We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1703
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
====G-Protein Recognition==== | ====G-Protein Recognition==== | ||
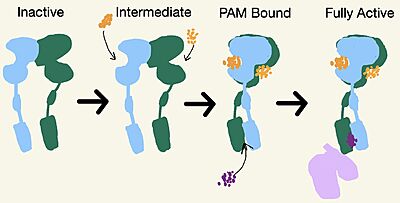
| - | Transition to the active state also reorients helix lll in both monomers to enable binding to the G-protein: Yet only one chain is required for full receptor activation. The intracellular region of helix lll contributes the main interactions with the alpha subunit of the G-protein. Intracellular Loop 2 also builds a polar interaction network with the G-protein through its ionic interactions with the <scene name='90/904308/Binding_recognition_site/2'> α-subunit</scene> of the G-protein. Lastly, mGlu2 residue E666 forms a salt bridge with | + | Transition to the active state also reorients helix lll in both monomers to enable binding to the G-protein: Yet only one chain is required for full receptor activation. The intracellular region of helix lll contributes the main interactions with the alpha subunit of the G-protein. Intracellular Loop 2 also builds a polar interaction network with the G-protein through its ionic interactions with the <scene name='90/904308/Binding_recognition_site/2'> α-subunit</scene> of the G-protein. Lastly, mGlu2 residue E666 forms a salt bridge with residue (R32) on the α-subunit which further destabilizes the inactive conformation<ref name="Lin"/>. |
====G-protein Binding==== | ====G-protein Binding==== | ||
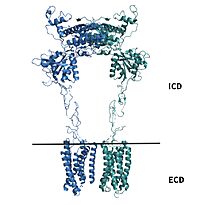
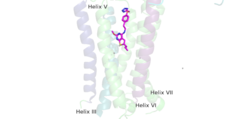
| - | The PAM induced downward shift of helix IV coupled with the reorientation of the transmembrane domain to a TM6-TM6 asymmetric interface, opens up a cleft on the intracellular surface of the receptor. This cleft allows a hook-like region (figure 4), from the last 4 terminals of the α-subunit of the G-protein, to move in adjacent to helix IV in the transmembrane domain. Within this interaction, <scene name='90/904308/ | + | The PAM induced downward shift of helix IV coupled with the reorientation of the transmembrane domain to a TM6-TM6 asymmetric interface, opens up a cleft on the intracellular surface of the receptor. This cleft allows a hook-like region (figure 4), from the last 4 terminals of the α-subunit of the G-protein, to move in adjacent to helix IV in the transmembrane domain. Within this interaction, <scene name='90/904308/Binding_site/4'>C351</scene> on the hook participates in hydrophobic interactions with Intracellular loop 2 and helix 4. These interactions allow the C-terminal region of the G-protein α-subunit to bind in the shallow groove formed by intracellular loops 2 and 3 and residues on helices 3 and lV<ref name="Lin" />.The receptor is now <scene name='90/904308/Active_structure/3'>fully active</scene> with the dimer coupled only to one G-protein. The ]VFT is in the closed conformation resulting in a tighter form. The TMD helices are also reoriented in both monomers to form an asymmetric dimer interface. |
==Clinical Relevance== | ==Clinical Relevance== | ||
Revision as of 15:26, 18 April 2022
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 2
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Lin S, Han S, Cai X, Tan Q, Zhou K, Wang D, Wang X, Du J, Yi C, Chu X, Dai A, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Liu H, Liu J, Yang D, Wang MW, Zhao Q, Wu B. Structures of Gi-bound metabotropic glutamate receptors mGlu2 and mGlu4. Nature. 2021 Jun;594(7864):583-588. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03495-2. Epub 2021, Jun 16. PMID:34135510 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03495-2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Seven, Alpay B., et al. “G-Protein Activation by a Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor.” Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, 30 June 2021, https://www.nature.com/articles/s1586-021-03680-3
- ↑ Du, Juan, et al. “Structures of Human mglu2 and mglu7 Homo- and Heterodimers.” Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, 16 June 2021, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-021-03641-w.>
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Muguruza C, Meana JJ, Callado LF. Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors as Targets for Novel Antipsychotic Drugs. Front Pharmacol. 2016 May 20;7:130. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00130. eCollection, 2016. PMID:27242534 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00130
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Ellaithy A, Younkin J, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Logothetis DE. Positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate 2 receptors in schizophrenia treatment. Trends Neurosci. 2015 Aug;38(8):506-16. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2015.06.002. Epub, 2015 Jul 4. PMID:26148747 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2015.06.002
Student Contributors
Frannie Brewer and Ashley Wilkinson