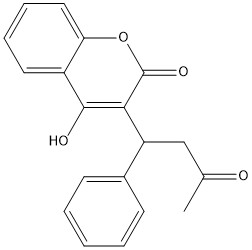
Figure 1. Closed Conformation of VKOR due to Warfarin Binding
Introduction
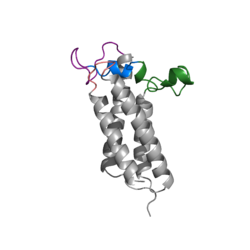
Figure 2. Overview of Vitamin K Cycle
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase (VKOR) is an endoplasmic membrane enzyme that generates the active form of Vitamin K to support blood coagulation. The vitamin K Cycle, and the VKOR enzyme specifically are common drug targets for thromboembolic diseases. This is because, as pictured, the vitamin K cycle is the process in which blood coagulant factors II, VII, IX, and X are activated. This promotes blood clotting, which (in extreme amounts) can be dangerous and cause thromboembolic diseases such as stroke, deep vein thrombosis, and/or pulmonary embolism.
Location of Enzyme
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase is found and primarily synthesized in the liver. It is embedded in the membrane known as the endoplasmic reticulum.
Structure
VKOR WIKI
The VKOR enzyme is made up of four transmembrane helices: T1, T2, T3, and T4.(Grey) Each of these helices come together to form a hydrophobic pocket, that is topped by a cap domain. In the cap domain are important regions that are significant for Vitamin K binding, and the overall function of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase. These important regions are the Anchor(Green), Cap Region (Blue), Beta Hairpin (Purple), and 3-4 Loop (Pink).
[1]
Transmembrane Helices
The Transmembrane helices are named Transmembrane Helix 1, Transmembrane Helix 2, Transmembrane Helix 3, and Transmembrane Helix 4. The residues on Transmembrane Helix 2 (TM2) and Transmembrane Helix 4 (TM4) are significant for the binding of Vitamin K to the hydrophobic pocket of the enzyme. Asparagine 83 on TM2 and Tyrosine 142 hydrogen bond to Vitamin K Epoxide, in order to hold it in place so that it may be reduced. The angle in which Vitamin K Epoxide binds is significant to the placement of the beta hairpin, and loop 3-4. Cysteine residues from the beta hairpin and loop 3-4 will donate their electrons to Vitamin K Epoxide to open the epoxide ring, and reform Vitamin K Quinone.
Cap Domain
The cap domain of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase plays an intricate role in its function. When Vitamin K Epoxide (or a similar substrate) binds in the hydrophobic pocket of VKOR, the cap domain undergoes a conformational change that will allow for specific cysteine residues to be able to open the epoxide ring and to recreate Vitamin K Quinone. The catalytic cycle begins in an open fully oxidized conformation. This conformation has slightly different parts. These include the Anchor (green), the cap region (blue), 3-4 Loop (pink), and luminal helix (yellow). When Vitamin K Epoxide binds, the entire cap domain undergoes a slight conformation change, but the luminal helix has a larger change. The luminal helix (yellow) bends forward where specific cysteines on this region are in proximity to other important cysteines. The luminal helix is then referred to as the beta hairpin (purple).
Significant Cysteines
A set of four cysteines is consistently conserved in all VKOR homologs. In the human homolog (HsVKOR) these cysteines are Cys43, Cys51, Cys132, and Cys 135. In the Pufferfish homolog (TrVKORL) these cysteines, due to Cryo-EM differences,are Cys52, Cys55, Cys141, and Cys144. These cysteines are the key factor that allow for Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase to perform its function, which is to open the epoxide ring on Vitamin K Epoxide in order to re-make Vitamin K Quinone. In the closed conformation, that is induced when Vitamin K binds in the hydrophobic pocket, Cys-132 binds to Cys-51 and Cys-135 will bind to the 3' hydroxyl group on Vitamin K Epoxide, which allows for the electron transfer to open up the epoxide ring.
Vitamin K Epoxide
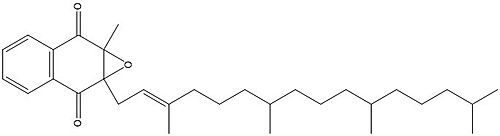
Figure 3. Vitamin K Epoxide structure
As mentioned above, Vitamin K epoxide is a part of the Vitamin K cycle, necessary for blood coagulation. In the cycle, Vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) reduces Vitamin K epoxide to quinone, or the active form of Vitamin K. What is occurring is VKOR donated electrons to Vitamin K epoxide, and those electrons come from the S-H of one of the cysteine pairs discussed above. The one cysteine pair has to be reduced for the transfer of electrons to the substrate can occur.
Binding
To start, VKOR is in its open conformation. The Vitamin K epoxide enters. The oxygens of the ketones bind to . With Vitamin K epoxide in its place, the conformation of VKOR is partially oxidized in regards to the cysteine pairs, which overall leads to the reduction of the substrate. A disulfide bond forms between Cys51 and Cys132, resulting in the closed conformation. This leaves the sulfur on Cys43 and the sulfur on Cys135 protonated. The available hydrogens on these cysteines are utilized in reducing the epoxide. First, the sulfur on Cys51 and Cys43 form a new bond. The hydrogen from Cys43 binds to the oxygen in the epoxide. The sulfur on Cys132 and the sulfur on Cys15 then form a new disulfide bond. The hydrogen that was present on Cys135 forms a new bond with the oxygen of the epoxide. With these cysteine pairs formed, VKOR is left in an open conformation. The end products are the Vitamin K/quinone and water.
Warfarin
scene name='90/904321/Closedconformation/4'>Warfarin Binding</scene>