the ALK.]] | ||
Revision as of 02:55, 28 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Murray PB, Lax I, Reshetnyak A, Ligon GF, Lillquist JS, Natoli EJ Jr, Shi X, Folta-Stogniew E, Gunel M, Alvarado D, Schlessinger J. Heparin is an activating ligand of the orphan receptor tyrosine kinase ALK. Sci Signal. 2015 Jan 20;8(360):ra6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005916. PMID:25605972 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005916
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ De Munck S, Provost M, Kurikawa M, Omori I, Mukohyama J, Felix J, Bloch Y, Abdel-Wahab O, Bazan JF, Yoshimi A, Savvides SN. Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors. Nature. 2021 Oct 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. PMID:34646012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5
- ↑ Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7