We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1705
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
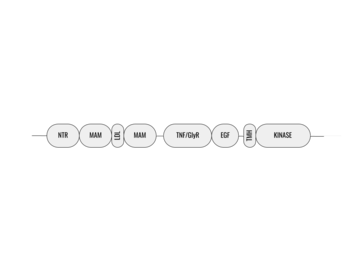
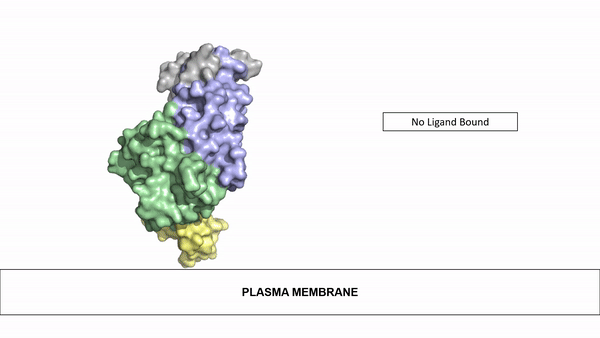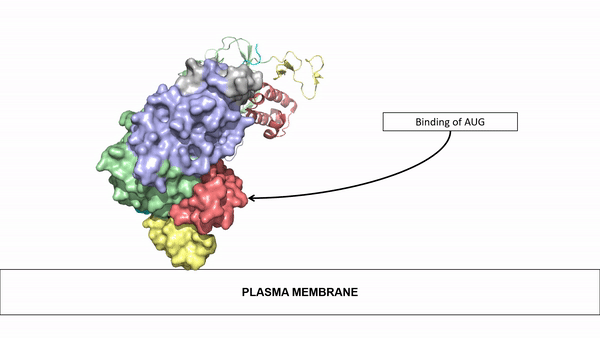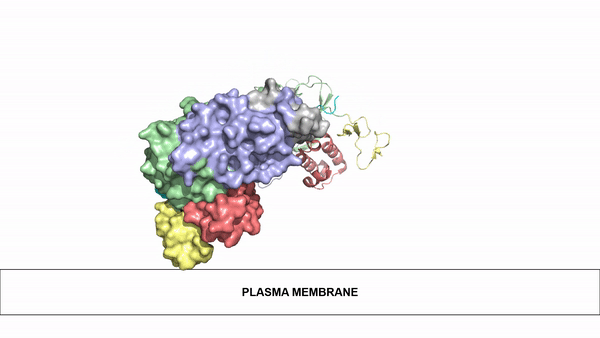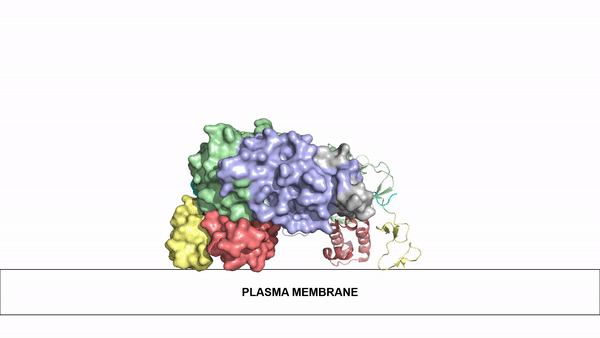
| - | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that is important in regulating functions within the central nervous system <ref name="Reshetnyak">PMID:34819673</ref>. The route to discovery of this protein's structure was rather complex, spanning almost 20 years; the kinase domain was discovered in 1994, the full protein structure in 1997, and the ligand structures in 2014. These structures were found using [https:// | + | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that is important in regulating functions within the central nervous system <ref name="Reshetnyak">PMID:34819673</ref>. The route to discovery of this protein's structure was rather complex, spanning almost 20 years; the kinase domain was discovered in 1994, the full protein structure in 1997, and the ligand structures in 2014. These structures were found using [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryogenic_electron_microscopy cryo-electron microscopy],[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_magnetic_resonance_spectroscopy nuclear magnetic resonance], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_crystallography X-ray crystallography]. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is a proto-oncogene with mutations associated with various types of cancers, including non-small-cell lung cancer, anaplastic large cell lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and inflammatory myofibroblastic cancer <ref name="Palmer">PMID:19459784</ref>. |
== General Structure == | == General Structure == | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 6 April 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ Palmer RH, Vernersson E, Grabbe C, Hallberg B. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: signalling in development and disease. Biochem J. 2009 May 27;420(3):345-61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090387. PMID:19459784 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20090387
- ↑ Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7
- ↑ Lewis RT, Bode CM, Choquette D, Potashman M, Romero K, Stellwagen JC, Teffera Y, Moore E, Whittington DA, Chen H, Epstein LF, Emkey R, Andrews PS, Yu V, Saffran DC, Xu M, Drew AE, Merkel P, Szilvassy S, Brake RL. The discovery and optimization of a novel class of potent, selective and orally bioavailable Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors with potential utility for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem. 2012 Jun 26. PMID:22734674 doi:10.1021/jm3005866
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sahu A, Prabhash K, Noronha V, Joshi A, Desai S. Crizotinib: A comprehensive review. South Asian J Cancer. 2013 Apr;2(2):91-7. doi: 10.4103/2278-330X.110506. PMID:24455567 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/2278-330X.110506
Student Contributors
- Kaylin Todor
- Rebekah White