We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1717
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
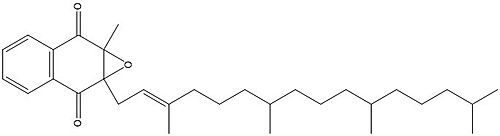
| - | <ref name="Goodstadt">PMID:15276181</ref> Goodstadt, L., & Ponting, C. P. (2004). Vitamin K epoxide reductase: homology, active site and catalytic mechanism. Trends in biochemical sciences, 29(6), 289–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2004.04.004 | + | <ref name="Goodstadt">PMID:15276181</ref> Goodstadt, L., & Ponting, C. P. (2004). Vitamin K epoxide reductase: homology, active site and catalytic mechanism. ''Trends in biochemical sciences, 29''(6), 289–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2004.04.004 |
| - | <ref name=”Shixuan”>PMID:33154105</ref> Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel | + | <ref name=”Shixuan”>PMID:33154105</ref> Liu, S., Li, S., Shen, G., Sukumar, N., Krezel, A. M., & Li, W. (2021). Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. ''Science (New York, N.Y.), 371''(6524), eabc5667. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667 |
| + | |||
| + | <ref name="Shen">PMID:33273012</ref> Shen, G., Cui, W., Cao, Q., Gao, M., Liu, H., Su, G., Gross, M. L., & Li, W. (2021). The catalytic mechanism of vitamin K epoxide reduction in a cellular environment. ''The Journal of biological chemistry'', 296, 100145. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015401 | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 29 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||