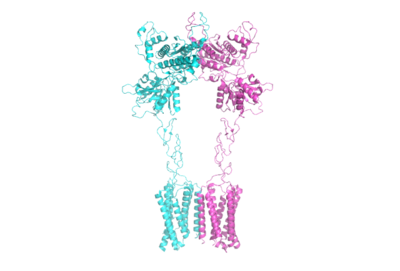Sandbox Reserved 1715
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
| - | mGlu receptors are dimeric proteins consisting of an <scene name='90/904320/Inactive_mglu2/1'>alpha and beta chain</scene>. While a heterodimer of different mGlu subtypes can form, only homodimeric receptors can become active. Both the alpha and beta chains are comprised of | + | mGlu receptors are dimeric proteins consisting of an <scene name='90/904320/Inactive_mglu2/1'>alpha and beta chain</scene>. While a heterodimer of different mGlu subtypes can form, only homodimeric receptors can become active. Both the alpha and beta chains are comprised of <scene name='90/905627/Mglu2_domains/9'>3 domains</scene>: the venus fly trap (VFT), cysteine rich domain (CRD), and the transmembrane domain (TMD). |
==== Domains ==== | ==== Domains ==== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
'''3.''' A second glutamate binds to the other binding pocket of the VFT. Mediated by L639, F643, N735, W773, and F776, a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) also binds within the seven TMD helices of the alpha chain. This closed conformation with an inter-lobe domain of 25 degrees is considered the active conformation. The binding of these ligands allows the CRD to compact and come together. This transformation causes the TMD to form another asymmetric conformation with a TM6-TM6 interface between the chains. | '''3.''' A second glutamate binds to the other binding pocket of the VFT. Mediated by L639, F643, N735, W773, and F776, a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) also binds within the seven TMD helices of the alpha chain. This closed conformation with an inter-lobe domain of 25 degrees is considered the active conformation. The binding of these ligands allows the CRD to compact and come together. This transformation causes the TMD to form another asymmetric conformation with a TM6-TM6 interface between the chains. | ||
| - | '''4.''' The change in the arrangement of the helices allows for intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) and the C-terminus to be properly ordered to interact with a G protein. While hydrogen bonding is present, this coupling is primarily driven by the hydrophobic interactions in the interface with the ɑ5 helix of the G protein.. This coupling can only occur in the presence of a PAM as the pocket in which the coupling occurs would be completely closed in its absence. | + | '''4.''' The change in the arrangement of the helices allows for intracellular loop 2 (ICL2) and the C-terminus to be properly ordered to interact with a G protein. While hydrogen bonding is present, this coupling is primarily driven by the hydrophobic interactions in the interface with the ɑ5 helix of the G protein.. This coupling can only occur in the presence of a PAM as the pocket in which the coupling occurs would be completely closed in its absence. [[Image: Protein Interaction with G Protein|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. The interaction between an active mGlu and a G-protein ]] |
'''5.''' Depending on the type of mGlu present, different signaling cascades will occur within the cell. These cascades are necessary for cellular function and can lead to various diseases. | '''5.''' Depending on the type of mGlu present, different signaling cascades will occur within the cell. These cascades are necessary for cellular function and can lead to various diseases. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
== Clinical Relevance == | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
<scene name='90/904320/Glutamate_in_active_site/2'>Glutamate Bound</scene> | <scene name='90/904320/Glutamate_in_active_site/2'>Glutamate Bound</scene> | ||
| - | === Role === | ||
=== Disease === | === Disease === | ||
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
<scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/3'>Active mGlu</scene> | <scene name='90/904320/Active_mglu/3'>Active mGlu</scene> | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 04:31, 28 March 2022
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Seven AB, Barros-Alvarez X, de Lapeyriere M, Papasergi-Scott MM, Robertson MJ, Zhang C, Nwokonko RM, Gao Y, Meyerowitz JG, Rocher JP, Schelshorn D, Kobilka BK, Mathiesen JM, Skiniotis G. G-protein activation by a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 2021 Jun 30. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3. PMID:34194039 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03680-3
Student Contributors
- Courtney Vennekotter
- Cade Chezem